Got swollen cheeks and a fever? It might not just be a regular cold—mumps could be the culprit! Up to one-third of infected individuals exhibit no symptoms but are still contagious, meaning they can unknowingly spread the virus to others 1.
In this guide, we’ll cover everything you need to know about mumps, including its causes, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment, and ways to prevent it.
Synopsis
What is Mumps?
Mumps are caused by a virus called the rubulavirus, which is part of a group of viruses known as the paramyxoviridae family. Mumps mainly affects children but can also occur in people of any age. The virus mainly targets the salivary glands, which are responsible for producing saliva (the watery fluid that helps with digestion and keeps the mouth moist).
One of the main glands affected is the parotid gland. These are two large glands located near your ears, and their job is to produce saliva. When someone has mumps, these glands become swollen, causing pain and making the face look puffy. Although mumps is usually mild, it can sometimes cause complications, especially in adults.
How Do You Get Mumps? Know the Cause
The mumps virus, which causes mumps, is easily transmitted from person to person. When an infected individual coughs, sneezes, or speaks, respiratory droplets are released into the air and can be transmitted to other people. Contact with contaminated surfaces or shared objects, like cups or cutlery, may also transmit it. The virus attacks the salivary glands after entering the body by the mouth, nose, or eyes.
Mumps Symptoms: How to Recognise the Signs?
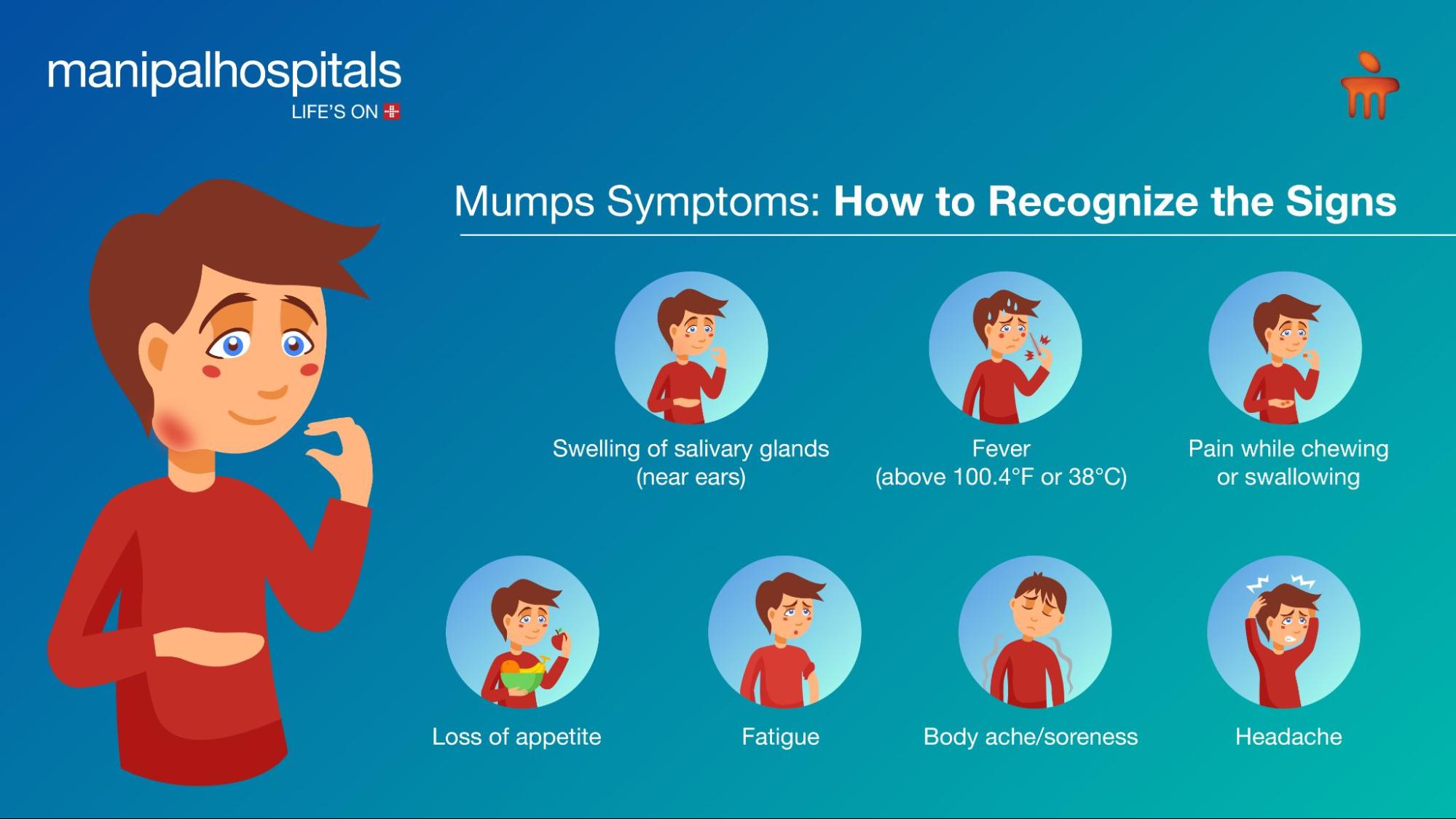
The mumps symptoms usually appear 12 to 25 days after exposure to the virus, during what is known as the incubation period. It is difficult to recognise mumps symptoms early as they resemble those of the common cold. But some important signs to watch out for are:
-
Swelling of the salivary glands (near the ears)
-
Fever (temperature above 100.4°F or 38°C)
-
Headache
-
Body ache or soreness
-
Fatigue
-
Loss of appetite
-
Complications like oophoritis (inflammation of the ovaries) or orchitis (inflammation of the testicles) can also occur in certain individuals; these conditions can be more severe.
