Blood clots in the brain pose a significant threat to the health and well-being of individuals. They obstruct the blood flow to the brain, leading to severe complications such as stroke and brain damage. Stroke caused 699,000 deaths in India in 2019, which was 7.4% of the total deaths in the country.1. Knowing the characteristics of these clots can aid in non-surgical treatment planning and help avoid further complications.
Synopsis
How to Remove Blood Clot(s) in the Brain Without Surgery
A blood clot in the brain is formed when blood cells and proteins stick together, leading to a gel-like clump of blood. Blood clots in the brain can occur for many reasons, such as family history, age (those over 55 are prone to brain stroke), atherosclerosis, smoking, high blood pressure, stroke, sedentary lifestyle, brain trauma, etc. In severe cases or without timely treatment, it can lead to disability and sometimes death.
Existing treatments offer several non-surgical and surgical options, with the latter mostly prescribed in severe cases. In this blog, we will mainly explore the available non-surgical treatments for brain blood clot(s), along with an overview of the symptoms and diagnosis.
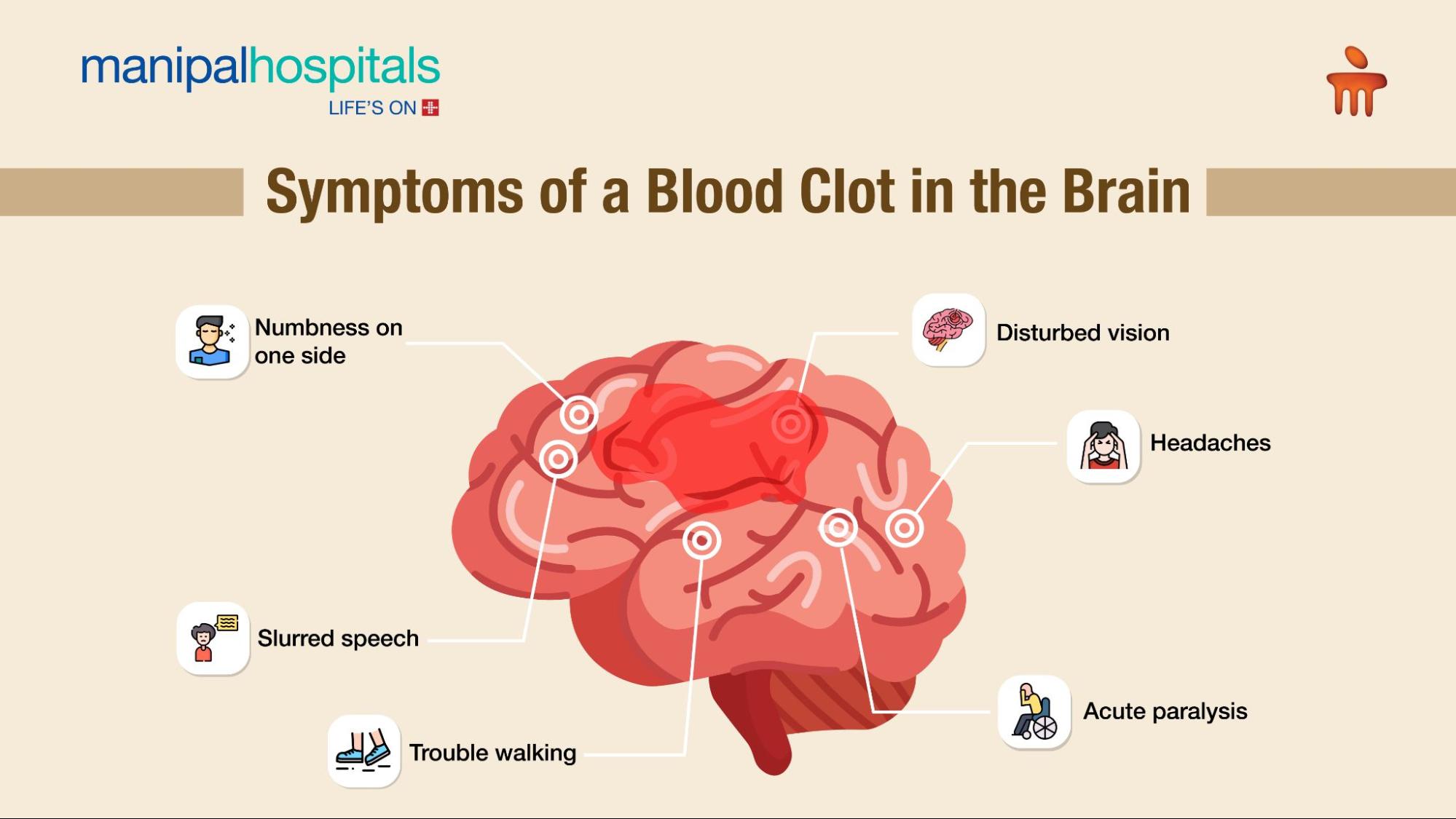
What are the Symptoms of Blood Clot(s) in the Brain?
