-
Centre of
Excellence
Centre of Excellence
Other Specialities
- Allergy and Immunology
- Andrology
- Anesthesiology
- Clinical Psychology
- Dental Medicine
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- Ear Nose Throat
- Epilepsy Clinic
- General Medicine
- General Surgery
- Geriatric Medicine
- GI Surgery
- Gynaec Oncology
- Heart Care Clinic
- Hemato Oncology
- Hematology
- Hepatobiliary Surgery
- ICU and Critical Care
- Infectious Disease
- Internal Medicine
- Interventional Radiology
- Medical Gastro
- Medical Oncology
- Microbiology
- Minimal Access Surgery
- Nutrition And Dietetics
- Ophthalmology
- Oral Maxillo Facial Surgery
- Pain Medicine
- Parkinson Disease and Movement Disorder
- Pathology
- Pharmacy
- Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation
- Physiotherapy
- Plastic And Cosmetic Surgery
- Podiatric Surgery
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology (Respiratory and Sleep Medicine)
- Radiology
- Renal Sciences
- Rheumatology
- Surgical Gastro
- Surgical Oncology
- Vascular and Endovascular Surgery
Speciality Clinics
- Doctors
- Broadway
- International Patients



Clinics








- Self Registration
- In-Patient Deposit
- Mars - Ambulance
- Corporate & PSU
- Insurance Helpdesk
- Awards And Achievements
- Careers
- Contact Us
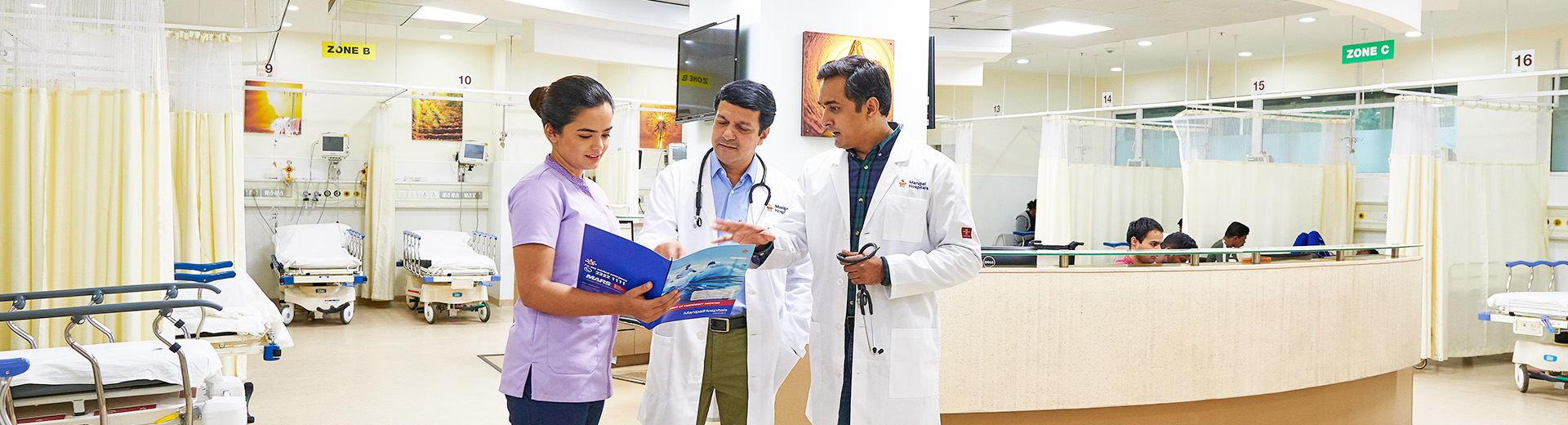

