-
Centre of
Excellence
Centre of Excellence
Other Specialities
- Allergy and Immunology
- Andrology
- Anesthesiology
- Clinical Psychology
- Dental Medicine
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- Ear Nose Throat
- Epilepsy Clinic
- General Medicine
- General Surgery
- Geriatric Medicine
- GI Surgery
- Gynaec Oncology
- Heart Care Clinic
- Hemato Oncology
- Hematology
- Hepatobiliary Surgery
- ICU and Critical Care
- Infectious Disease
- Internal Medicine
- Interventional Radiology
- Medical Gastro
- Medical Oncology
- Microbiology
- Minimal Access Surgery
- Nutrition And Dietetics
- Ophthalmology
- Oral Maxillo Facial Surgery
- Pain Medicine
- Parkinson Disease and Movement Disorder
- Pathology
- Pharmacy
- Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation
- Physiotherapy
- Plastic And Cosmetic Surgery
- Podiatric Surgery
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology (Respiratory and Sleep Medicine)
- Radiology
- Renal Sciences
- Rheumatology
- Surgical Gastro
- Surgical Oncology
- Vascular and Endovascular Surgery
Speciality Clinics
- Doctors
- Broadway
- International Patients



Clinics








- Self Registration
- In-Patient Deposit
- Mars - Ambulance
- Corporate & PSU
- Insurance Helpdesk
- Awards And Achievements
- Careers
- Contact Us
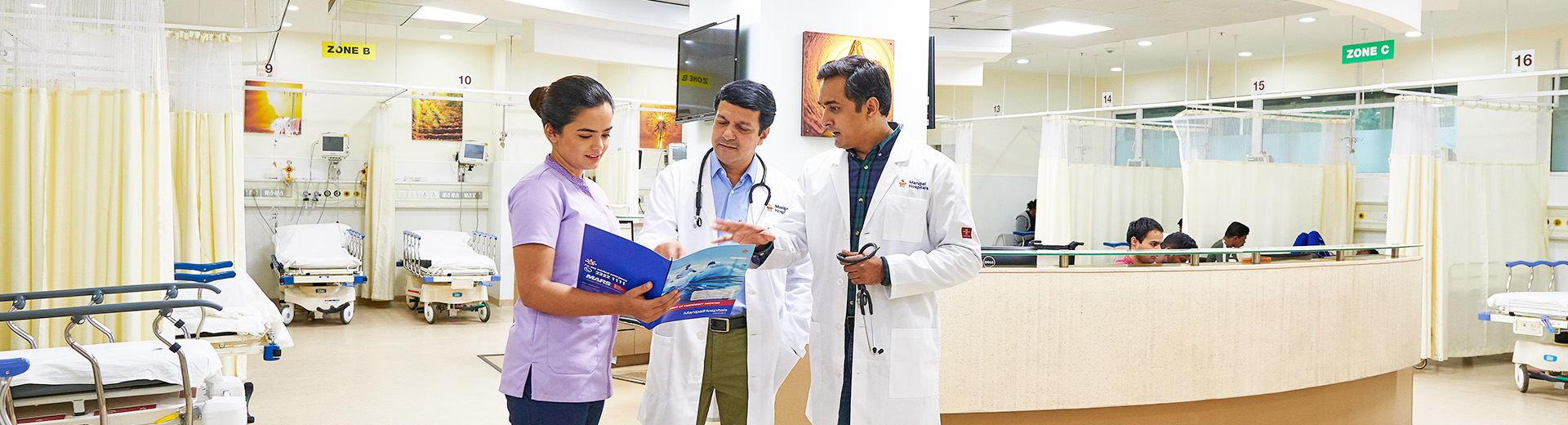

