
Gangrene is a serious condition that occurs when a significant mass of body tissue dies. This can happen due to a lack of blood flow, a bacterial infection, or a combination of both. Recognizing the early signs of gangrene is crucial for timely medical intervention and preventing severe complications. In this guide, we will explore the early signs of gangrene, the different types, and the risk factors associated with this condition.
Synopsis
Early Signs of Gangrene
One of the most noticeable early signs of gangrene is the discolouration of the affected tissue. The tissue may turn black, blue, or green due to the lack of oxygen and blood supply. This discolouration is often accompanied by a foul-smelling discharge, which results from the tissue breaking down and becoming infected.
Other early signs and symptoms of gangrene include:
-
Swelling and pain: The affected area may become swollen and extremely painful.
-
Blisters or sores: These can develop on the skin and may ooze pus or other fluids.
-
Numbness: As the tissue dies, you may lose sensation in the affected area.
-
Fever and malaise: If an infection is present, you might experience fever, chills, and a general feeling of being unwell.
Types of Gangrene
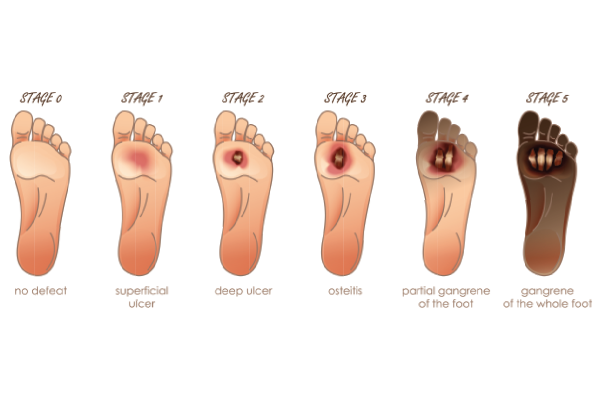
Gangrene can be classified into several types, each with distinct characteristics and causes.
-
Dry Gangrene: This type occurs when there is a lack of blood flow to the affected area, often due to conditions like atherosclerosis or diabetes. The tissue dries up, shrinks, and turns black. Dry gangrene typically develops slowly and is less likely to be infected than wet gangrene.
-
Wet Gangrene: This type is caused by a bacterial infection in the affected tissue. It can develop rapidly and is characterized by swelling, blistering, and a wet appearance due to pus. Wet gangrene is a medical emergency and requires immediate treatment to prevent the spread of infection.
-
Gas Gangrene: This rare but severe form of gangrene is caused by Clostridium bacteria, which produce gas within the tissue. It spreads quickly and can be life-threatening. Symptoms include severe pain, swelling, and the presence of gas bubbles under the skin.
-
Internal Gangrene: This type affects internal organs such as the intestines, gallbladder, or appendix. It is often caused by a blockage of blood flow to the organ and can lead to severe complications if not treated promptly.
Also Read: Varicose Veins: Causes, Symptoms, Types, & Treatment
Timeline of untreated gangrene progression
|
Type of Gangrene |
Cause |
Symptoms |
Affected Areas |
|
Dry Gangrene |
|
|
|
|
Wet Gangrene |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Risk Factors
Several factors can increase the risk of developing gangrene, including:
-
Diabetes: High blood sugar levels can damage blood vessels, reducing blood flow to certain areas of the body and increasing the risk of infection.
-
Smoking: Smoking damages blood vessels and impairs circulation, making it harder for wounds to heal and increasing the risk of gangrene.
-
High Cholesterol: Elevated cholesterol levels can lead to atherosclerosis, a condition where arteries become narrowed and hardened, reducing blood flow.
-
High Blood Pressure: Hypertension can damage blood vessels and reduce blood flow, contributing to the development of gangrene.
Complications of Gangrene
Gangrene is a serious condition that requires prompt medical attention. If left untreated, it can lead to severe complications, including:
-
Sepsis: This is a life-threatening response to infection that can lead to tissue damage, organ failure, and death. Gangrene can cause bacteria to enter the bloodstream, leading to sepsis.
-
Amputation: In severe cases, the affected limb or tissue may need to be amputated to prevent the spread of gangrene and save the patient's life.
