The ageing population in India has contributed to a rise in non-communicable neurological disorders, significantly impacting quality of life. Neurological disorders account for 10% of the total disease burden in India. Among these, stroke, headache, and epilepsy are the leading contributors, with stroke being the third leading cause of death. Understanding how the brain adapts to these conditions is essential for developing effective treatments and improving patient outcomes. This blog explores neurological disorders, the brain's adaptability, and the implications for recovery.
Synopsis
What Are Neurological Disorders?
Neurological disorders encompass conditions that affect the brain, spinal cord, and nervous system (central and peripheral). Common causes include high blood pressure, air pollution, high fasting plasma glucose, high body mass index, and poor dietary habits. Infections, congenital anomalies, genetic issues, traumatic injuries, or environmental factors often lead to these disorders.
Neurological disorders are categorized based on the affected system: central nervous system (CNS) or peripheral nervous system (PNS).
Common Neurological Disorders
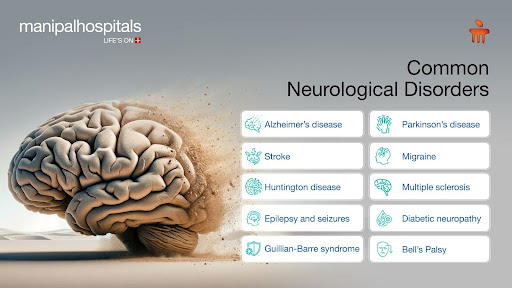
Here is a list of the most common neurological disorders or diseases:
-
Alzheimer’s disease
-
Parkinson’s disease
-
Migraine
-
Huntington’s disease
-
Multiple sclerosis
-
Epilepsy and seizures
-
Diabetic neuropathy
-
Guillain-Barré syndrome
-
Bell’s Palsy
For a comprehensive understanding of these conditions, refer to the most common neurological disorders list and consult our best neurology doctor in Bhubaneswar to plan an effective treatment strategy.
How the Brain Adapts to Neurological Diseases?
Neuroplasticity is called the brain’s ability to adapt and reorganize itself in response to damage or disease. This adaptability is crucial for recovery from neurological disorders. There are two main types of neuroplasticity:
-
Structural plasticity: The brain forms new neural pathways based on experiences or memories.
-
Functional plasticity: The brain transfers functions from damaged to undamaged areas to maintain cognitive and physical abilities.
The Role of Neuroplasticity in Neurological Disorders
In children, rapid brain growth allows neurons to form strong connections, while unused ones are pruned away. This adaptability continues to play a crucial role in recovery from neurological diseases:
-
Stroke: During a stroke, the brain cells are damaged due to insufficient blood flow. Through neuroplasticity, the brain forms new connections or reallocates functions to healthy areas, restoring motor and cognitive abilities with the help of therapies like physical, cognitive, and occupational therapy.
-
Parkinson’s Disease: Patients can enhance motor and mental functions through specific exercises and cognitive therapies.
-
Multiple Sclerosis: Adaptive strategies such as using assistive devices and conserving energy help maintain independence.
-
Alzheimer’s Disease: Patients use compensatory mechanisms like notes and routines to manage daily tasks and cope with memory loss.
Managing Neurological Disorders
Effective management of neurological diseases requires understanding how the brain adapts. For example, therapies focusing on neuro disorders enhance recovery by leveraging the brain’s neuroplasticity.
Seek consultation at our neurology hospital in Bhubaneswar to develop personalized treatment plans. Understanding the types of neurological disorders and their management can significantly improve outcomes and quality of life.
Conclusion
Neurological disorders, though challenging, can be managed effectively with ongoing research and advancements in therapeutic strategies. The adaptability of the brain, driven by neuroplasticity, offers hope for recovery and a better quality of life.
Stay informed about the latest in healthcare by visiting our blog page. Book an appointment with our expert neurologists today and take the first step toward enhanced well-being.
FAQ's
The brain's ability to adapt to disease changes can be improved in the following ways:
-
Enrich your environment by stimulating the brain to learn a new language, travel, read, etc
-
Take plenty of rest, as good sleep is essential for mental health
-
Regular physical activity
-
Practice mindfulness
-
Playing different games
The symptoms may differ among individuals, but the common signs include:
-
Numbness or tingling
-
Unexplained weakness
-
Loss of sight
-
Persistent or sudden headache
-
Memory loss
-
Mood or behaviour changes
-
Seizures
-
Movement and coordination changes
Some neurological conditions, like stroke, may require immediate attention, so if you experience any of these symptoms, seek consultation promptly.
Three major types of brain scans are used for diagnosing diseases affecting the nervous system. These are computed tomography (CT), magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), and positive emission tomography (PET).
Though neurological disorders cannot be fully cured, with therapies and medications, daily functioning can be restored. Also, making lifestyle changes, physiotherapy, and pain management can help minimise their effects on your overall health.
To schedule an appointment at Manipal Hospitals, contact our Neurology Department or visit our website.






















 4 Min Read
4 Min Read












9.png)




