
PCOS (Polycystic Ovary Syndrome) is a hormonal disorder that affects women of reproductive age. It is a common condition that is caused by an imbalance of reproductive hormones, which can lead to a range of symptoms.
It is characterised by a range of symptoms, including irregular periods, excessive hair growth, acne, weight gain, and infertility. PCOS is caused by an imbalance of hormones in the body, specifically an excess of androgens (male hormones) and insulin resistance. The exact cause of PCOS is not fully understood, but it is believed to be genetic. Women who have a family history of PCOS are more likely to develop the condition. Other factors that may contribute to the development of PCOS include obesity, insulin resistance, and inflammation. PCOS can be diagnosed through a combination of symptoms, a physical exam, and blood tests to check hormone levels.
There is no definitive test for PCOS, but doctors will look for a combination of symptoms and lab results to make a diagnosis. There is no cure for PCOS, but its symptoms can be managed through lifestyle changes, such as diet and exercise, and medications to regulate menstrual cycles and control symptoms such as excessive hair growth and acne. Women with PCOS who are trying to conceive may also benefit from fertility treatments. Women with PCOS need to manage their condition to reduce the risk of long-term complications, such as type 2 diabetes, high blood pressure, and heart disease. With proper management, women with PCOS can lead healthy and fulfilling lives. In this blog, we will discuss polycystic ovary syndrome and treatments available for PCOS.
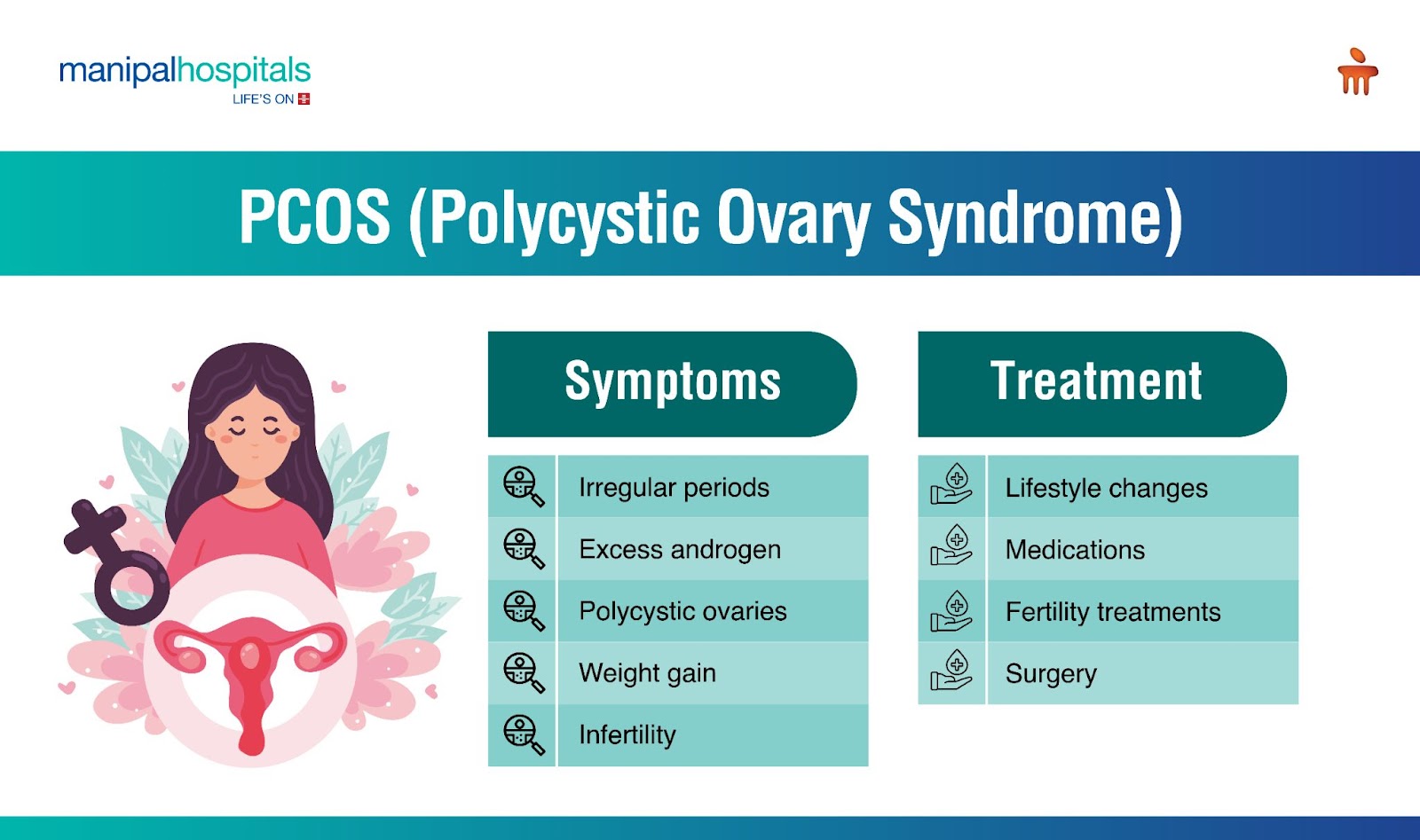
Symptoms of PCOS
Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS) is a hormonal disorder that affects women of reproductive age. It is a common condition that affects up to 10% of women worldwide and is characterised by a range of symptoms. The symptoms of PCOS can vary from woman to woman but typically include irregular periods, excessive hair growth, acne, weight gain, and infertility.
1. Irregular Periods: Women with PCOS may experience irregular periods or no periods at all.
2. Excess Androgen: Androgen is a male hormone that is also present in women. Women with PCOS may have high levels of androgen, which can cause excess hair growth and acne.
3. Polycystic Ovaries: Women with PCOS may have enlarged ovaries that contain small cysts.
4. Weight Gain: Women with PCOS may struggle with weight gain, particularly in the abdominal area.
