Knock knee, also known as genu valgum, is a condition characterised by an inward bending of the knees, causing the legs to touch or "knock" against each other when standing upright. While commonly observed in children and adolescents, knock knee can also affect adults. Understanding the knock knee causes, symptoms and treatment options is essential for proper management and prevention of complications.
| Interesting Fact: Did you know that knock knee is quite common in children between the ages of 2 to 5 years? In most cases, it naturally corrects itself as the child grows older without needing any medical intervention. |
Synopsis
Cause of Knock Knees
Several factors can contribute to the development of knock knee. These include:
-
Genetics: Some individuals may have a genetic predisposition to developing knock knee.
-
Uneven Bone Growth: If the bones in the leg grow at different rates, it can lead to a knock knee.
-
Muscle Imbalances: Weak or tight muscles in the leg can pull the knee joint out of alignment.
-
Excess Weight: Being overweight or obese can put additional stress on the knee joint, increasing the risk of knock knee.
-
Injury or Trauma: A direct blow to the knee or a sudden twisting motion can cause a knock-knee.
-
Neurological Conditions: Certain neurological disorders, such as cerebral palsy, can affect muscle control and lead to knock knee.
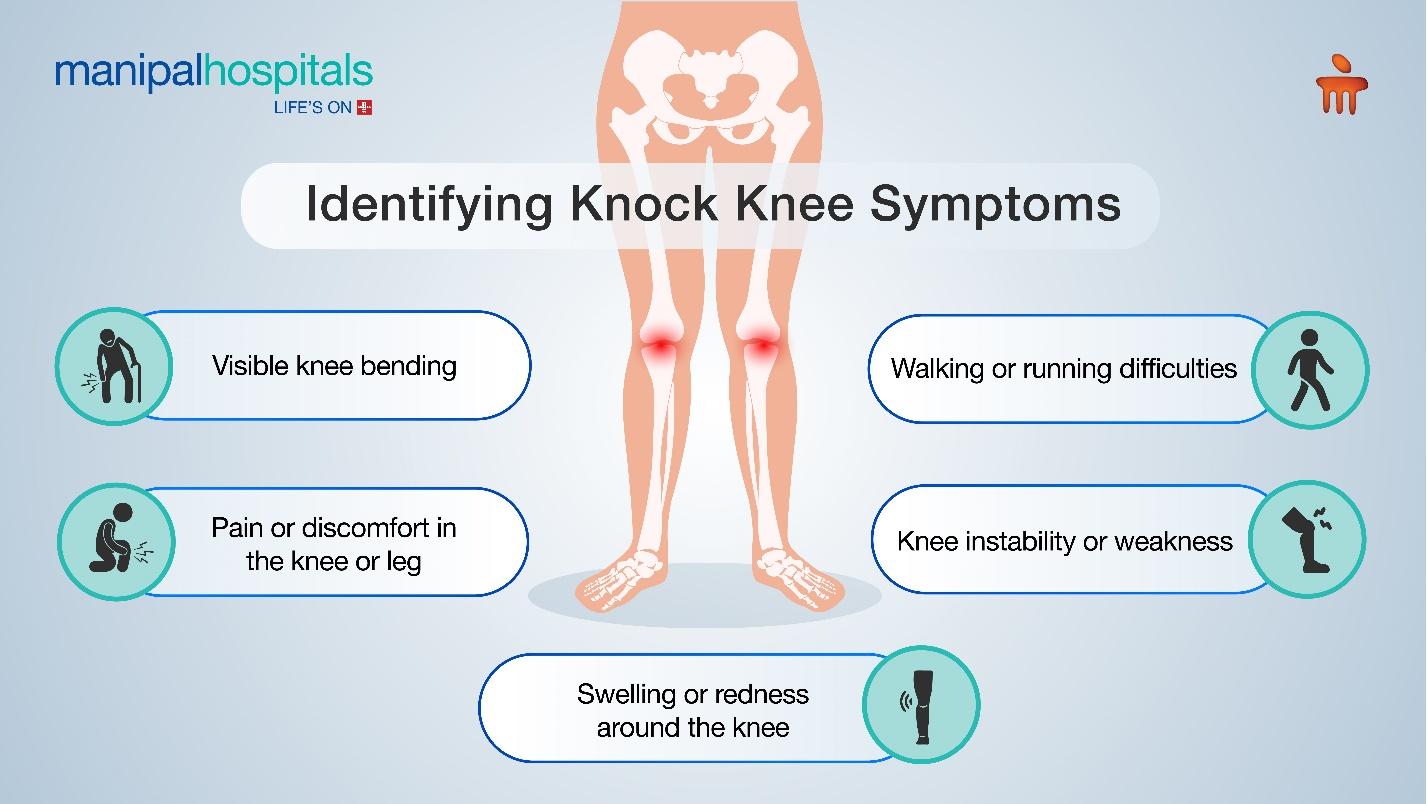
Symptoms of Knock Knee
The severity of knock knee symptoms can vary from person to person. Some common signs and symptoms include:
-
Visible inward bending of the knees
-
Pain or discomfort in the knee or leg
-
Difficulty walking or running
-
Swelling or redness around the knee joint
-
Instability or weakness in the knee
It is important to note that in some cases, a knock knee may not cause any noticeable symptoms. However, if left untreated, it can lead to more serious complications, such as osteoarthritis or chronic pain.
