Hyperthermia, characterised by an abnormally high body temperature, can result from various factors, including heat-related illnesses like heatstroke. Another term for hyperthermia is Heat Treatment or Hyperthermia Treatment which is the carefully regulated application of heat to enhance the cancer treatment. Although 9.4% of deaths worldwide each year are linked to heat or cold exposure, which translates to 74 additional deaths per 100,000 people.1 However, Hyperthermia Therapy has recently gained recognition in the field of cancer. This blog will help to understand hyperthermia, its symptoms, and its causes, and shed light on how Hyperthermia Therapy is being utilised to help fight cancer.
Synopsis
What is Hyperthermia?
Hyperthermia is a medical condition in which the body temperature is higher than normal, typically above 104°F (40°C). In hyperthermia, the body cannot cool itself efficiently, leading to dangerous overheating, which may result in serious health consequences if not addressed promptly. Hyperthermia mainly occurs due to external factors or internal malfunctions, unlike fever, which results from the body’s immune response to infections.
There are several hyperthermia stages. An example of a common condition is heat exhaustion. Other stages include heat stress, fatigue, heat syncope, heat cramps, heat oedema, heat rash, and heat exhaustion.
Hyperthermia, when used correctly, can play a significant role in cancer treatment.
Causes of Hyperthermia
The most common causes of hyperthermia include:
-
Heat stress/heat exhaustion/heat stroke: Prolonged exposure to hot weather, especially during physical exertion, can overwhelm the body's cooling mechanisms, leading to heat-related illnesses.
-
Dehydration: Lack of adequate fluid intake can impair the body's ability to sweat and regulate temperature.
-
Infections: Some infections, such as bacterial or viral infections, can cause fever as the body attempts to fight the infection. However, if the body's temperature regulation system malfunctions, it can lead to hyperthermia.
-
Medical Treatment: Hyperthermia Therapy is used in cancer treatment to raise the temperature of tumours but can sometimes lead to an unsafe rise in overall body temperature.
-
Prescription drugs: Certain drugs can dangerously increase body temperature. Examples include antipsychotic drugs, some anaesthesia drugs (malignant hyperthermia), and drugs that raise serotonin levels in the body (serotonin syndrome).
Symptoms of Hyperthermia
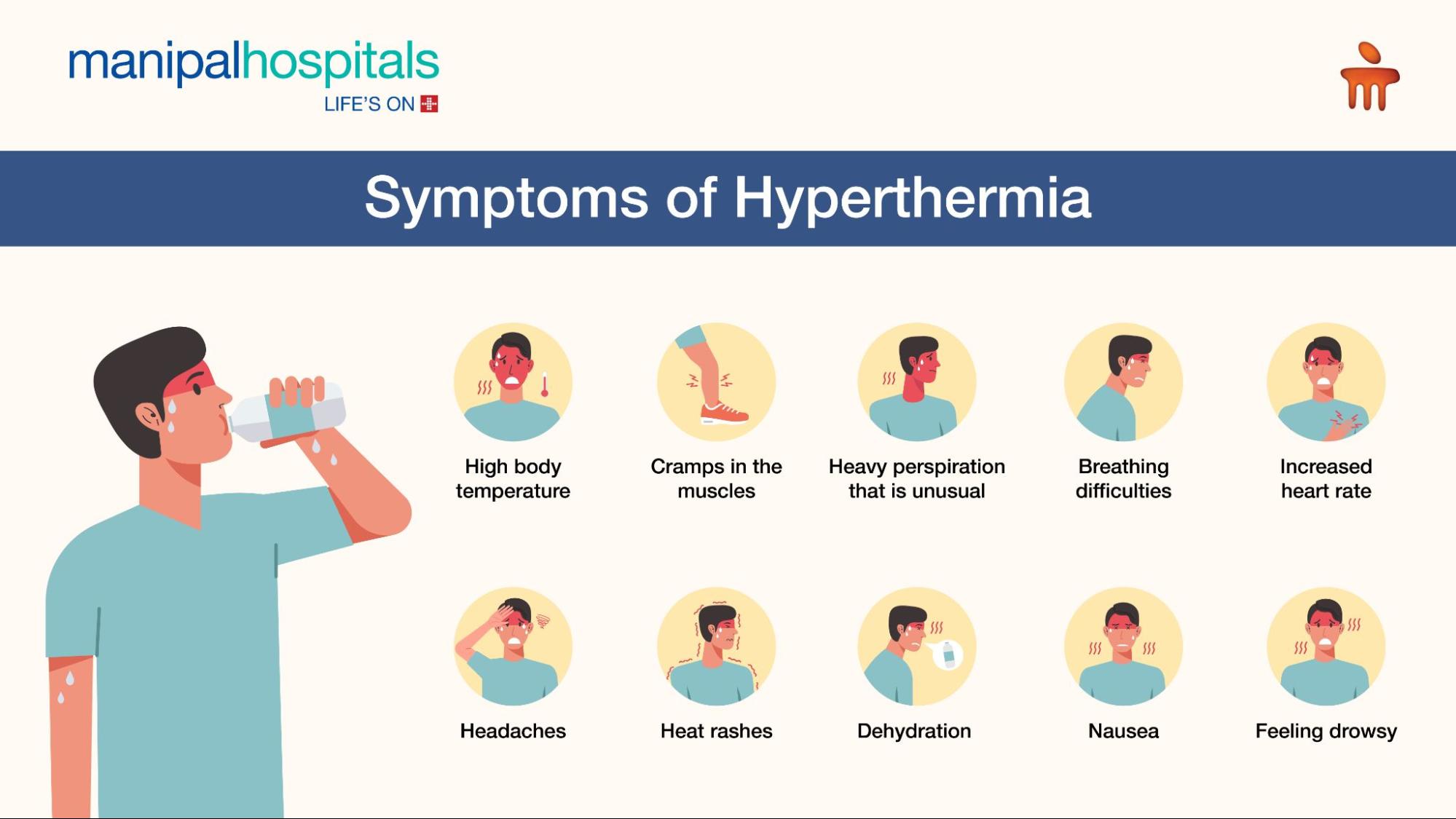
The degree of the temperature increase and the underlying cause can affect the symptoms of hyperthermia. This heat-related illness can be either a type of heat rash, heat cramps, heat exhaustion, or heat stroke, each exhibiting different symptoms.
The common symptoms of hyperthermia include:
-
High body temperature
-
Cramps in the muscles
-
Heavy perspiration that is unusual
-
Breathing difficulties
-
Feeling drowsy
-
Heat rashes
-
Dehydration
-
Increased heart rate
In severe cases, the symptoms can become more intense, such as seizures, loss of consciousness, and organ failure.
How Does Hyperthermia Work in Cancer Treatment?
Nowadays, many research studies have led to the use of hyperthermia as a treatment for cancer, known as Hyperthermia Therapy. This involves intentionally using heat to target cancer cells, as they are generally more sensitive to heat. When exposed to high temperatures (around 40–45°C), the proteins and essential structures within these malignant cells begin to break down, ultimately leading to their destruction.
Additionally, these changes can enhance the sensitivity of cells to treatments such as Chemotherapy and Radiation therapy. This form of Heat Treatment is also referred to as Thermotherapy or Thermal Therapy.
Types of Hyperthermia Treatment
