-
Centre of
Excellence
Centre of Excellence
- Accident and Emergency Care
- Cancer Care/Oncology
- Cardiology
- Cardiothoracic Vascular Surgery
- Dialysis
- Gastrointestinal Science
- Laparoscopic Surgery
- Liver Transplantation Surgery
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Neurosurgery
- Obstetrics and Gynaecology
- Organ Transplant
- Orthopaedics
- Paediatric And Child Care
- Spine Care
- Urology
Other Specialities
- Allergy and Immunology
- Andrology
- Anesthesiology
- Bone Marrow Transplantation
- Clinical Psychology
- Dental Medicine
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- Ear Nose Throat
- Epilepsy Clinic
- General Medicine
- General Surgery
- Geriatric Medicine
- GI Surgery
- Gynaec Oncology
- Heart Care Clinic
- Hemato Oncology
- Hematology
- Hepatobiliary Surgery
- ICU and Critical Care
- Infectious Disease
- Internal Medicine
- Interventional Radiology
- IVF and Infertility
- Medical Gastro
- Medical Oncology
- Microbiology
- Minimal Access Surgery
- Neonatology & NICU
- Nutrition And Dietetics
- Ophthalmology
- Oral Maxillo Facial Surgery
- Paediatric Surgery
- Paediatric Urology
- Pain Medicine
- Parkinson Disease and Movement Disorder
- Pathology
- Pharmacy
- Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation
- Physiotherapy
- Plastic And Cosmetic Surgery
- Podiatric Surgery
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology (Respiratory and Sleep Medicine)
- Radiology
- Renal Sciences
- Rheumatology
- Surgical Gastro
- Surgical Oncology
- Vascular and Endovascular Surgery
Speciality Clinics
- Doctors
- Broadway
- International Patients



Clinics








- Self Registration
- In-Patient Deposit
- Mars - Ambulance
- Corporate & PSU
- Insurance Helpdesk
- Awards And Achievements
- Careers
- Contact Us

