-
Centre of
Excellence
Centre of Excellence
Other Specialities
- Allergy and Immunology
- Andrology
- Anesthesiology
- Clinical Psychology
- Dental Medicine
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- Ear Nose Throat
- Epilepsy Clinic
- General Medicine
- General Surgery
- Geriatric Medicine
- GI Surgery
- Gynaec Oncology
- Heart Care Clinic
- Hemato Oncology
- Hematology
- Hepatobiliary Surgery
- ICU and Critical Care
- Infectious Disease
- Internal Medicine
- Interventional Radiology
- Medical Gastro
- Medical Oncology
- Microbiology
- Minimal Access Surgery
- Nutrition And Dietetics
- Ophthalmology
- Oral Maxillo Facial Surgery
- Pain Medicine
- Parkinson Disease and Movement Disorder
- Pathology
- Pharmacy
- Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation
- Physiotherapy
- Plastic And Cosmetic Surgery
- Podiatric Surgery
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology (Respiratory and Sleep Medicine)
- Radiology
- Renal Sciences
- Rheumatology
- Surgical Gastro
- Surgical Oncology
- Vascular and Endovascular Surgery
Speciality Clinics
- Doctors
- Broadway
- International Patients



Clinics








- Self Registration
- In-Patient Deposit
- Mars - Ambulance
- Corporate & PSU
- Insurance Helpdesk
- Awards And Achievements
- Careers
- Contact Us

