-
Centre of
Excellence
Centre of Excellence
Other Specialities
- Allergy and Immunology
- Andrology
- Anesthesiology
- Clinical Psychology
- Dental Medicine
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- Ear Nose Throat
- Epilepsy Clinic
- General Medicine
- General Surgery
- Geriatric Medicine
- GI Surgery
- Gynaec Oncology
- Heart Care Clinic
- Hemato Oncology
- Hematology
- Hepatobiliary Surgery
- ICU and Critical Care
- Infectious Disease
- Internal Medicine
- Interventional Radiology
- Medical Gastro
- Medical Oncology
- Microbiology
- Minimal Access Surgery
- Nutrition And Dietetics
- Ophthalmology
- Oral Maxillo Facial Surgery
- Pain Medicine
- Parkinson Disease and Movement Disorder
- Pathology
- Pharmacy
- Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation
- Physiotherapy
- Plastic And Cosmetic Surgery
- Podiatric Surgery
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology (Respiratory and Sleep Medicine)
- Radiology
- Renal Sciences
- Rheumatology
- Surgical Gastro
- Surgical Oncology
- Vascular and Endovascular Surgery
Speciality Clinics
- Doctors
- Broadway
- International Patients



Clinics








- Self Registration
- In-Patient Deposit
- Mars - Ambulance
- Corporate & PSU
- Insurance Helpdesk
- Awards And Achievements
- Careers
- Contact Us
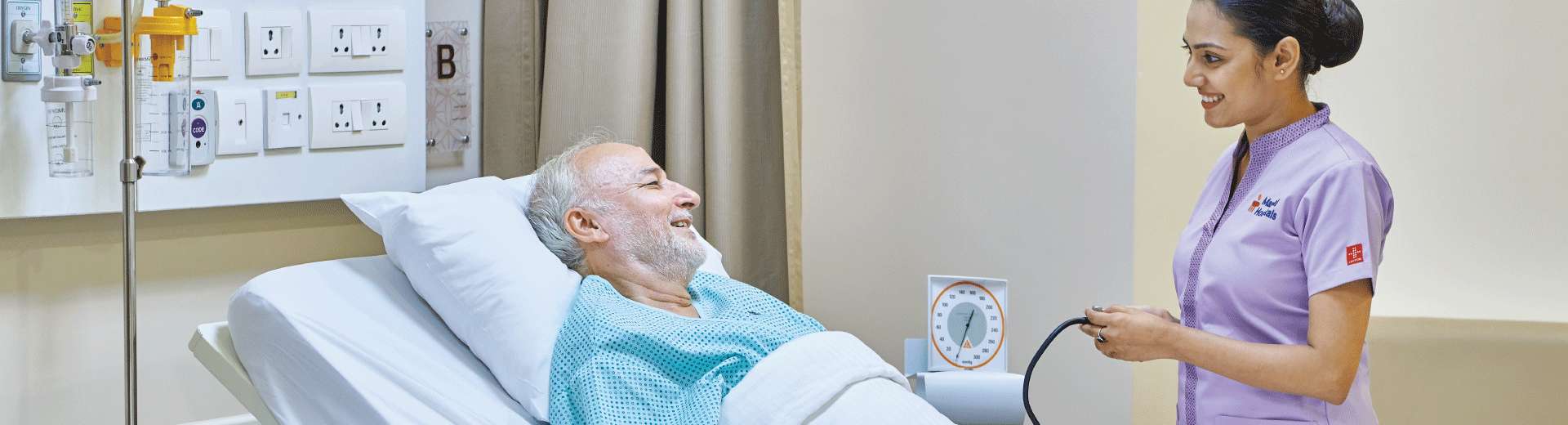