5. Infertility: PCOS can make it difficult for women to conceive due to irregular ovulation.
Treatment for PCOS
Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS) is a hormonal disorder that affects women of reproductive age. While there is no cure for PCOS, its symptoms can be managed through a variety of treatment options. Treatment for PCOS typically involves a combination of lifestyle changes, such as diet and exercise, and medications to regulate menstrual cycles and control symptoms such as excessive hair growth and acne. In some cases, women with PCOS may also benefit from fertility treatments.
- Lifestyle Changes: Women with PCOS can benefit from making healthy lifestyle changes, such as eating a balanced diet, exercising regularly, and managing stress.
- Medications: Medications such as birth control pills and metformin can help regulate periods, reduce androgen levels, and improve insulin resistance.
- Fertility Treatments: Women who are struggling with infertility due to PCOS can benefit from fertility treatments such as in vitro fertilisation (IVF) and intrauterine insemination (IUI). PCOS and pregnancy are almost correlated.
- Surgery: In some cases, surgery may be necessary to remove cysts from the ovaries.
PCOS is a common condition that affects many women of reproductive age. If you are experiencing symptoms of PCOS, it is important to speak with your healthcare provider to determine the best course of treatment for you. By making healthy lifestyle changes and working with your healthcare team, you can manage the symptoms of PCOS and improve your overall quality of life.
FAQs
1. What is PCOS?
PCOS stands for Polycystic Ovary Syndrome, which is a hormonal disorder that affects women of reproductive age.
2. What are the symptoms of PCOS?
The symptoms of PCOS include irregular periods, excessive hair growth, acne, weight gain, and infertility.
3. How is PCOS diagnosed?
A diagnosis of PCOS is usually based on a combination of symptoms, a physical exam, and blood tests to check hormone levels.
4. What are the treatment options for PCOS?
Treatment options for PCOS include lifestyle changes, such as diet and exercise, medications to regulate menstrual cycles, and fertility treatments for women who are trying to conceive.
5. Can PCOS be cured?
While PCOS cannot be cured, its symptoms can be managed through lifestyle changes and medications. With proper management, women with PCOS can lead healthy and fulfilling lives.





















 3 Min Read
3 Min Read









