
Dengue fever is a disease caused by viruses that are transmitted by mosquitoes. It can affect anyone but is likely to be more harmful to people with compromised immune systems. There are five serotypes of dengue virus which can cause the disease. Hence, a person can get dengue fever multiple times. However, an attack of dengue virus produces immunity to that particular serotype to which the person was exposed.
One in every four people infected will become unwell. The incidence of new dengue cases has increased in recent decades. According to the World Health Organisation (WHO), shifting land use patterns, increased international travel and trade, and the climate crisis have all contributed to dengue's spread.
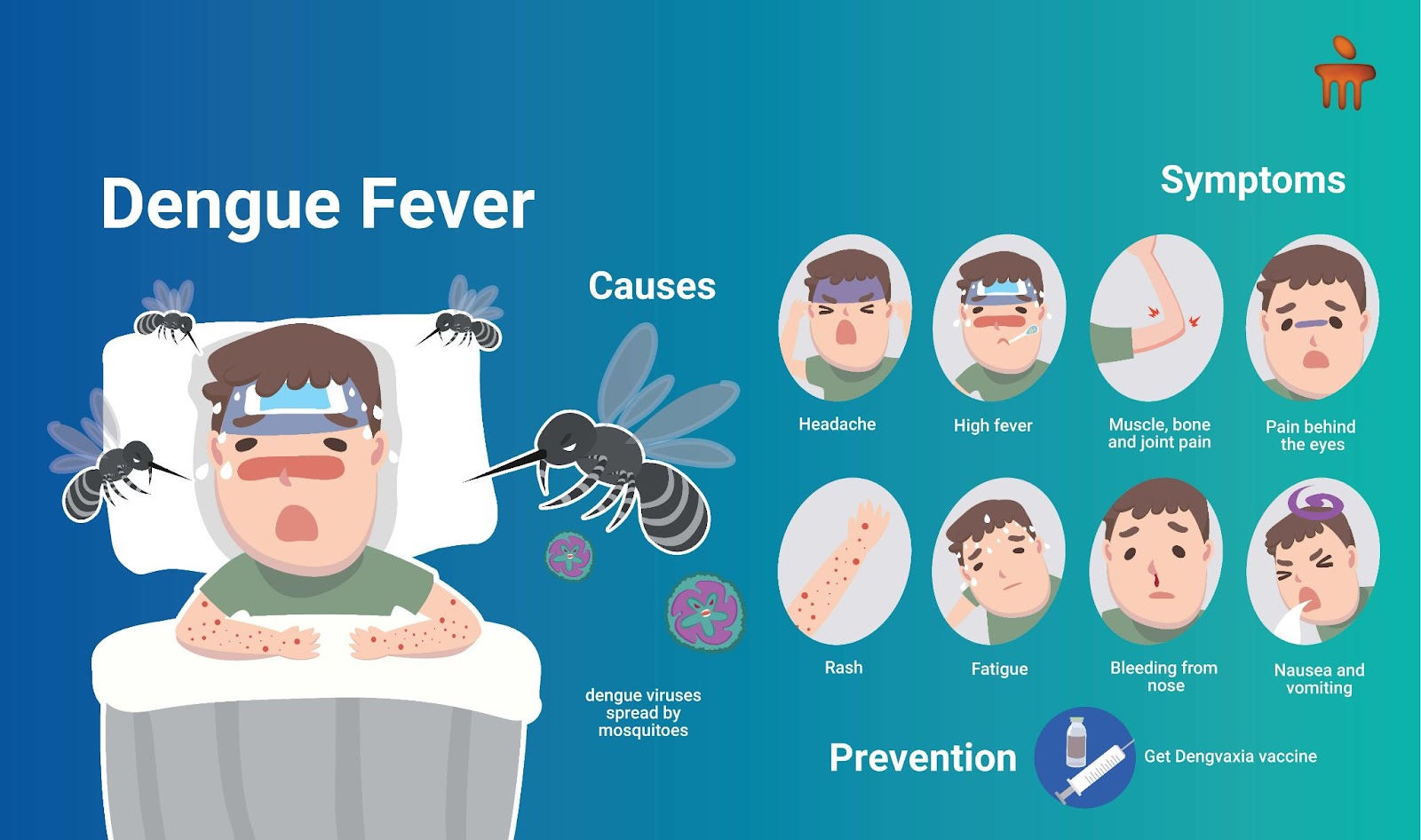
Signs and Symptoms of Dengue Fever
A few of the symptoms of dengue fever are:
-
Sudden, high fever
-
Pain behind eyes
-
Severe joint and muscle pain
-
Nausea
-
Vomiting
-
Skin rash (which appears 2 to 5 days after the inception of fever)
-
Mild bleeding (such as nose bleed, bleeding gums or easy bruising).
Sometimes, symptoms can be mild and mistaken as those of the flu or other viral infections. However, serious problems can occur if taken mildly. These include dengue haemorrhagic fever, which is characterized by high fever, damage to blood vessels and lymph, enlargement of the liver, failure of the circulatory system and bleeding from the nose and gums. If dengue haemorrhagic fever is left untreated, then the symptoms can progress to massive bleeding, shock and death. This is known as dengue shock syndrome (DSS).
If someone experiences one or more of the symptoms given above, then immediately consult a doctor for the treatment.