Hemodialysis
Hemodialysis Centre in Kolkata
Hemodialysis is a medical procedure to eliminate toxic substances, poisons, and extra fluid from the blood. This procedure is preferred when the kidneys cannot filter the blood efficiently. It involves pumping the patient's blood into a dialyzer, which filters the blood using a specific filter. Within the dialyzer, a semipermeable membrane has blood flowing on one side and dialysate solution on the other. The dialysate is disposed of after waste materials and extra fluid pass through the membrane. The filtered blood is pumped back into the patient’s circulatory system. Depending on the patient's health, this procedure can take several hours and must be performed several times a week. Hemodialysis improves patients' general health and quality of life by helping to control kidney failure consequences such as fluid excess and electrolyte abnormalities. Consult our nephrologists at our Hemodialysis Centre in Kolkata if need this treatment.
FAQ's
Kidney failure often results from the following:
-
Diabetes
-
Hypertension, or elevated blood pressure
-
Inflammation of the kidney (glomerulonephritis)
-
Polycystic kidney disease or kidney cysts
-
Renal disorders inherited from birth
-
Long-term use of pharmaceuticals that could damage the kidneys, such as nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs
Dialysis is required if your kidneys cannot filter out enough waste and water from your blood. This often occurs when your kidney function declines to 10 and 15 percent. You could experience symptoms like exhaustion, oedema, nausea, and vomiting. Even if you don't currently have any of these symptoms, you can still have a high blood waste level that could be dangerous to your health. The best person to advise you on when to begin Dialysis is your doctor.
The dialyzer, or a filter, has two sections: one stores your blood, and the other contains dialysate, a cleaning agent. A thin membrane divides these two portions. Because blood cells and other essential components are too large to travel through the membrane, they stay in your blood. Smaller waste materials in the blood are washed away by passing through the membrane, including potassium, creatinine, urea, and excess fluid.
There are two ways to get dialysis:
-
Hemodialysis: When kidney function is compromised, Hemodialysis is a life-saving medical technique that removes waste materials and extra fluid from the blood. It is essential for treating renal failure and preserving patients' health because it includes pumping blood through a device that filters out impurities and replenishes the body with clean blood.
-
Peritoneal Dialysis: In Peritoneal Dialysis, waste materials and extra fluid are filtered out of the blood by infusing a dialysis solution into the belly. This kidney replacement therapy is known as Peritoneal Dialysis. It's flexible and can be done at home, but there's a chance of peritonitis, and frequent swaps are needed.
You will have a little surgical procedure to facilitate bloodstream access before beginning Hemodialysis. You might have:
-
Arteriovenous fistula (AV fistula): A surgeon will join an artery and vein in your arm to create an arteriovenous fistula.
-
Arteriovenous graft (AV graft): Your surgeon will use a graft, which is a soft, hollow tube, to connect the artery and vein, if the blood vessels are too short to do so.
Dialysis access is made easier by AV fistulas and grafts, which expand the linked vein and artery. They also facilitate quicker blood flow into and out of your body. Your doctor may insert a catheter, or tiny tube, temporarily into a vein in your leg, chest, or neck if dialysis is required right away. You will learn from your provider how to keep the graft or fistula clean. If you decide to continue Hemodialysis at home, the provider will also teach you how to do it.
In the course of Hemodialysis, the Dialysis machine will:
-
Extracts blood from your arm's needle.
-
The blood is circulated through a dialyzer filter, to extract waste into a dialysis solution.
-
In addition to salt and water, this cleaning solution contains other ingredients.
-
Returns filtered blood to your body via another needle inserted into your arm.
-
Regulates the rate at which blood enters and leaves your body by monitoring your blood pressure.
Hemodialysis may result in the following complications:
-
Hypotension is brought on by the fast loss of fluid during or after therapy.
-
Fluid and electrolyte imbalances that result in cramping in the muscles.
-
Infection at the site of vascular access can lead to infections in the bloodstream.
-
Blood clotting needs to be addressed inside the access site or dialysis machine.
-
Anaemia is brought on by the kidneys' reduced ability to produce erythropoietin.
-
Dialysis disequilibrium syndrome manifests as headaches, nausea, and convulsions, among other neurological symptoms.
-
Electrolyte abnormalities that impact muscle and cardiac rhythm, such as Hypocalcemia or Hyperkalemia.
-
Amyloidosis is a disorder brought on by extended dialysis where proteins accumulate in tissues and joints.
-
Chronic problems with vascular access, such as thrombosis or stenosis.
If you are unable to get a Kidney Transplant, you may undergo dialysis for the rest of your life. Most patients lead a good quality of life while undergoing Dialysis treatment. How long you can live on Dialysis, depends on several factors, which include your health, attitude, and the quality of healthcare you receive.
Home Broadway Specialities Nephrology Hemodialysis

You’re on Our Indian Website
Visit the Global site for International patient services











