Listen to article
Loading audio...
Insulin is an essential hormone produced by your pancreas. It plays a crucial role in controlling blood sugar levels in diabetes. In diabetic patients, the body either produces insufficient amounts of insulin or cannot use it effectively, resulting in increased blood sugar levels. Over time, diabetes can lead to certain complications affecting your heart, nerves, kidneys, eyes, and other organs.
A recently published study in The Lancet Diabetes and Endocrinology estimates that 101 million people in India are affected by diabetes. Hence, gaining a clear understanding of the role of insulin in diabetes management helps patients take better control of their health. This blog delves into how insulin works to control blood sugar levels in diabetes.
Synopsis
About Insulin
Insulin is a peptide hormone produced by the beta cells in the pancreas, specifically the beta cells of the pancreas. It works in conjugation with the glucagon hormone to regulate blood sugar (glucose) levels, ensuring that glucose is released into the bloodstream when levels are low and stored when levels are high. Insulin helps to regulate glucose levels in the blood by promoting the storage of glucose in the muscles, adipose tissues, and liver.
The Function of the Insulin
Insulin plays a key role in ensuring that the sugar absorbed from food is properly utilised and stored in the body. In healthy individuals without diabetes, the insulin helps in:
-
Regulating blood sugar levels: After eating, the body breaks down carbohydrates into glucose, a type of sugar that serves as the body’s main source of energy. It is often referred to as blood glucose, and it rises after meals. Once glucose enters the blood circulation, the pancreas produces insulin, which allows the glucose to enter the body’s cells and be used for energy.
-
Store excess glucose for energy: After eating, insulin levels increase, and any extra glucose is stored in the liver as glycogen. Between meals, insulin levels are low, and during this time, the liver releases glycogen back into the blood circulation as glucose, helping maintain stable blood sugar levels.
Consult our diabetes hospital in Bhubaneswar if you need to know more about " sugar level: how to control "
Role of Insulin in Controlling Blood Sugar in Diabetes
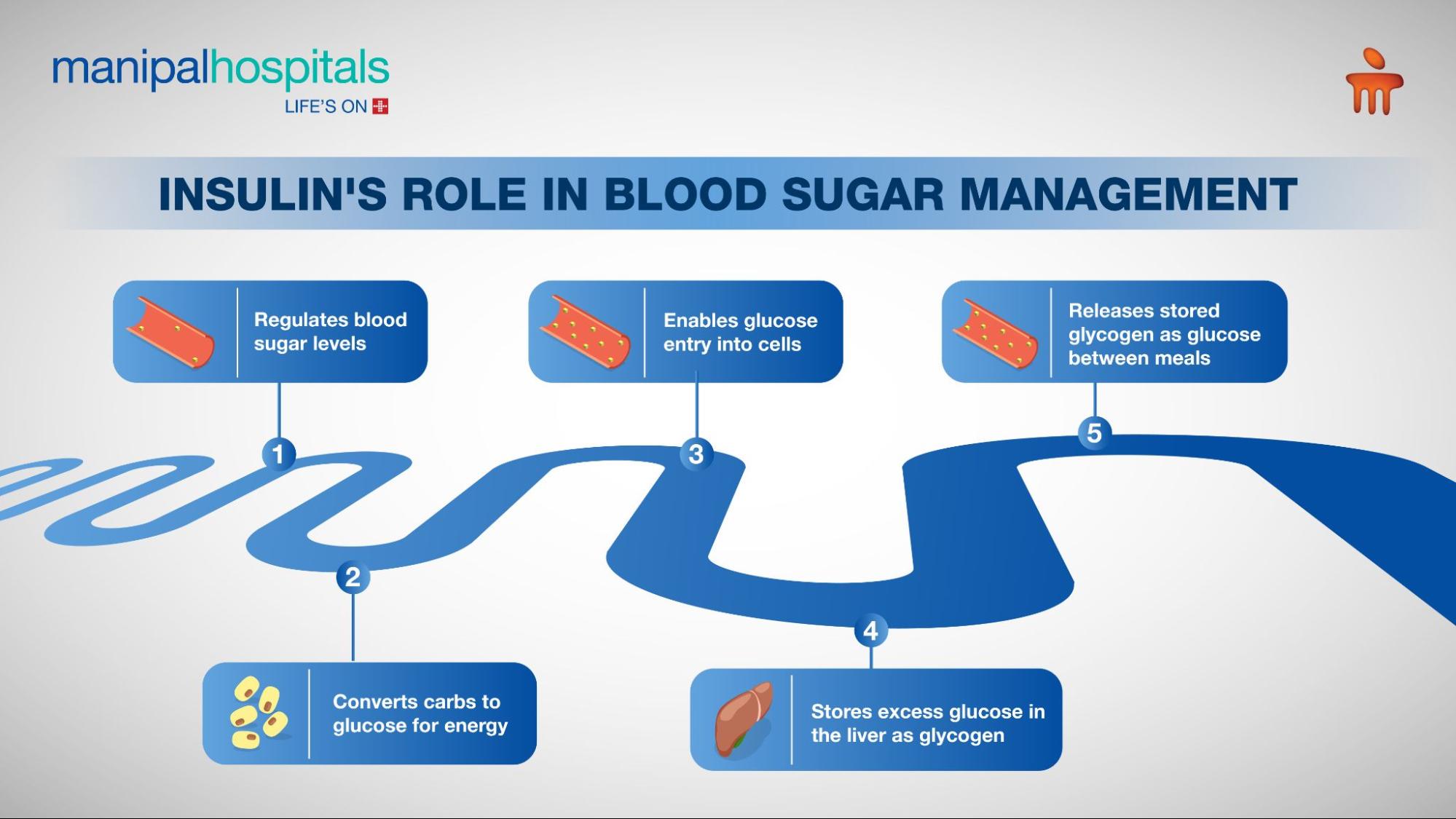
After eating, the rise in blood glucose levels signals the pancreas to release insulin, which helps transport glucose into the cells. This process gets disturbed due to the diminished insulin function in diabetes, leading to persistently elevated blood sugar levels after meals. In type 1 diabetes, the beta cells in the pancreas stop producing insulin, resulting in elevated blood sugar levels. In type 2 diabetes, the pancreas produces insufficient insulin, or the insulin does not function properly (insulin resistance).