Epididymitis
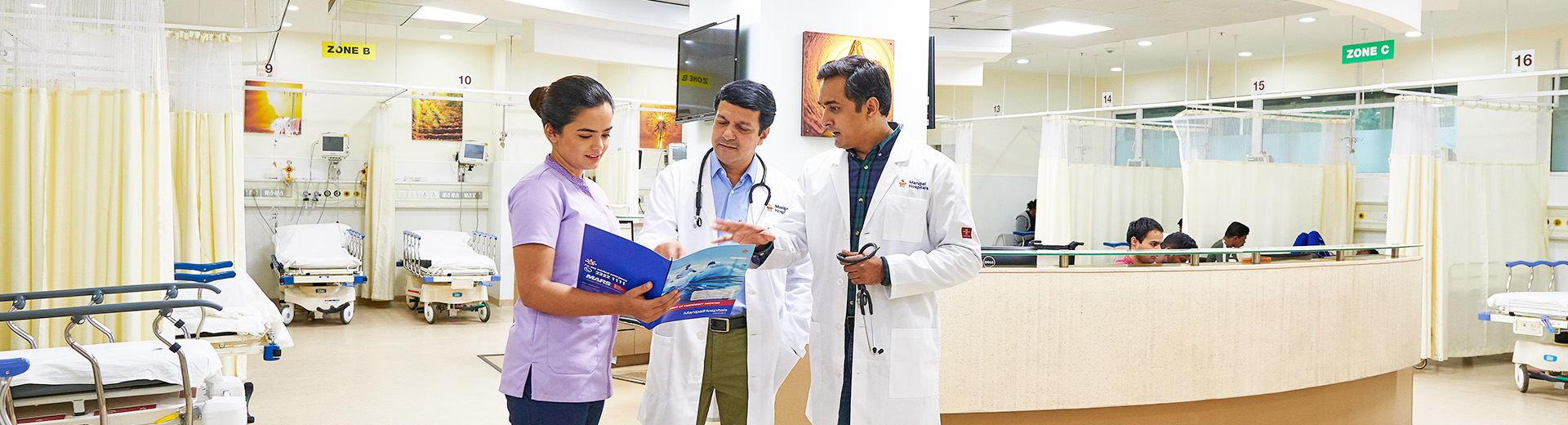
Epididymitis Treatment in Broadway
Manipal Hospitals in Broadway, Kolkata, offers world-class treatment for epididymitis, a condition involving inflammation of the epididymis, a coiled tube located at the back of the testicle. Epididymitis can cause pain, swelling, and discomfort in the scrotum and may be caused by bacterial infection or other factors. To ensure a correct diagnosis and the best therapy to bring about the greatest clinical outcome, we have a team of highly qualified urologists, andrologists, surgeons, radiologists, and nurses, supported by state-of-the-art equipment. Our top priority is providing personalised care, ensuring that each patient receives high-quality treatment tailored to their specific needs. Manipal Hospitals has an exceptional history of treating epididymitis with success and offering patient and their families regular professional counselling. Since urological illnesses require long-term treatment, we are committed to offering you regular check-ups, expert counselling, and continuing support. Additionally, the hospital guarantees that each patient has access to comprehensive medical care and a long-term benefit from the treatment.
Consult our andrology hospital if you need Epididymitis Treatment in Broadway.
FAQ's
Epididymitis is inflammation of the epididymis, the tube at the back of the testicle that stores and transports sperm. It is often caused by bacterial infections or sexually transmitted infections (STIs). Symptoms include pain and swelling in the testicle area. Antibiotics are typically used as a form of treatment for curing the infection. In rare cases, surgery may be needed to drain pus or remove part of the affected epididymis. It's important to seek early treatment to manage symptoms and prevent complications.
There are several factors that may cause epididymitis such as,
-
Urinary tract infections (UTIs)
-
Infections that are spread through sexual contact (STIs) such as chlamydia or gonorrhoea
-
Latest genito-urinary procedures, such as prostatectomy (surgical excision of the prostate gland entirely or in part)
-
Urine catheter
-
Certain genetic issues with the kidneys and bladder
Some early signs and symptoms of epididymitis include,
-
Inflated, red, or heated testicles
-
Testicle discomfort or soreness
-
Sensation of heaviness
-
Abdominal or pelvic pain
-
Frequent urge to urinate
-
Burning sensation during urination
-
Fever and chills
Although men of any age can get epididymitis, most instances affect those between the ages of 20 and 39, and they are typically linked to sexually transmitted diseases.
Diagnosing epididymitis can be done using,
-
Medical history and physical assessment: Your healthcare provider will discuss your symptoms and medical history, including any recent illnesses or sexual activity. They will then perform a physical examination, focusing on the testicles and groin area to check for swelling, tenderness, or signs of infection.
-
Sexually transmitted infection examinations: If an STI is suspected as the cause of epididymitis, additional tests such as swabs or urine tests may be done to detect specific pathogens like Chlamydia or Gonorrhea.
-
Urine examinations: A urine sample checks for signs of infection.
-
Blood examinations: Blood tests may be conducted to check for markers of infection or to rule out other conditions causing similar symptoms.
-
Ultrasound: Scans the scrotum to visualise the epididymis and rule out other issues.
If not diagnosed early, epididymitis can cause severe and permanent damage to the testicles which may lead to infertility. Early diagnosis can help you to get a successful treatment and avoid future complications.
Absolutely. Sexual interaction can spread epididymis. Although not officially classified as a sexually transmitted disease (STD), epididymitis is a typical symptom of several STDs, such as gonorrhoea and chlamydia. It is crucial to take necessary preventive measures to avoid the spread of epididymitis.
The treatment approach for epididymitis typically involves:
-
Antibiotics: Since bacterial infections are a common cause, antibiotics are prescribed to target and eliminate the infection. The choice of antibiotic depends on the suspected or identified bacteria and its sensitivity to specific medications.
-
Pain Relief: Over-the-counter pain relievers such as ibuprofen or acetaminophen may be recommended to alleviate discomfort and reduce inflammation.
-
Surgical Intervention (in rare cases): If an abscess forms or if conservative measures fail to resolve the condition, surgical drainage of the abscess or removal of the affected portion of the epididymis may be necessary.
Follow your doctor's advice closely and complete the full course of antibiotics to ensure the infection clears up completely. This approach helps relieve symptoms, prevent complications, and speed up recovery.
There is a possibility of epididymitis occurring again in a patient and that is termed as ‘’chronic epididymitis’’. Any epididymitis that recurs frequently or lasts longer than six weeks is classified as chronic.
To minimise the risk of epididymitis, one should have protected intercourse. Along with this, one should follow proper intimate hygiene practices. Sitting for a longer time and heavy lifting activities should be avoided as they put excessive strain on your lower abdomen.
Epididymitis itself does not directly lead to testicular cancer. However, chronic inflammation in the testicles or epididymis could potentially increase the risk over time. It's important to monitor for any changes in your testicles and seek medical attention if you notice new lumps, swelling, or persistent pain. Regular check-ups and prompt evaluation of any concerns can help ensure early detection and proper management if needed.
The following problems may arise from epididymitis if treatment is not received:
-
Abscess Formation: Pus-filled pockets may develop in severe cases, requiring drainage.
-
Chronic Epididymitis: Some cases may lead to persistent or recurrent inflammation despite treatment.
-
Infertility: Infections can potentially affect sperm production or transport, leading to temporary or permanent infertility.
-
Epididymal Cysts: Fluid-filled sacs may form within the epididymis, causing discomfort or requiring treatment.
-
Spread of Infection: Rarely, infections can spread to nearby structures, causing more serious health issues.
Home Broadway Specialities Andrology Epididymitis

You’re on Our Indian Website
Visit the Global site for International patient services