Diagnosing Knock Knee
To diagnose knock knee, a doctor will typically conduct a physical examination, which may involve:
-
Observing your gait and posture
-
Checking the alignment of your legs and knees
-
Assessing the strength and flexibility of your leg muscles
-
Performing imaging tests, such as X-rays or MRI, to rule out other conditions
In some cases, the doctor may refer you to an orthopaedic specialist or a physical therapist for further evaluation and treatment.
Treatment Options for Knock Knee
The treatment approach for knock knee will depend on the severity of the condition and the underlying cause. Some common knock knees treatment options include:
-
Physical Therapy: Strengthening exercises can help improve muscle strength and alignment, reducing the inward bending of the knees.
-
Bracing: Wearing a brace or splint can provide support to the knee joint and help improve alignment.
-
Orthotics: Custom shoe inserts or arch supports can help redistribute pressure on the knee joint and alleviate symptoms.
-
Surgery: In severe cases, surgery may be necessary to correct the alignment of the knee joint.
Lifestyle Changes to Manage Knock Knee
Incorporating certain lifestyle changes can help with knock knee correction and prevent further complications:
-
Maintain a Healthy Weight: Excess body weight puts additional stress on the knee joint, so maintaining a healthy weight can help reduce the risk of a knock knee.
-
Improve Posture: Practicing good posture can help reduce the stress on the knee joint and improve alignment.
-
Wear Supportive Shoes: Choosing shoes with good arch support can help reduce the stress on the knee joint.
-
Avoid Aggravating Activities: Steering clear of activities that exacerbate the condition, such as running or jumping, can help reduce the risk of further injury.
Complications of Untreated Knock Knee
Leaving knock knee untreated can lead to various complications, such as:
-
Osteoarthritis: The abnormal alignment of the knee joint can cause excessive wear and tear, increasing the risk of developing osteoarthritis.
-
Chronic Pain: Untreated knock knee can cause persistent pain and discomfort in the knee or leg.
-
Reduced Mobility: Knock knees can make it difficult to walk or participate in physical activities.
-
Increased Risk of Injury: The altered alignment of the knee joint can make you more susceptible to injuries.
When to Seek Medical Attention
If you or your child experiences persistent pain, difficulty walking, or visible changes in the alignment of the knees, it is important to consult with a specialist. Early intervention and proper knock-knee treatment can help prevent complications and improve overall quality of life.
Knock knee, or genu valgum, often affects children but can persist into adulthood, leading to complications like osteoarthritis and chronic pain if untreated. Early diagnosis and appropriate knock-knee treatment, including physical therapy, bracing, and lifestyle changes, are crucial. While most cases in children resolve naturally, adults may require more intensive interventions for knock knee correction. Maintaining a healthy weight, practising good posture, and wearing supportive footwear can help manage the condition. If symptoms like persistent knee pain or difficulty walking occur, seek medical advice promptly. Addressing knock-knee causes early can prevent complications and improve overall quality of life.
FAQ's
Seek medical advice if your child has severe or worsening alignment, pain in the legs or knees, difficulty walking, or if one leg appears significantly different from the other. Early consultation can help determine appropriate treatment options.
Most children with knock knees naturally outgrow the condition by around age 7. However, if it persists or worsens, it's important to consult a doctor for further evaluation and potential treatment.
Strengthening exercises can help manage knock knee symptoms. Focus on activities that strengthen the quadriceps (front thigh muscles), hamstrings (back thigh muscles), and hip abductors (outer hip muscles). Always consult a physiotherapist before starting any exercise regimen.
Excess body weight puts additional strain on the legs and joints, potentially worsening knock knee symptoms. Maintaining a healthy weight through balanced diet and regular physical activity is crucial for effectively managing this condition.
Wearing shoes without proper arch support or cushioning can exacerbate pain and discomfort associated with knock knees. Corrective shoes or orthotic inserts can provide better support and alleviate some symptoms.



















 4 Min Read
4 Min Read