-
Centre of
Excellence
Centre of Excellence
Other Specialities
- Allergy and Immunology
- Andrology
- Anesthesiology
- Clinical Psychology
- Dental Medicine
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- Ear Nose Throat
- Epilepsy Clinic
- General Medicine
- General Surgery
- Geriatric Medicine
- GI Surgery
- Gynaec Oncology
- Heart Care Clinic
- Hemato Oncology
- Hematology
- Hepatobiliary Surgery
- ICU and Critical Care
- Infectious Disease
- Internal Medicine
- Interventional Radiology
- Medical Gastro
- Medical Oncology
- Microbiology
- Minimal Access Surgery
- Nutrition And Dietetics
- Ophthalmology
- Oral Maxillo Facial Surgery
- Pain Medicine
- Parkinson Disease and Movement Disorder
- Pathology
- Pharmacy
- Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation
- Physiotherapy
- Plastic And Cosmetic Surgery
- Podiatric Surgery
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology (Respiratory and Sleep Medicine)
- Radiology
- Renal Sciences
- Rheumatology
- Surgical Gastro
- Surgical Oncology
- Vascular and Endovascular Surgery
Speciality Clinics
- Doctors
- Broadway
- International Patients



Clinics








- Self Registration
- In-Patient Deposit
- Mars - Ambulance
- Corporate & PSU
- Insurance Helpdesk
- Awards And Achievements
- Careers
- Contact Us
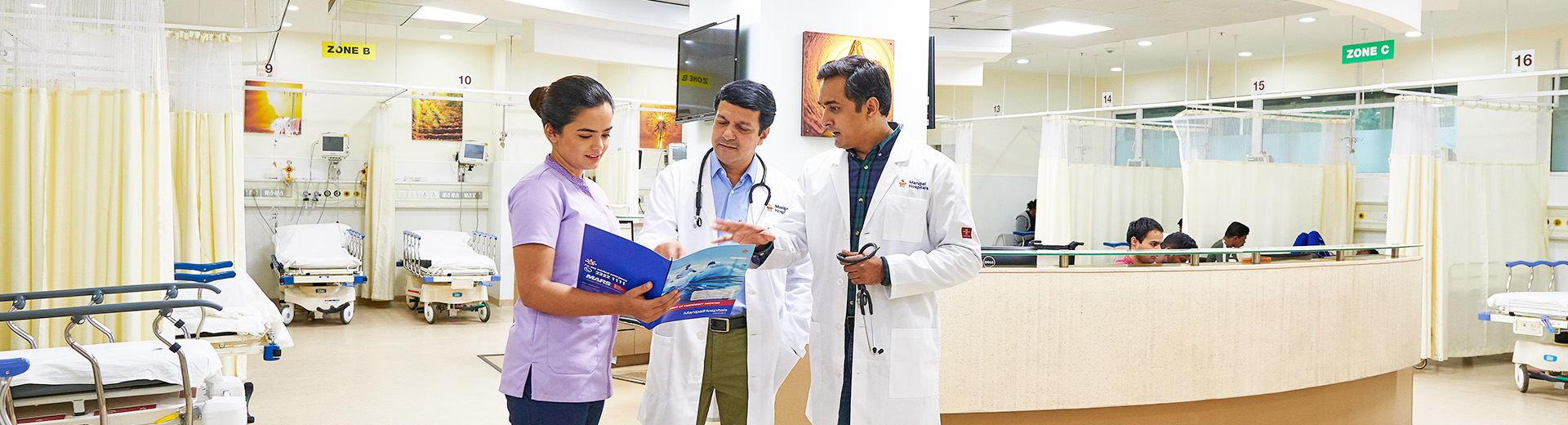