-
Organ Failure: If gangrene spreads to internal organs, it can cause them to fail. This is particularly dangerous and often requires intensive medical intervention.
-
Shock: The body can go into shock due to severe infection and blood loss, which can be fatal if not treated immediately.
-
Death: Without timely treatment, gangrene can lead to death due to the spread of infection and the body's inability to cope with the damage.
Statistics and Case Studies
-
Sepsis: According to the World Health Organization (WHO), sepsis affects millions of people worldwide each year, with a significant number of cases resulting from untreated infections like gangrene.
-
Amputation: Studies show that diabetic patients with gangrene have a high risk of amputation. For instance, a study published in the Journal of Vascular Surgery found that about 50% of patients with diabetic foot gangrene required amputation.
-
Mortality Rates: Research indicates that the mortality rate for patients with gangrene can be as high as 20-30%, especially if treatment is delayed.
These statistics highlight the critical importance of early detection and treatment of gangrene to prevent these severe complications. If you suspect gangrene, seek medical attention immediately to improve outcomes and reduce the risk of serious health issues.
Gangrene Treatment
Gangrene prevention involves managing underlying health conditions and maintaining good hygiene. Here are some tips to reduce your risk:
-
Control diabetes: Keep blood sugar levels within the target range through diet, exercise, and medication.
-
Quit smoking: Seek support to stop smoking and improve your overall vascular health.
-
Manage cholesterol and blood pressure: Follow a healthy diet, exercise regularly, and take prescribed medications to keep cholesterol and blood pressure levels in check.
-
Practice good wound care: Clean and dress wounds promptly, and seek medical attention for any signs of infection.
-
Don't wait until it's too late. Schedule your consultation with our expert Vascular surgeons at Manipal Hospitals Dwarka. Explore the wide range of medical services we offer to ensure your health and well-being.
If gangrene is suspected, immediate medical treatment is essential. Treatment options may include:
-
Antibiotics: To treat any underlying infection.
-
Surgery: To remove dead tissue and prevent the spread of gangrene.
-
Amputation: In severe cases, removing the affected limb may be necessary to save the patient's life.
-
Revascularization: Procedures such as angioplasty, stenting, and bypass to restore blood flow to the affected area.
Here are some lifestyle changes to prevent gangrene:
-
Exercise Regularly: Aim for 30 minutes of moderate exercise most days to improve circulation.
-
Healthy Diet:
-
Manage Diabetes: Eat whole grains, lean proteins, and vegetables; avoid sugary foods.
-
Lower Cholesterol: Use heart-healthy fats; reduce saturated and trans fats.
-
Control Blood Pressure: Reduce sodium; eat potassium-rich foods like bananas.
-
-
Quit Smoking: Improves blood flow and overall health.
-
Foot Care: Inspect feet regularly, keep them clean, and wear comfortable shoes.
-
Maintain Healthy Weight: Balanced diet and regular exercise.
-
Stay Hydrated: Drink at least 8 glasses of water daily.
These changes can help reduce the risk of gangrene and improve overall health.
Conclusion
Gangrene is a serious condition that requires prompt medical attention. By understanding the early signs and risk factors, you can take steps to prevent its development and seek timely treatment if necessary. Managing underlying health conditions, maintaining good hygiene, and being vigilant about changes in your body is key to preventing gangrene and ensuring overall health.
If you suspect you or someone you know may have gangrene, do not hesitate to seek medical help immediately. Early intervention can make a significant difference in outcomes and help preserve health and quality of life.
Experience world-class healthcare at Manipal Hospitals Dwarka. Book your appointment now!
FAQ's
Early signs include discolouration of the skin (black, blue, or green), swelling, pain, blisters or sores, numbness, and a foul-smelling discharge.
People with chronic conditions like diabetes, peripheral artery disease, or those who smoke are at higher risk. Severe injuries and weakened immune systems also increase the risk.
Seek immediate medical attention. Early treatment is crucial to prevent the spread of gangrene and serious complications.
Quitting smoking, eating a healthy diet, exercising regularly, and keeping wounds clean
Untreated gangrene can lead to severe infections, and loss of limbs, and can be life-threatening.



















 6 Min Read
6 Min Read












