
Testicular cancer might not be a topic many openly discuss, but it’s one every man should be aware of it especially if you're in your 20s, 30s or 40s. This type of cancer affects the testicles, part of the male reproductive system and is responsible for producing sperm and testosterone. While testicular cancer is rare compared to other cancers, it’s the most common cancer in younger men. However, most cases are highly treatable, even when diagnosed at a later stage.
This blog explains everything you need to know, from early signs of testicular cancer to its causes, diagnosis, and treatment options. We aim to help you or your loved ones recognise testicular cancer symptoms early and feel empowered to take the right steps.
Let’s start with the basics.
Synopsis
What Is Testicular Cancer?
To put it simply, testicular cancer occurs when cells in one or both testicles begin to grow uncontrollably. These can form a lump or tumour. While the condition is rare compared to other cancers, it is most likely to affect young and middle-aged men.
We observed two main types of testicular cancer:
-
Seminomas - slow-growing and usually found in older men.
-
Non-seminomas – more aggressive and tend to grow quickly.
No matter the type, most cases respond well to treatment, especially when diagnosed early.
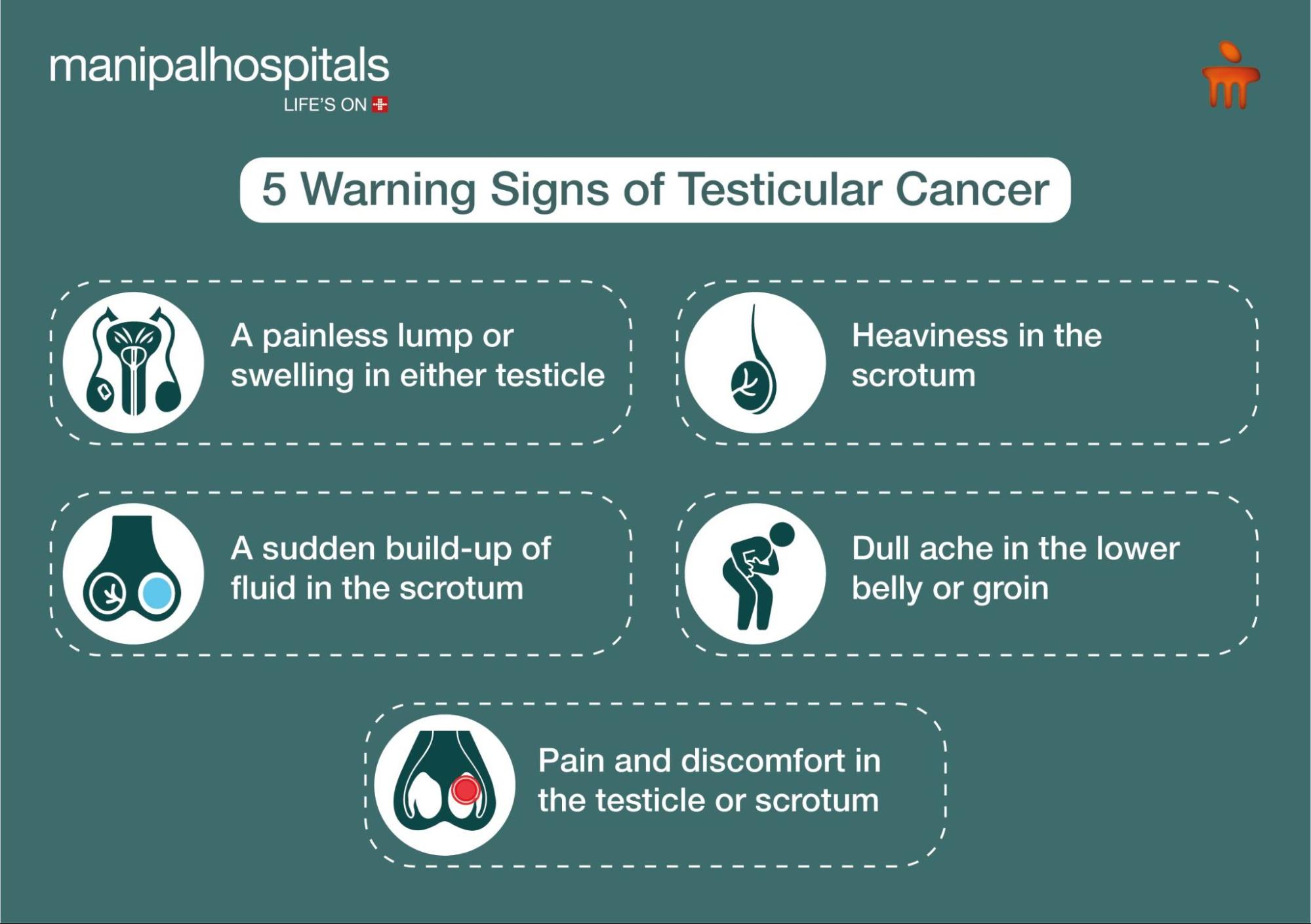
What are the Symptoms of Testicular Cancer?
The early signs of testicular cancer are often subtle, but paying attention to your body can help you spot them early. It’s important to know the early signs of testicular cancer so you can act quickly.