Chronic Diseases
Chronic Disease Treatment In Broadway
The gastrointestinal tract (GI) comprises the mouth, throat, oesophagus, stomach, intestines, rectum, anus, liver, gallbladder, and pancreas, which combine to digest food, absorb nutrients, and expel waste. Any disruption in their structure or functioning can give way to a range of symptoms, from cramps and vomiting to changes in stool.
GI disorders can significantly impact a patient’s quality of life. Some of the common GI disorders include inflammatory bowel disease, diverticulitis, colorectal cancer, gastroparesis, gastric cancer, hernia, chronic pancreatitis, and more. Since there are many GI disorders, ranging from common to rare, they may exhibit similar symptoms, making the diagnosis difficult.
If you experience any abnormal GI symptoms, seek expert gastroenterologist care for chronic illness treatment in Kolkata at Manipal Hospitals, to rule out serious conditions, receive a diagnosis, and begin treatment.
FAQ's
Chronic gastrointestinal diseases are long-term conditions affecting the digestive system that cause persisting symptoms and require ongoing treatment. GI diseases encompass a wide range of conditions, each with its own set of symptoms, causes, and treatment approaches. Since chronic GI diseases are complex, they require a comprehensive approach to diagnosis and management.
Functional GI disorders
Functional GI disorders are when the organs appear normal but do not move properly. The common conditions affecting GI disorders are constipation, irritable bowel syndrome, and bloating.
Structural GI disorders
Abnormalities in appearance and impaired functioning of the GI tract are called structural GI diseases. They may have to be surgically removed. For example, strictures, stenosis, colon cancer, haemorrhoids, etc.
Common symptoms of gastrointestinal diseases are:
- Abdominal pain
- Bloating
- Diarrhoea
- Constipation
- Nausea
- Vomiting
- Changes in bowel movements
- Rectal bleeding
- Unexplained weight loss
The prevalence of GERD in India ranges from 7.6 to 30%, which is attributed to the increased use of spices and consumption of non-vegetarian food. Lifestyle modifications and dietary changes can help with managing GERD symptoms.
Individuals at risk for developing haemorrhoids are:
- Individuals who strain during bowel movements
- Individuals who sit on the toilet for a long time
- Individuals suffering from chronic constipation or diarrhoea
- Individuals who consume a low-fiber diet
- Pregnant women
- Individuals over the age of 50 years
Common GI conditions like constipation, diarrhoea, and bloating are common and develop in several patients. These conditions do not pose major health issues and resolve on their own or with over-the-counter (OTC) treatment. However, if you notice your GI symptoms worsening, you will have to seek medical attention.
Diagnostic testing for GI diseases typically involves a combination of taking a medical history and a physical examination. Other recommended tests are:
- Laboratory tests: They are crucial for diagnosing GI disorders. Blood tests such as complete blood count (CBC), liver function tests, inflammatory markers, pancreatic enzyme tests, or nutritional deficiency tests are commonly ordered. In some patients, their stool samples may also be analysed to look for infections or occult blood.
- Imaging tests: Abdominal X-ray, ultrasound imaging, computed tomography (CT), and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) can visualise the structures of the digestive system and identify abnormalities.
- Endoscopic procedures: Upper endoscopy, colonoscopy, and flexible sigmoidoscopy are employed to directly visualise the gastrointestinal tract. They help detect inflammatory bowel disease and colorectal cancer.
- Specialised tests: Capsule endoscopy, small intestinal bacterial overgrowth (SIBO), or manometry may be recommended based on the clinical suspicion.
The tests prescribed depend on the individual's condition and presenting symptoms.
Dietary changes are a part of treatment for individuals suffering from GI diseases. Depending on the condition you have, your healthcare provider may recommend the necessary dietary modifications.
For example, patients with celiac disease may need to avoid foods, drinks, or products containing gluten. Individuals diagnosed with diverticulitis may have to restrict their intake to clear fluids, then advance to full liquids and transition to regular foods once symptoms resolve.
The main goal of treating gastrointestinal disease is to control symptoms, reduce inflammation, prevent complications, and improve quality of life. Depending on the gastrointestinal disease, treatment involves medication, dietary modifications, lifestyle changes, and surgical interventions.
The prognosis of GI disease can vary depending on the condition, its severity, and the patient’s health status. While some GI diseases can effectively be treated, achieving a complete cure is not always possible for all chronic GI conditions. However, early diagnosis and appropriate treatment can improve the patient’s quality of life.
According to research, GI disorders can be prevented by avoiding alcohol, tobacco, or non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs). Additionally, maintaining a healthy lifestyle, practising good bowel habits, and undergoing cancer screening are crucial for optimal GI health.
Home Broadway Specialities Gi-surgery Chronic-diseases

You’re on Our Indian Website
Visit the Global site for International patient services