The human brain is a vital organ that coordinates essential mental and physiological functions. Blood vessels ensure a steady flow of oxygen and nutrients, the removal of waste, and protection against infections and toxins. Blood clots can disrupt this flow, which causes brain cells to die due to a lack of oxygen.
Delayed treatment can lead to severe complications such as ischaemic stroke, cerebral venous thrombosis (CVT), intracranial hypertension, aneurysm rupture, haemorrhagic stroke, seizures, and cognitive impairments.
Common symptoms of a blood clot(s) in the brain include disturbed vision, headaches, acute paralysis, trouble walking, slurred speech, and numbness on one side.
How are Blood Clot(s) in the Brain Diagnosed?
Neurologists/Neurosurgeons perform various screening or diagnostic procedures to identify the presence of blood clot(s) in the brain, some of which include:
-
Physical examination, which involves examining the head and neck for signs of clots or abnormalities. Any indication, like pain or swelling around a particular area, as well as symptoms such as fever or tingling sensations, are reviewed.
-
Blood tests, e.g., D-dimer test
-
Diagnostic imaging like ultrasound, computed tomography (CT) scan, or magnetic resonance angiography (MRA)
-
Screening procedures like electrocardiograms (ECGs) to check for cardiac abnormalities
-
Other, such as spinal taps to see for signs of bleeding for cerebrospinal fluid, genetic testing, and Doppler ultrasound or angiography to identify the location and extent of blood vessel blockage
More Reads: Understanding Neurology Diseases & Disorders
Non-surgical Treatments That Exist to Treat Blood Clot(s) in the Brain
Several factors are considered to decide a suitable treatment for a brain blood clot(s). These include location, size, and the causes behind the formation of blood clot(s) in the brain. Existing non-surgical treatments include the following:
1. Anticoagulant Medications:
Anticoagulants like heparin, warfarin, etc., work by inhibiting the clotting process; they either prevent new clot formation or stop existing ones from growing larger. They are effective in preventing future clot formation and promoting the gradual breakdown of the clots; however, they are not as effective in directly dissolving the clots. They are typically used as a part of a broader treatment strategy, combined with medications or other therapies.
2. Thrombolytic medications:
Thrombolytic therapy, such as tissue plasminogen activator, is primarily used to treat patients with blood clots in the brain. They are powerful drugs that help break down fibrin in blood clots, dissolving the clots and restoring the blood flow to the brain. However, it carries the risk of excessive bleeding and is generally used for patients with early-stage ischaemic stroke.
In emergencies, recombinant tissue plasminogen activator (alteplase) is a gold standard treatment that is administered intravenously within 4.5 hours of the initial symptom onset to break down the clots in the brain.
Conclusion
Brain clots are often life-threatening, but the right choice of treatment and timely intervention can help prevent complications and improve patient recovery. Non-surgical treatments like anticoagulant and thrombolytic medications, along with supportive therapy and rehabilitation, serve as the first line of treatment for early symptoms of brain clots. If you or someone you know has experienced a stroke, visit Manipal Hospitals, Bhubaneswar, for guidance and optimal care from our expert neurospecialist.
FAQ's
Currently, there is no permanent cure for patients with blood clots in the brain. Usual advice includes healthy lifestyle changes, minimising stress, and consuming medications as prescribed by doctors to reduce symptoms and improve overall well-being.
Complications for delayed treatment for brain blood clots include extensive swelling and damage in the brain, stroke, pulmonary embolism, coronary artery disease, renal failure, and deep vein thrombosis. Among pregnant women, there is an increased risk of blood clot formation in veins of the lower limb area.
Lifestyle changes you can choose to make include refraining from smoking and drinking, sticking to your medication schedule, having a balanced diet, exercising regularly, drinking plenty of water, taking ample rest, and minimising anything that causes stress.
You will require follow-ups after treatment for brain blood clots. Your first follow-up is usually scheduled within the first few weeks. Moreover, an evaluation of what led to the formation of clots in the brain will be conducted, and treatment for those may also be initiated. This is done to prevent another episode and further complications.
To schedule an appointment with the Neurology Department at Manipal Hospitals, Bhubaneshwar, you can contact us or visit our website below.
Visit: https://www.manipalhospitals.com/bhubaneswar/
Contact no: 03369070001





















 4 Min Read
4 Min Read












9.png)