So, below are the 5 testicular cancer symptoms:
-
A painless lump or swelling in either testicle
-
Heaviness in the scrotum
-
A sudden build-up of fluid in the scrotum
-
Dull ache in the lower belly or groin
-
Pain and discomfort in the testicle or scrotum
Some people also experience below listed signs as testicular cancer symptoms:
-
Due to hormone changes, there might be breast tenderness or growth
-
Lower back pain may occur if the cancer has spread.
These signs may not always mean cancer. But if they persist for more than a few days, get them checked.
Testicular Cancer Causes and Risk Factors
The exact causes of testicular cancer are still unclear, but doctors believe it’s linked to genetic and developmental factors.
Common risk factors include:
-
Undescended testicle (cryptorchidism)
-
Family history of testicular cancer
-
Abnormal testicle development (conditions like Klinefelter syndrome)
-
Age – most common between 15 and 45
-
Ethnicity – higher risk in white men
Having one or more risk factors doesn’t guarantee you’ll get it, but it’s a reason to be more aware of your body.
Stages of Testicular Cancer
Once diagnosed, doctors will try to figure out how far the cancer has spread. This is called staging.
Testicular Cancer Stages:
-
Stage 0: This is also called Carcinoma in situ. In this stage, the cancer cells are only in the testicle and haven’t spread.
-
Stage 1: Cancer is only in the testicle but may have invaded nearby tissues.
-
Stage 2: Cancer has spread to the lymph nodes.
-
Stage 3: Cancer has spread to distant parts of the body (lungs, liver, etc.)
Early-stage cancers have an excellent survival rate, over 95% if caught early. That’s why early detection is key.
Testicular Cancer Diagnosis: Tests and Exams
So, how is testicular cancer found?
It usually starts with a physical check-up. If your doctor suspects anything unusual, they may suggest:
-
Ultrasound of the scrotum: to get a closer look at any lumps
-
Blood tests: to check for tumour markers (proteins made by cancer cells)
-
MRI or CT scan: to detect if the cancer has spread
-
Surgical removal (orchiectomy): Sometimes the testicle may be removed to confirm the diagnosis and stop the spread
Testicular Cancer Treatment Options
The treatment for testicular cancer depends on the type, stage, and overall health. The doctor will personalise the care, but here are the most common testicular cancer treatment paths:
1. Surgery (Orchiectomy)
This is the first step in almost all cases. The affected testicle is removed to prevent the cancer from spreading. It’s a simple, safe procedure. Most men live healthy lives with one testicle.
2. Radiation Therapy
Mainly used for seminomas. In this treatment, powerful X-rays are used to kill cancer cells. It may be used after surgery to reduce the risk of cancer returning.
3. Chemotherapy
This is more common when cancer has spread or for non-seminomas. In this treatment, drugs are used to destroy cancer cells in the body. While it may cause side effects like nausea and hair loss. This is a very effective testicular cancer treatment.
4. Active Surveillance
For early-stage cancer, your doctor may recommend watchful waiting. You’ll have regular check-ups, scans, and blood tests. This avoids unnecessary treatment and works well when the risk is low.
Living with and Beyond Testicular Cancer
Most men with testicular cancer go on to live long and healthy lives. However, you may need to consider other treatments for fertility if you're planning to have children in the future.
Regular follow-ups, healthy lifestyle choices, and emotional support are key to long-term wellness.
Don’t be afraid to ask for help, talk to your doctor, connect with a support group, or speak to a counsellor if needed.
How to Check Yourself for Testicular Cancer?
Monthly self-exams are one of the easiest ways to catch issues early.
-
Do it during or after a warm shower when the skin is relaxed.
-
Gently roll each testicle between your fingers.
-
Feel for any lumps, hardness, or swelling.
If anything feels unusual, don’t panic, but do speak to a doctor. Early action can save your life.
When to See a Doctor?
One should consult a doctor if the following symptoms are there:
-
Swelling and a lump in the testicle
-
A heavy feeling in the scrotum
-
Any change in the testicles' size or shape
Don’t feel embarrassed. These could be signs of testicular cancer or another health issue that needs care.
Conclusion
Testicular cancer may sound scary, but it’s one of the most treatable cancers. When caught early, the chances of a full recovery are very high. So don’t ignore changes in your body.
Check yourself regularly, stay aware of the early signs of testicular cancer, and speak to your doctor if anything doesn’t feel right. Stay informed. Stay alert. And take care of your health.
FAQ's
Testicular cancer can sometimes run in families, especially if a close male relative (like a father or brother) has had it. However, most cases of testicle cancer have no family history. If you have a family history, it’s better to talk to your doctor about regular screening.
Yes, if not detected early, testicular cancer can spread to lymph nodes, lungs, liver, or even the brain. This makes the early diagnosis and treatment critical.
Some forms, like non-seminomas, can grow and spread quickly. Others, like seminomas, are slower. Regular check-ups and acting fast when symptoms appear help in early detection and treatment.
Yes, especially if both testicles are removed or if the remaining one isn’t working properly. In such cases, hormone replacement therapy may be needed to maintain normal testosterone levels.
Yes, in some cases, it can return, especially within the first few years after treatment. This is why regular follow-ups and scans are so important to monitor for recurrence.
There’s no guaranteed way to prevent testicular cancer, but regular self-checks, a healthy lifestyle, avoiding exposure to harmful chemicals, and managing existing health conditions can help reduce the overall cancer risk.




















 7 Min Read
7 Min Read