Colposcopy Clinic
Best Colposcopy Examination Hospitals in Broadway
A Colposcopy is a medical diagnostic used to examine the vulva, vaginal wall, and cervix for signs of precancerous or cancerous tissue. The procedure is often recommended in patients with abnormal Pap smear results or concerning symptoms. This painless procedure helps in the early detection of cancer or precancerous cells, allowing for timely intervention, which can potentially cure cervical cancer. Additionally, Colposcopy is used to rule out cancer.
Before your Colposcopy, discuss with your provider any concerns you may have regarding the risk of cancer and any consequences. Feeling anxious before the procedure is normal, but understanding what to expect from the procedure can make you feel more relaxed. If you are looking for a Colposcopy clinic in Kolkata, reach out to Manipal Hospitals.
FAQ's
During a diagnostic technique called a Colposcopy, your doctor might look for abnormal tissue in the wall of your vagina and on your cervix, the bottom section of your uterus. Throughout the process, the tissue lining your cervix and vagina is magnified using a special illuminated microscope known as a colposcope. Your doctor may perform tissue samples or biopsies if they notice any irregularities. These samples can be examined in a lab to check for malignant or precancerous cells.
The main purpose of Colposcopy is to look for cancerous cells or cells that, if left untreated, could develop into cancer (also termed cervical dysplasia). Your doctor will examine your vagina, cervix, and external genitalia (vulva) for these cells. Moreover, genital warts, polyps, and non-cancerous growths can be checked for during a Colposcopy. In certain cases, your doctor may advise a Colposcopy to assess additional symptoms such as irregular vaginal bleeding or vulvar irritation.
Colposcopy may be necessary for individuals who were designated female at birth (DFAB), such as cisgender women, transgender men, and nonbinary people with vaginas, to look into test results that might point to abnormalities. A Colposcopy could be advised by your doctor if you:
-
Pap test or Pap smear results were abnormal.
-
Had unusual findings from a pelvic check.
-
Had a positive human papillomavirus (HPV) test.
A Colposcopy can be done by your gynaecologist or primary care physician. Colposcopists are skilled individuals who occasionally carry out this process. Precancerous cells are more likely to be discovered early if the treatment is carried out by a medical practitioner with experience, according to research.
- Inform your healthcare practitioner about your pregnancy status. You can have a Colposcopy while pregnant, but if your doctor does a biopsy as part of the process, you might be more likely to bleed.
-
Choose a time when you won't be menstruating to have your Colposcopy done. The operation can be done while you are menstruating. When you are not bleeding, it will be simpler for your healthcare physician to examine your cervix.
-
Before your Colposcopy, refrain from any type of vaginal penetration for 48 hours. Steer clear of finger intercourse and penetration with sex devices. Tampons and vaginal drugs (such as creams or suppositories) should not be used. Any of these factors could change the Colposcopy's outcomes.
-
You might be told to take pain medication on the day of the procedure. Acetaminophen (Tylenol) and ibuprofen (Advil, Motrin)-containing medications can help you feel more comfortable throughout the process.
A Colposcopy can happen in a clinic or doctor's office. Typically, the process takes ten to twenty minutes. You should be able to go back home on the same day as your surgery.
-
You are required to lie down on a table for inspection.
-
Your cervix will be visible after your physician inserts a device called a speculum, which widens your vagina.
-
Your doctor will examine your vagina and cervix more closely using the colposcope. With the built-in light and binocular-style lenses on the colposcope, your doctor may easily examine your cervix while seated at your feet. During the entire procedure, the colposcope will stay outside of your vagina.
-
Your healthcare professional will clean your cervix with a vinegar solution containing acetic acid using a cotton swab. There can be a faint burning feeling. Any suspect locations are highlighted by the solution.
-
Your physician may perform a biopsy to remove tissue for testing if your Colposcopy reveals one or more regions of suspicious tissue.
A Colposcopy does not hurt too much. A small amount of pressure could be felt as the speculum penetrates your vagina. When the solution comes into contact with your cervix, you could experience a little burning or stinging sensation. When the tissue sample is removed during a biopsy, you can experience a strong squeeze or anything similar to a menstrual cramp. Before the exam, taking over-the-counter pain medicines can help with the pain.
Following a Colposcopy: If a biopsy is not performed, you may experience some spotting for the following two days.
Following a biopsy, you can encounter:
-
A few days of minor vaginal bleeding
-
A brief but persistent ache in your vagina
-
Black or brown vaginal discharge (caused by the acetic solution)
-
A one- to two-hour stay following the surgery in the hospital or outpatient facility
-
Bloating or abdominal pains could happen in the first hour following the surgery
Home Broadway Specialities Cancer-care Colposcopy-clinic-2

You’re on Our Indian Website
Visit the Global site for International patient services











