
Sudden Infant Death Syndrome, or SIDS, is a devastating and tragic occurrence that can happen to any family. It is the sudden and unexpected death of an otherwise healthy infant under the age of one year. Despite years of research and preventative measures, SIDS remains one of the leading causes of death for infants in developed countries.
While the exact cause of SIDS is still unknown, several risk factors have been identified. These include placing an infant to sleep on their stomach or side, exposure to second-hand smoke, overheating during sleep, and premature birth or low birth weight.
To reduce the risk of SIDS, it is recommended that infants be placed on their backs to sleep for every nap and bedtime until they are one year old. Additionally, it is important to ensure that the sleeping environment is safe and free from any potential hazards, such as loose bedding or soft objects. Parents should also avoid exposing their infants to smoke and maintain a comfortable room temperature during sleep.
While there is no guaranteed way to prevent SIDS from occurring, following these guidelines can significantly reduce the risk. Parents and caregivers need to stay informed about this condition so they can take necessary precautions and keep their little ones safe.
Synopsis
What are the Causes of Sudden Infant Death Syndrome (SIDS)?
A combination of factors can lead to the causes of SIDS, but by definition, the cause is still unknown. However, researchers have studied the potential of SIDS causes to try to understand better how and why it occurs. Based on the research, the most commonly accepted interpretation is that the babies who die of SIDS have an underlying vulnerability, such as a genetic pattern or brain abnormality. Then slowly, with time, they have become exposed to a trigger during early brain or immune system development that vulnerability causes sudden death.
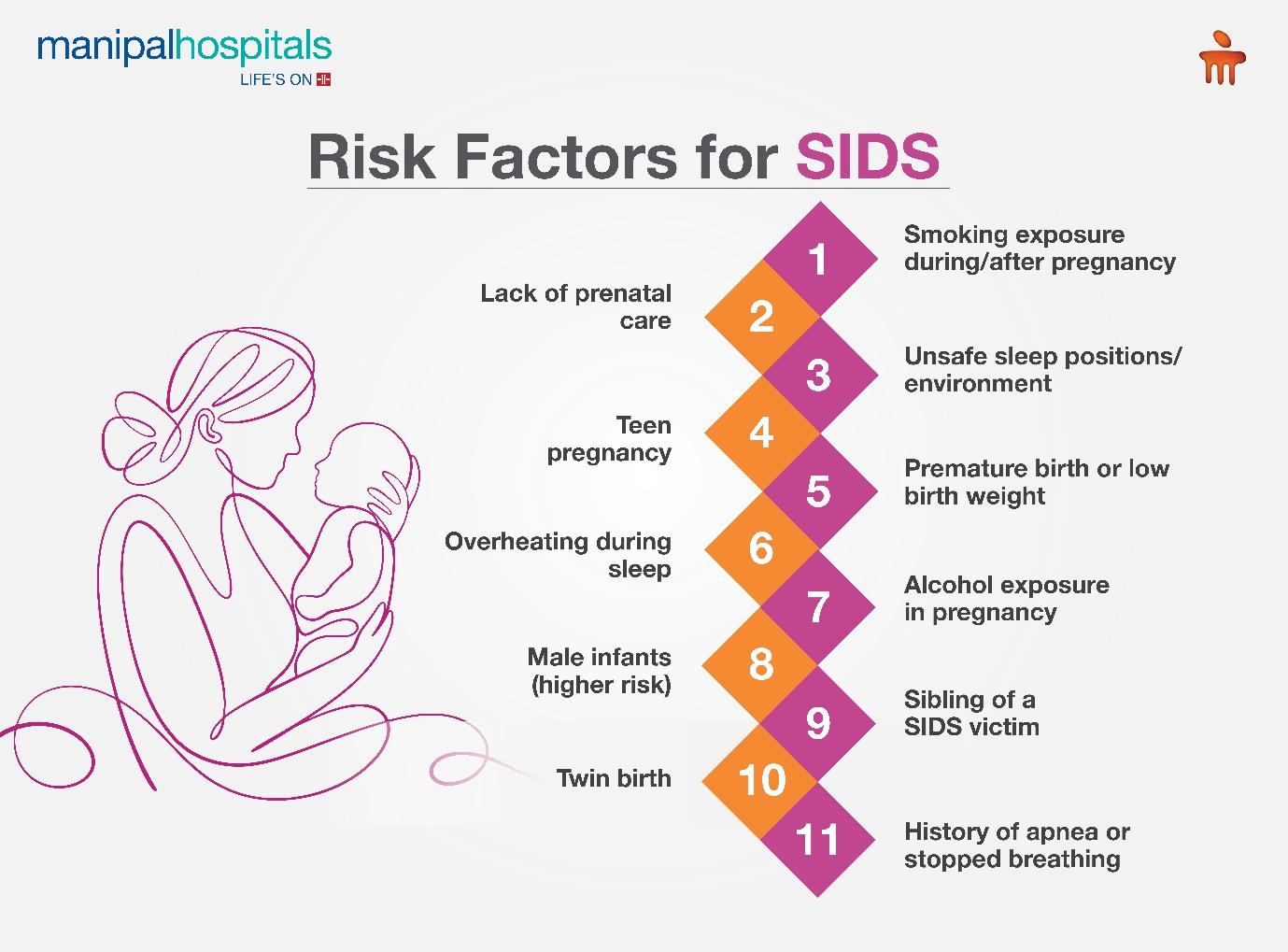
Risk Factors of Sudden Infant Death Syndrome or SIDS
-
Exposure to smoking during or after pregnancy
-
Late or no prenatal care
-
An unsafe sleeping position or sleeping environment
-
Teen pregnancy
-
Preterm birth or low birth weight
-
Overheating
-
Exposure to beverages containing alcohol during pregnancy
-
Being assigned male at birth (AMAB)
-
Being a sibling of SIDS victims
-
Being a twin
-
Having a history of stopping breathing or Apnea
Preventive Measures for Sudden Infant Death Syndrome (SIDS)
Parents who are aware of SIDS could consider it to be their worst nightmare. SIDS, sometimes called cot death, is the medical term for sudden infant death. It occurs when an infant who is 12 months or younger passes away while asleep without any prior symptoms or a known cause.