Cardiac Device Implantation
Cardiac Device Implantation in Broadway
Cardiac Device Implantations involve devices such as Pacemakers, Implantable Cardioverter Defibrillators (ICD), Cardiac Loop Recorders, Biventricular Pacemakers, and Cardiac Resynchronisation Therapy (CRT), which help maintain the cardiac rhythm through electric stimulation or defibrillation. They are designed and implanted to consistently gather data about heart rhythm, enabling specialists to assess a patient's cardiac health and electric activity and eliminating the need for frequent in-person appointments.
Cardiac Device Implantations help in addressing several heart-related conditions, including arrhythmias, heart failure, ventricular fibrillation, myocardial infarction, long QT syndrome, and certain variations of congenital heart diseases. At Manipal Hospitals, Broadway, Kolkata, our cardiologists hold immense expertise and proficiency in implantation procedures, ensuring patients receive comprehensive care that is specific to their needs and medical history.
Consult our cardiologists if you need Cardiac Device Implantation in Kolkata.
FAQ's
The procedure for implanting a cardiac device, such as Pacemakers or Implantable Cardioverter Defibrillators (ICD), usually involves making a small incision under the collarbone. A sheath is inserted into the blood vessel to create access, and then a pace lead wire is inserted into the blood vessel and passed through the heart. The location is verified through imaging scans, like fluoroscopy. The device is then placed under the skin near the collarbone, and the incision is closed with stitches or adhesive strips. An electrocardiogram (ECG) is used to ensure that the devices connected are working properly.
Just like any other risks that can manifest in any procedure, complications may occur with Cardiac Device Implantation, some of which include:
-
Excessive bleeding or bruising
-
Collapsed lung or pneumothorax
-
Blood vessel damage
-
Malfunctioning devices
-
Mispositioning of devices, particularly due to internal tissue
-
Generator-lead interface problems
-
Infection at the site
-
Cardiac perforation
-
Haematoma
-
Minor conditions, such as deep vein thrombosis (DVT), stroke, or myocardial infection
-
In severe and rare cases, prolonged hospital stays, readmissions, and additional outpatient visits due to complications
The recovery period is based on factors like age, overall health, and the individual pace of recovery. Most patients can typically resume their normal daily routines within 6 to 4 weeks post-implantation of cardiac devices, although this can vary. You may have to restrict yourself from performing strenuous physical work or exercise for a certain period until your specialist gives you the green light. Moreover, your specialist will schedule follow-up appointments to monitor your pacemaker's functionality and ensure continued well-being
You should seek immediate medical attention if you exhibit any symptoms after your implantation procedure, which include:
-
Inconsistent or troubled breathing
-
High-temperature fever or chills
-
Unexplained weight gain or swelling in the ankles or lower legs
-
Mild to moderate chest pain
-
Severe nausea and vomiting
-
Discolouration or redness
-
Fainting or dizziness
-
Bleeding or drainage from the insertion site
-
Pulse is too fast or too slow
Cardiac implantable devices, such as Pacemakers and Implantable Cardioverter Defibrillators (ICDs), generally have a lifespan of 10 years or more, depending on the usage and type of device. Specialists may perform Cardiac Implantable Electronic Device (CIED) Replacement procedures when the battery of the existing implantable device is reaching the end of its lifespan, experiencing low charge, or experiencing an inability to retain its charge. Other reasons could be due to malfunctioning or when your specialist recommends a newer model with advanced capabilities.
Wearing a cardiac device requires certain precautions, and specialists will provide general instructions on what and where individuals need to be alert and practice caution. General precautions include the following:
-
Let your airport security know that you are wearing an implantable device. Although security systems are generally safe for patients with implantable devices, there are chances that the devices may set off alarms. Staying away from radar machines or high-voltage machines, such as TV or radio
-
Keeping a safe distance when using mobile phones or MP3 players
-
Informing your surgeons that you have implantable devices in case you are undergoing interventions for other diseases or illnesses
-
Carrying an ID card or an alert bracelet in case of emergencies
-
Being alert when using car battery charges or jumper cables
-
Make sure that your implantable devices are safe when undergoing medical imaging scans, like magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scans
You may need to make certain lifestyle changes after getting a cardiac device implanted, which may include:
-
Abstaining from rigorous sporting activities which may cause injuries or blows, especially in the areas where the device is placed
-
Refrain from lifting heavy objects, particularly where the device is implanted. However, you can perform moderate physical exercise
-
Avoid driving or operating heavy vehicles
-
Maintaining a healthy weight and diet, such as consuming foods that increase good high-density lipoprotein (HDL) fats
-
Staying away from smoking, alcohol, and chewing tobacco
Home Broadway Specialities Cardiology Cardiac-device-implantation

You’re on Our Indian Website
Visit the Global site for International patient services