Hydrocele
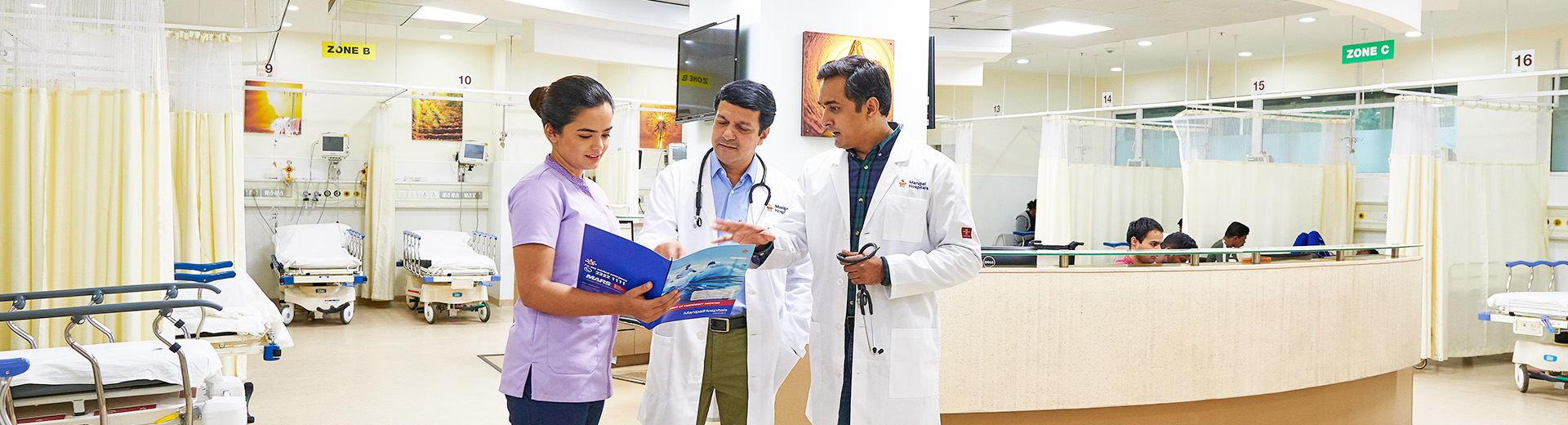
Hydrocele Treatment In Broadway
Manipal Hospitals is a leading hydrocele treatment location in India that is renowned for its exceptional diagnosis and treatment. A hydrocele is a fluid-filled sac that surrounds a testicle and frequently causes swelling without any pain. It may arise from a congenital issue, an injury, inflammation, or infection. Although hydroceles are usually painless, if they get large or become symptomatic, they may need to be treated.
Our team of expert urologists, surgeons, radiologists and nursing staff is committed to offering complete patient care, guaranteeing that each patient gets a rapid and most effective treatment for hydrocele. We emphasise empathetic assistance and advice at every stage of the treatment, from first consultations to post-therapy care, since we understand that hydrocele is a critical condition that requires special medical attention and comprehensive care. We stand out as a reputable facility to treat hydrocele because of our proven track record of success, constant dedication to technological developments in medicine, and individualised care.
Consult our andrology hospital if you need Hydrocele Treatment (surgical) In Broadway, Kolkata.
FAQ's
A kind of swelling known as hydrocele, or "water in balls," occurs when fluids pool around the testicles, causing swelling and occasionally pain. This is common in newborns and normally goes away on their own. Infections or injuries can result in hydrocele in boys and adult men.
There are two types of hydroceles: communicative and noncommunicating.
Noncommunicating hydrocele: A noncommunicating hydrocele happens when the sac that surrounds the testicle closes, but the fluid inside the sac is not absorbed by the body. This type of hydrocele can develop before birth or later in life, even in adulthood.
Communicative hydrocele: When the processus vaginalis, a thin membrane that connects the abdominal cavity to the scrotum during foetal development, stays open, a communicative hydrocele develops. This causes swelling by allowing fluid to move between the scrotum and the abdomen.
Scrotal swelling on one or both sides is the most typical symptom. Other signs and symptoms include:
-
Uncomfortable feeling in the Groyne region when seated
-
Scrotal pain
-
Swelling that fluctuates in size during the day
The diagnostic approach for hydrocele includes:
-
In addition to performing a physical examination, the urologist inquires about your symptoms. Your doctor can typically identify hydroceles based only on a physical examination.
-
To assess the swelling, the doctor may push on the groyne during the examination and ask the patient to cough. This is done to rule out testicular or inguinal hernias.
-
To confirm their diagnosis of hydrocele, the doctor may occasionally request imaging tests like X-rays, CT scans, or ultrasounds.
Most hydroceles go away by themselves without any treatment. However, if you feel pain or see redness around the affected area, your doctor may prescribe some medicines to provide you with symptomatic relief such as painkillers and topical antiinflammatory drugs.
If it doesn’t go away by itself, it is advised to consider surgery to treat the hydrocele. If a hydrocele persists and causes discomfort or other issues, a surgical procedure called hydrocelectomy is recommended. Hydrocelectomy is a relatively simple and minimally invasive surgery to remove the fluid and repair the scrotal enlargement. After the treatment, most patients are able to return home the same day.
The majority of hydroceles are benign and do not result in problems. Complications might, however, occasionally arise. Among them are:
-
Infection: Rarely, an infection of a hydrocele can result in fever, scrotal enlargement, redness, and discomfort. Antibiotic treatment for the infection can be necessary.
-
Hernia: A hydrocele may occasionally be connected to a hernia, which is a tissue protrusion via a weak point in the abdominal wall.
-
Testicular torsion: A hydrocele may raise the chance of developing testicular torsion, a painful twisting of the testicle inside the scrotum that can impair tissue and cut off blood supply. This side effect is quite rare.
Some of the measures to prevent hydrocele include:
-
Hydrocele can be avoided by sporting protective clothing during sports and activities that expose the scrotum. Testicles can be shielded by protective clothing such as an athletic supporter or jockstrap.
-
It is essential to practise excellent hygiene to avoid illnesses such as hydrocele. Frequent washing and avoiding strong chemicals or soaps can help prevent skin irritation.
-
Hydrocele can be avoided by treating infections like epididymitis and orchitis as soon as possible. Getting medical care for symptoms like pain, oedema, or fever might also be beneficial.
-
Hydrocele can also result from trauma to the scrotum, therefore getting medical help right away is crucial.
-
Avoid activities that put excessive strain on muscles: It's advisable to stay away from physically demanding activities like sports or heavy lifting that might strain the scrotum.
-
Apply cold compresses: The scrotum might experience less pain and swelling by having a cold compress applied to it.
-
Take pain relievers: Ibuprofen or paracetamol, two over-the-counter pain relievers, can help reduce pain and discomfort.
-
Keep an eye out for changes: Get medical help right away if the hydrocele seems to be changing in size or shape or if you suddenly feel painful.
Home Broadway Specialities Andrology Hydrocele

You’re on Our Indian Website
Visit the Global site for International patient services