You can do several things to reduce your baby's risk of SIDS, even though there is no way to avoid it altogether. The SIDS rate has significantly decreased since the American Academy of Paediatrics released its safe sleep guidelines in 1992 and began its "Back to Sleep" campaign in 1994.
What Can Be Done to Avoid SIDS?
-
Putting a sleeping baby on their back for infant sleep safety
Any time the baby sleeps on their side or stomach, their risk of SIDS increases significantly. (A baby turned on its side can flip over and land on its stomach.) These poses might suffocate your infant because they place their face against the bed or other sleeping surfaces. Key steps include:
-
Always lay the baby down on their back.
-
Avoid letting them sleep in swings, car seats, or strollers for long periods.
-
Ensure all caregivers follow these infant sleep safety practices.
-
Use a Firm Mattress and Avoid Soft Bedding
Babies should always sleep on a firm mattress without soft objects or bedding in the cot or bassinet to avoid smothering or asphyxia. One should avoid using soft toys or cushions in the baby’s crib to avoid suffocation risks. Remember to:
-
Use a firm crib mattress with a fitted sheet
-
Avoid placing blankets, pillows, plush toys, or crib bumpers inside the crib
-
Keep the baby close while sleeping, in Their Own Sleep Space
Studies have shown that having a baby sleep in the same room as the mother reduces the incidence of SIDS. However, it is risky for a baby to share the same bed, armchair, or couch with another child or an adult. When the mother is ready to go to bed, place the baby back in their own cradle, bassinet or crib. The recommendations are:
-
Place the crib or bassinet near your bed for close monitoring
-
Avoid bed-sharing or letting the baby sleep on couches or armchairs
-
If sleepy, avoid breastfeeding in risky positions like chairs or couches
-
Breastfeed as long as the mother can
The risk of SIDS can be reduced by up to 50% by exclusively breastfeeding the baby, though researchers aren't entirely sure why. Some believe breast milk may shield babies from illnesses that increase their risk of SIDS. To maximise benefits:
-
Breastfeed exclusively if possible
-
Avoid alcohol consumption while breastfeeding
-
Engage in skin-to-skin contact, which is important for infant development
SIDS is a heart-breaking condition, but there are effective ways to reduce the risks. Simple practices like infant sleep safety, maintaining a safe sleeping environment, and avoiding smoking around the baby can make a big difference. Breastfeeding and regular check-ups are also key. Parents can create a safer space for their babies and ease their worries with the correct knowledge and by taking precautions.
FAQ's
Sudden Infant Death Syndrome (SIDS) refers to the sudden and unexpected death of an otherwise healthy infant under the age of one year during sleep, without any apparent cause. It remains one of the leading causes of infant mortality in developed countries despite extensive research.
Several risk factors have been identified, including placing infants to sleep on their stomach or side, exposure to second-hand smoke, overheating during sleep, premature birth or low birth weight, and unsafe sleeping environments. However, the exact cause of SIDS remains unknown.
While there's no guaranteed way to prevent SIDS, certain precautions can significantly reduce the risk. These include placing infants on their backs to sleep for every nap and bedtime until they are one year old, ensuring a safe sleeping environment free from hazards like loose bedding or soft objects, avoiding exposure to smoke, and maintaining a comfortable room temperature during sleep.
Safe sleep practices recommended by pediatric experts include placing babies on their backs to sleep, using a firm mattress or surface without soft toys or bedding, keeping the baby close during sleep but avoiding sharing the same bed, and breastfeeding for as long as possible, as it may reduce the risk of SIDS by up to 50%.
Following safe sleep guidelines, such as placing babies on their backs to sleep and creating a safe sleeping environment, has significantly reduced the incidence of SIDS since initiatives like the "Back to Sleep" campaign were introduced. While these practices cannot completely eliminate the risk of SIDS, they are crucial steps in minimizing it and keeping infants safe during sleep.





















 6 Min Read
6 Min Read