If you experience any of the above symptoms, consult at Manipal Hospitals, Bhubaneswar.
How Is Mumps Diagnosed?
A physical examination, laboratory testing, and a review of medical history are done to diagnose mumps. In addition to asking you about your symptoms, your doctor will examine you and look for any obvious swelling in your parotid glands. Additional tests that may be required include:
-
Blood Tests: If you have an active infection, a blood test can identify antibodies to the mumps virus.
-
PCR Test (Polymerase Chain Reaction): This test confirms the diagnosis by identifying the genetic material of the virus in a sample of urine, saliva, or cerebrospinal fluid.
-
Imaging: Imaging tests like ultrasound may be utilised if issues are suspected, particularly to check for male testicular enlargement.
Mumps Treatment: What to Do if You’re Infected
Mumps treatment focuses on symptom relief and aiding in the body's recovery because there is no specific antiviral medication. Here are some tips for handling mumps symptoms:
Pain relief: To reduce pain and fever, you can take over-the-counter medicines like acetaminophen (Tylenol) or ibuprofen (Advil). Consult your doctor before taking any medications
Hydration: Drink plenty of fluids but avoid acidic drinks like citrus juices, which can irritate the swollen glands
Cold or Warm Compresses: Pain and swelling may be reduced by applying a cold or warm compress to the swollen areas
Soft Foods: Eat soft foods that are easy to swallow because chewing can hurt
Rest: Get enough sleep to support your immune system's defences against infections
Further treatment can be necessary in cases of complications, such as orchitis, and your doctor might suggest particular procedures to deal with those problems.
Prevention of Mumps
Mumps can be prevented by a vaccination called the MMR vaccine. This vaccine protects against three diseases - measles, mumps, and rubella. The MMR vaccine is given to children during their immunisation schedule. Two doses of vaccine are given; the first dose is given at 12–15 months of age and the second dose at 4–6 years.
Adults who have not taken the vaccine or are unsure about their immunisations should consult with their doctor about receiving the MMR vaccine. However, because it is a live vaccine and may cause dangers during pregnancy, pregnant women should avoid it.
Conclusion
Mumps is a viral infection that can cause discomfort, but with prompt recognition and proper care, most people recover without any long-term issues. The two most important things you can do to avoid mumps and protect others are to learn about its symptoms and be vaccinated. For a precise diagnosis and suitable treatment, it is crucial to speak with a healthcare professional if you think you or someone you know may have mumps.
Our goal at Manipal Hospitals, Bhubaneswar, is to give you and your family the finest care possible. Our network of medical professionals is available to help if you have any questions or need more information on mumps.
FAQ's
Yes, it is safe. The MMR vaccine has been thoroughly investigated and is advised by international health agencies such as the Centres for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) and the World Health Organisation (WHO).
In some cases, mumps can lead to complications such as:
-
Orchitis (testicular swelling in males),
-
Oophoritis (ovarian inflammation in females),
-
Meningitis (brain and spinal cord inflammation),
-
Hearing loss,
-
Arthritis (Inflammation of the joints),
-
Encephalitis (swelling of the brain),
-
Pancreatitis (inflammation of the pancreas),
-
Thyroiditis (inflammation of the thyroid gland).
It is rare to get mumps twice. Once you recover, your body usually develops lifelong immunity against the virus.
Mumps usually lasts around 7 to 10 days. Most people recover completely without complications.
To avoid spreading the virus, stay at home if you think you may have the mumps. You should also see a doctor for a correct diagnosis and treatment. After symptoms start, stay away from people for at least five days.






















 6 Min Read
6 Min Read













