-
Centre of
Excellence
Centre of Excellence
Other Specialities
- Allergy and Immunology
- Andrology
- Anesthesiology
- Clinical Psychology
- Dental Medicine
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- Ear Nose Throat
- Epilepsy Clinic
- General Medicine
- General Surgery
- Geriatric Medicine
- GI Surgery
- Gynaec Oncology
- Heart Care Clinic
- Hemato Oncology
- Hematology
- Hepatobiliary Surgery
- ICU and Critical Care
- Infectious Disease
- Internal Medicine
- Interventional Radiology
- Medical Gastro
- Medical Oncology
- Microbiology
- Minimal Access Surgery
- Nutrition And Dietetics
- Ophthalmology
- Oral Maxillo Facial Surgery
- Pain Medicine
- Parkinson Disease and Movement Disorder
- Pathology
- Pharmacy
- Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation
- Physiotherapy
- Plastic And Cosmetic Surgery
- Podiatric Surgery
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology (Respiratory and Sleep Medicine)
- Radiology
- Renal Sciences
- Rheumatology
- Surgical Gastro
- Surgical Oncology
- Vascular and Endovascular Surgery
Speciality Clinics
- Doctors
- Broadway
- International Patients



Clinics








- Self Registration
- In-Patient Deposit
- Mars - Ambulance
- Corporate & PSU
- Insurance Helpdesk
- Awards And Achievements
- Careers
- Contact Us
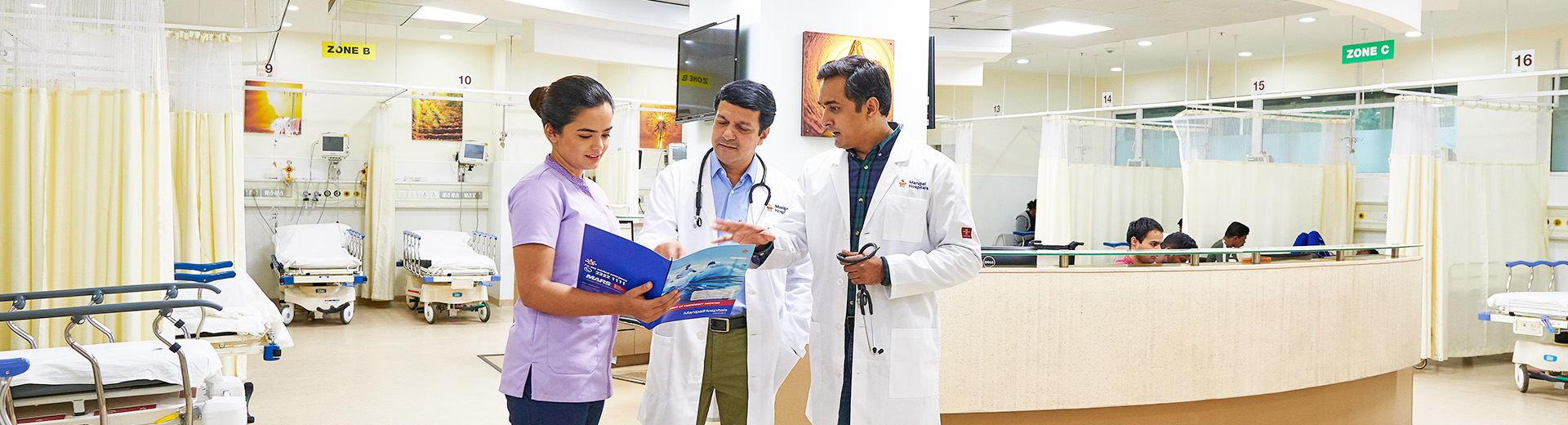