Causes of Dengue Fever
Dengue is primarily transmitted through the bite of a mosquito. When a mosquito bites someone who is infected with dengue, the virus is passed on to the mosquito. If the same mosquito then bites another person, the virus is transmitted to the new host. The disease is commonly found in human-inhabited areas, particularly where there is stagnant water, such as open drains and discarded tires. While there have been some documented cases of sexual and intravenous transmission, these modes of transmission are relatively rare.
Stages of Dengue Fever
Dengue can be contagious and affects around 40% of the global population. Early diagnosis significantly improves the chances of a prompt recovery. The disease progresses through different stages, each with varying severity and impact on the individual:
-
Stage I: Lasting 1-5 days, this stage is characterized by acute fever. Symptoms may include stomach discomfort, nausea, vomiting, and high fever. If children experience a lack of appetite, decreased fluid intake, and weakness, it is advisable for parents to promptly seek medical consultation.
-
Stage II: This crucial stage occurs from Day 5 to Day 7. During this period, the body temperature drops within 24 hours, leading to plasma leakage (the fluid component of blood) and a decrease in blood pressure. Symptoms can include weakness, restlessness, cold and clammy skin, rapid pulse, and in severe cases with low platelet levels, vomiting of blood or internal bleeding.
-
Stage III: This stage marks the recovery phase, typically taking a few days for patients to return to a normal state. During this stage, the patient's appetite starts to improve, their pulse rate slows down, and they may develop a convalescent rash on their legs and arms.
Diagnosis of Dengue Fever
The diagnosis of dengue involves a combination of clinical assessment and laboratory tests. Healthcare providers will evaluate your symptoms and medical history to determine if dengue is a likely diagnosis. Common symptoms of dengue include high fever, severe headache, joint and muscle pain, rash, and nausea or vomiting. It is crucial to inform your healthcare provider if you have recently travelled to an area where dengue is prevalent. During the physical examination, healthcare providers will look for signs of dengue, such as a skin rash, enlarged lymph nodes, and indications of bleeding or low blood pressure. Laboratory tests play a key role in confirming the presence of the dengue virus or detecting antibodies produced by the immune system in response to infection.
Molecular tests, like RT-PCR, directly detect the dengue virus in your blood. Serology tests, on the other hand, identify dengue antibodies in your blood, indicating a current or past infection. The most commonly used serology tests are IgM and IgG antibody tests. In addition to specific diagnostic tests, a complete blood count (CBC) may be performed. The CBC measures the number of platelets, white blood cells, and red blood cells in your blood. A decrease in platelet count is a characteristic feature of dengue infection.
Treatment of Dengue Fever
Treatment for dengue involves managing symptoms, preventing complications, and supporting the patient's recovery. It includes maintaining hydration through oral rehydration solutions or intravenous fluids, relieving symptoms with medications like acetaminophen, resting, monitoring vital signs, and addressing potential complications such as bleeding or organ impairment. Supportive care, including emotional support and proper nutrition, is also important. There is no specific antiviral treatment for dengue, so seeking medical attention and following healthcare professionals' guidance is crucial for effective management.
Prevention of Dengue Fever
Unfortunately, there is no vaccine discovered to prevent dengue fever. The best way to prevent the disease is to prevent bites by infected mosquitoes which involves protecting yourself and also taking measures to keep the mosquito population down.
A few of the things which one can do for protection from dengue are:
-
Use mosquito repellents
-
When outdoors, wear long-sleeve shirts and long pants
-
Use air-conditioning, if available
-
Safeguard yourself indoors by making sure that window and door screens are secure and free from holes.
-
Use mosquito nets while sleeping if air-conditioning is not available.
-
Keep yourself away from heavily populated residential areas
-
Keep yourself away from garbage.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) on Dengue Fever
-
What are the 5 symptoms of dengue?
While the majority of individuals infected with the dengue virus remain asymptomatic, those who do exhibit symptoms commonly experience high fever, headaches, body aches, nausea, and a rash. Fortunately, most of these cases are resolved within 1 to 2 weeks. However, a small percentage may progress to severe dengue, necessitating hospitalisation. For expert advice on your condition, kindly contact the best hospital for infectious disease and antibiotics treatment in Bangalore.
-
What are the 3 stages of dengue fever?
There are a total of three stages of dengue fever:
-
Stage I: Lasting 1-5 days, it includes symptoms like stomach discomfort, nausea, vomiting, and high fever; parents should seek medical advice if children show decreased appetite and weakness.
-
Stage II: Occurs from Day 5 to Day 7, marked by temperature drop, plasma leakage, low blood pressure, and symptoms like weakness, restlessness, cold skin, and, in severe cases, bleeding.
-
Stage III: The recovery phase, lasting a few days, brings improved appetite, slower pulse rate, and the possibility of a convalescent rash on the limbs.
-
What is the best treatment for dengue?
Dengue fever doesn't have a specific treatment, but recovery can be aided by staying hydrated with fluids like water, juice, and soup, avoiding caffeine, getting ample rest, and using acetaminophen for fever and joint pain relief. However, it is crucial to contact a doctor immediately if signs of dehydration, like reduced urination, are observed.
-
How many days does dengue fever last?
Dengue induces flu-like symptoms lasting 2-7 days, typically emerging 4-10 days after a mosquito bite. High fever (40°C/104°F) is commonly accompanied by at least two of these symptoms, including headaches.




















 4 Min Read
4 Min Read