There are several types of Hyperthermia Treatment used in Cancer Therapy based on the size of the affected area, such as:
-
Local Hyperthermia: In this, a small area, such as a tumour, is heated to extremely high temperatures. These damage the surrounding blood vessels and kill the cancer cells. External methods, such as electromagnetic energy (radiofrequency ablation), ultrasound, or heating devices, are used.
-
Regional Hyperthermia: An organ, limb, or body cavity (a hollow space inside the body) may be targeted in the case of Regional Hyperthermia. The temperature is not high enough to completely eradicate the cancer cells. Usually, it is used in conjunction with Radiation Therapy or Chemotherapy.
-
Deep tissue Hyperthermia: is another approach for Regional Hyperthermia treatment. This method involves directing high-energy waves to a specific area using devices placed on the surface of the organ or body cavity. These devices emit microwave or radiofrequency energy to heat the targeted region.
-
Whole-body Hyperthermia: Whole-body Hyperthermia may be needed if cancer has spread throughout your body. There are several methods to heat your entire body, such as using a heated blanket, an incubator, or a warm water bath. This treatment may induce a short, controlled fever, which can help stimulate your immune system to target and fight cancer cells.
Prevention of Hyperthermia
The body's risk of overheating can be reduced by:
-
Wearing breathable, loose-fitting apparel when it's hot outside
-
Maintaining constant hydration, irrespective of whether you are engaged in physical activity or not
-
Using fans and/or air conditioning to maintain a cool, comfortable temperature in your house
-
Identifying locations to visit in hot weather, such as shopping centres or community centres, if your house is too hot
-
Avoiding or limiting physical exertion when it is hot outside
-
Taking a cooling shower after being in the heat for a while
Conclusion
Hyperthermia, while often seen as a dangerous condition when uncontrolled, holds promise as a therapeutic tool in cancer treatment. With its ability to target cancer cells and enhance the efficacy of other treatments, Hyperthermia Therapy shows potential for advancing cancer treatment in the future.
To learn more about this advanced cancer treatment option and how it can be beneficial to your cancer treatment plan, consult the oncology experts at Manipal Hospitals, Bhubaneswar.
FAQ's
Treatment plans are personalised to patients' needs in each instance. The average duration of each Hyperthermia treatment is between 45 minutes to an hour. For instance, a patient should receive Hyperthermia treatment on the same day as they receive Radiation therapy. Each patient's Chemotherapy treatment plan is in line with their Hyperthermia treatment plan.
Hyperthermia is a serious risk for those who operate in extremely hot conditions or are exposed to high temperatures on the job. These include farmers, construction workers, and other people who spend a lot of time outside in the heat. Additionally, you may be more susceptible to hyperthermia if you have certain medical conditions or use certain drugs. Example: Diuretics and other heart and blood pressure drugs can make it harder for you to cool down through perspiration.
The cancers that can be treated with Hyperthermia Therapy include:
-
Head and Neck
-
Brain
-
Lung
-
Melanoma
-
Neuroblastoma
-
Endometrial
Hyperthermia Treatment might be advantageous for you if you have:
-
Deep tumours that cannot be removed by surgery
-
Conditions that keep you from undergoing surgery
-
Small tumours near the surface of your skin
-
Tumours in a body cavity
You can email us or visit our website to make an appointment at Manipal Hospitals, Bhubaneswar.
Check out: https://www.manipalhospitals.com/bhubaneswar/specialities/medical-oncology/
Number to call: 0674 666 6600



















 6 Min Read
6 Min Read


21.png)






.png)