Bladder Cancer
Bladder Cancer Treatment in Broadway, Kolkata
Bladder cancer is the abnormal growth of cells lining the bladder, the hollow organ in the lower abdomen that stores urine. Treatment can cure bladder cancer, but the rate of recurrence is high.
Types
-
Urothelial carcinoma
-
Squamous cell carcinoma
-
Adenocarcinoma
There are other less common types of bladder cancer, including sarcoma and small-cell carcinoma of the bladder.
Treatment
Bladder cancer is treated with Surgery, Chemotherapy, Radiotherapy, or a combination of the three. Surgical procedures include Transurethral Resection of Bladder Cancer (TURBT) and Cystectomy. After the surgical removal of the bladder, reconstruction procedures are necessary for urinary diversion. Some patients may also have to undergo Immunotherapy or Targeted Therapy to treat bladder cancer.
Consult our urologists if you need Bladder Cancer Treatment in Broadway, Kolkata.
FAQ's
Bladder cancer is one of the common types of cancer. It begins when the cells lining the bladder begin to grow out of control. Cancer can also develop anywhere in the urethra, renal pelvis, and ureters.
The primary symptom of bladder cancer is blood in the urine. Other symptoms experienced by patients with bladder cancer are frequent urination, urinary urgency, or irritation while urinating. Some patients also develop urinary tract infections. Visit Manipal Hospitals, Broadway, Kolkata, if you experience any of the above symptoms.
Bladder cancer typically presents with symptoms at early stages before it spreads, increasing the probability of diagnosing the cancer early. In advanced stages, symptoms of bladder cancer include the inability to urinate, lower back pain on one side, abdominal pain, and feeling the need to urinate but being unable to do so.
If you or your loved ones experience any of the above symptoms, visit our expert oncologists at Manipal Hospitals, Broadway, Kolkata.
The risk factors for developing bladder cancer are:
-
Smoking: Individuals who smoke or use tobacco have a higher risk of developing bladder cancer
-
Occupational chemical carcinogens: Exposure to cancer-causing chemicals in the workplace and the environment increases the risk of bladder cancer. Workers in the dye, rubber, chemical, metal, textile, and leather industries have a higher risk of developing bladder cancer
-
History of bladder cancer: Individuals with a history of bladder cancer have a higher risk
-
Cancer treatment: People with cancer who have been treated with cyclophosphamide may be at an increased risk of bladder cancer. Patients receiving radiation to the abdomen and pelvis have a higher risk
-
Arsenic: It increases the risk of bladder cancer
-
Family history: Individuals with a family history have a higher risk of bladder cancer
Bladder cancer can be diagnosed with ultrasound, CT scans, and MRI scans to detect irregularities in the bladder wall. A Cystoscope may also be used to visualise the structures within the bladder and take samples for tissue biopsy. Urine Cytology can be performed to identify cancer cells in urine.
Depending on the type, grade, and stage of bladder cancer the following treatment options can be considered:
-
Surgery: If the tumour has the potential to invade the muscle wall, the surgical removal of the tumour is suggested
-
Transurethral Resection of Bladder Tumour: The patients are administered anaesthesia, which helps examine the bladder and remove tumours.
-
Radical Cystectomy: The procedure involves the removal of the whole bladder and possibly nearby tissues and organs
-
Urinary diversion: After the Radical Cystectomy procedure, a part of the intestine is used to create a urinary diversion that facilitates urine to flow out from the kidneys to outside the body. The common procedures for urinary diversions are an ileal conduit, continent cutaneous pouch, and neobladder
-
-
Chemotherapy: This treatment method is preferred for treating bladder cancer that has metastasised beyond the bladder to other organs.
-
Radiation Therapy: A high-energy X-ray or other particles are used to destroy cancer cells
-
Immunotherapy: Local and systemic Immunotherapy is used to enhance the body’s natural defences to fight against cancer
Local Immunotherapy
Bacille Calmette-Guerin: (BCG): A weakened form of tuberculosis bacteria causes an immune or allergic reaction which is known to kill cancer cells, that causes bladder cancer.
Systemic Immunotherapy
-
Immune checkpoint inhibitors are prescribed to treat advanced bladder cancer.
-
Targeted therapy: The treatment involves targeting specific genes, proteins, or tissue environments that contribute to cancer growth and survival.
A neobladder is a type of urinary diversion performed during surgery to remove the bladder. A part of the intestine creates a sphere connecting the kidneys and urethra to facilitate the emptying of the urine. Although there is no external pouch required, some patients may need a catheter for complete emptying of the urine.
An ileal conduit is a form of urinary diversion that uses an external bag for urinary drainage. A stoma is created to the right of the belly button, which drains into a bag.
Home Broadway Specialities Urology Bladder-cancer

You’re on Our Indian Website
Visit the Global site for International patient services