The role of insulin therapy in type 1 diabetes is essential, as it replaces the insulin that your body is unable to produce. If you have type 2 diabetes, insulin therapy may be included in your treatment plan when healthy lifestyle changes and other oral diabetes medicines are not sufficient to effectively control your blood sugar levels.
Types of Insulin Used to Treat Diabetes
Insulin comes in various forms; most of them are injectables (needle, pen, or pump). Your healthcare provider will help you choose the most suitable type and dose of insulin in diabetes for optimal management.
There are two main types of insulin based on their onset and duration of action:
-
Long-acting, ultralong-acting, and intermediate-acting insulins. When you're not eating, your liver releases glucose to supply energy to your body. Long--, ultralong-, or intermediate-acting insulin helps prevent blood sugar levels from rising during this time, even without food intake. Long-acting insulin usually lasts around 24 hours, intermediate-acting insulin works for 12 to 18 hours, and ultralong-acting insulin can remain effective for about 36 hours or more.
-
Rapid-acting or short-acting insulins. These insulins are best used before meals to help control blood sugar spikes after eating. They work much faster than long-acting or intermediate-acting insulins. Rapid-acting insulin typically remains effective for 2 to 3 hours. Short-acting insulin lasts for 3 to 6 hours.
Consult our diabetologist in Bhubaneswar if you need treatment or learn about home remedies for sugar control.
Conclusion
Insulin is an important hormone used to control blood sugar, levels in diabetes. Understanding how insulin works in diabetes can help you stay on top of your health and reduce the risk of complications. Therefore, take care of your health by scheduling a consultation with our expert team at Manipal Hospitals, Bhubaneswar, to ensure you receive the best guidance and personalised diabetes care.
FAQ's
Several factors influence the timing and management of insulin, including:
-
The type of insulin you’re using
-
Your food choices and portion sizes
-
Your level of physical activity
-
Any other health conditions
-
The insulin delivery method (such as injections, a pump, or an inhaler)
Your doctor may recommend taking insulin about 30 minutes before meals to ensure it's active when sugar from food enters your bloodstream. Be sure to discuss with your doctor the exact timing for each injection and what to do if you miss a dose.
Most people inject insulin into the lower belly area for ease of access but be sure to stay at least 2 inches away from your belly button. You can also inject insulin into your thighs, buttocks, or arms.
Ask your doctor or diabetes educator to demonstrate the correct injection technique, including how to keep the needle and skin clean to avoid infections. It’s also important to rotate your injection sites to prevent hard, fatty deposits from forming under your skin due to repeated injections.
Certain medicines can enhance the blood sugar-lowering effects of insulin, increasing the risk of hypoglycemia. Make sure to inform your doctor about all the medications you are taking, including any over-the-counter drugs and supplements.
Ask your doctor for specific dietary recommendations to optimise the effectiveness of your insulin. You should know how much to eat at each meal, which foods are best for managing blood sugar, whether you need to include snacks and the timing of your meals. If you drink alcohol, check with your doctor to ensure it’s safe and to determine the appropriate amount to consume while using insulin.
Your doctor will advise you on how frequently to check your blood sugar using a glucose meter. It’s important to understand your target blood sugar range before and after meals, as well as before bedtime. The target levels for most individuals with diabetes are:
-
Before food: 70 to 130 mg/dL
-
2 hours after food: less than 180 mg/dL
To schedule an appointment at Manipal Hospitals, contact our Diabetes and Endocrinology department or visit our website.



















 6 Min Read
6 Min Read










