Parkinson's disease is a progressive neurodegenerative disorder that affects movement and can significantly impact one's quality of life if left untreated. Early detection and intervention are crucial for managing symptoms and improving long-term outcomes.
Synopsis
Early Signs of Parkinson's Disease
Here are some early signs of Parkinson's disease that you shouldn't ignore:
1. Tremors
One of the most recognizable early symptoms of Parkinson's disease is tremors. This often begins as a slight shaking of the hands, fingers, or chin. It's important to distinguish between tremors associated with Parkinson's and those caused by other conditions, such as anxiety or essential tremor. Parkinson's tremors typically start on one side of the body and progress as the disease advances.
2. Loss of Smell
A lesser-known early sign of Parkinson's is the loss of the ability to smell foods or scents. This symptom can appear years before movement-related symptoms become noticeable. While it might seem minor, it can be an early indicator of Parkinson's disease.
3. Stiffness or Rigidity
Muscle stiffness or rigidity can make it difficult to move or stretch. This symptom might be mistaken for normal ageing or arthritis, but if it doesn't go away, it could signify an underlying problem. Stiffness can also lead to painful muscle cramps, known as dystonia.
4. Slowness of Movement (Bradykinesia)
Bradykinesia refers to the slowness of movement, making everyday tasks like buttoning a shirt or walking labour-intensive. This isn't due to weakness but rather a decrease in motor coordination, which is an early sign of Parkinson's disease.
5. Trouble Sleeping
Sleep problems, such as restlessness or difficulty staying asleep, can also be early signs of Parkinson's disease. These issues can disrupt daily life and may be an early indicator of the condition.
What is Parkinson's Disease?
Parkinson's disease is a chronic and progressive movement disorder that affects the nervous system. It primarily impacts the part of the brain responsible for controlling movement. The disease is characterized by the gradual loss of dopamine-producing neurons in the brain, leading to Parkinson's disease symptoms such as tremors, stiffness, slowness of movement, and balance problems.
Causes and Risk Factors of Parkinson's Disease
Parkinson's disease is a complex condition with no single known cause. Instead, it is believed to result from a combination of genetic and environmental factors. Understanding these causes and risk factors can help in early detection and management of the disease. Here are the major Parkinson's disease causes.
Genetic Factors
While most cases of Parkinson's disease are sporadic, meaning they occur without a clear family history, about 10-15% of cases are linked to genetic mutations. Specific genes, such as LRRK2, PARK7, PINK1, PRKN, and SNCA, have been associated with an increased risk of developing Parkinson's disease. Having a family member with Parkinson's can slightly increase your risk, but it does not guarantee that you will develop the disease.
Environmental Factors
Exposure to certain environmental factors may increase the risk of developing Parkinson's disease. These include:
-
Pesticides and Herbicides: Prolonged exposure to these chemicals, often used in farming, has been linked to a higher risk of Parkinson's.
-
Heavy Metals: Exposure to heavy metals like manganese and lead can contribute to the development of Parkinson's disease.
-
Industrial Chemicals: Certain industrial chemicals, such as trichloroethylene (TCE), have been associated with an increased risk of Parkinson's.
Age
Age is the most significant risk factor for Parkinson's disease. The likelihood of developing the condition increases with age, with most cases occurring in individuals over 60. However, early-onset Parkinson's can occur before the age of 50.
Gender
Men are more likely to develop Parkinson's disease than women. The reasons for this gender difference are not entirely understood but may involve genetic and hormonal factors.
Other Risk Factors
-
Head Trauma: A history of head injuries may increase the risk of developing Parkinson's disease.
-
Lifestyle Factors: Certain lifestyle factors, such as a sedentary lifestyle and poor diet, may contribute to the risk of Parkinson's disease.
Understanding these causes and risk factors can help in identifying early signs and seeking timely medical intervention. If you or a loved one are experiencing symptoms of Parkinson's disease, it's important to consult with a healthcare professional for a thorough evaluation and appropriate management.
Consult our neurology hospital in Delhi if you are experiencing signs and symptoms of Parkinson's disease.
Diagnosis of Parkinson’s Disease
Diagnosing Parkinson’s disease is a critical step in managing and treating this progressive neurological disorder. Understanding the diagnostic process can help patients and their families feel more informed and engaged in their healthcare journey. Here are
- Neurological Exams: The diagnosis of Parkinson’s disease typically begins with a comprehensive neurological exam. During this exam, a neurologist will evaluate motor skills, looking for key symptoms such as tremors, rigidity, bradykinesia (slowness of movement), and postural instability. These motor symptoms are essential indicators and help differentiate Parkinson’s from other neurological conditions.
-
Imaging Techniques: While there is no definitive test for Parkinson’s disease, imaging techniques can support the diagnosis. MRI and CT scans are often used to rule out other conditions that might cause similar symptoms, such as strokes or brain tumours. A specialized imaging test called DaTscan can be particularly useful. DaTscan helps visualize the dopamine system in the brain, providing valuable information that can distinguish Parkinson’s disease from other disorders with overlapping symptoms.
-
Medical History and Symptoms Checklist: A thorough medical history is crucial in diagnosing Parkinson’s disease. The neurologist will ask about the onset and progression of symptoms, family history of neurological disorders, and any other relevant medical conditions. A detailed symptoms checklist helps in identifying the core motor symptoms and any non-motor symptoms, such as cognitive changes, mood disorders, and sleep disturbances, which are also common in Parkinson’s disease.
-
Importance of Early Diagnosis: Early diagnosis of Parkinson’s disease is vital for effective treatment planning. Identifying the disease in its initial stages allows for timely intervention, which can help manage symptoms more effectively and improve the quality of life. Early diagnosis also opens up opportunities for patients to participate in clinical trials and access new treatments that may slow disease progression.
By understanding the diagnosis of Parkinson's disease process, patients and their families can better navigate the complexities of Parkinson’s disease. This knowledge fosters trust and engagement, empowering them to take an active role in their healthcare decisions.
Role of Physical Activity in Managing Parkinson’s Disease
Physical activity is a cornerstone in managing Parkinson’s disease, offering numerous benefits that can significantly improve the quality of life for those affected. Exercise not only helps in maintaining mobility but also plays a crucial role in reducing rigidity and other motor symptoms associated with the disease. Here are a Parkinson's disease diagnosis methods:
-
Exercises Tailored for Parkinson’s: Certain exercises are particularly beneficial for individuals with Parkinson’s disease. Activities such as tai chi and yoga are highly recommended due to their focus on balance, flexibility, and controlled movements. Tai chi, with its slow and deliberate movements, helps improve balance and prevent falls. Yoga enhances flexibility, strength, and relaxation, which can alleviate muscle stiffness and improve overall well-being.
-
Benefits of Maintaining Mobility and Reducing Rigidity: Regular physical activity helps maintain mobility and reduces the rigidity that often accompanies Parkinson’s disease. Engaging in exercises that promote cardiovascular health, such as walking, cycling, or swimming, can improve gait and posture. Strength training exercises help build muscle strength, which is essential for maintaining balance and performing daily activities. Additionally, exercises that focus on stretching can reduce muscle stiffness and improve range of motion.
-
Guidance for Safe Workouts and Physical Therapy: It is important for individuals with Parkinson’s disease to follow safe workout guidelines to avoid injury. Consulting with a physical therapist can provide personalized exercise plans tailored to individual needs and abilities. Physical therapists can teach proper techniques and recommend modifications to exercises to ensure safety. They can also introduce specialized exercises that target specific symptoms, such as tremors or balance issues.
Why Early Detection Matters
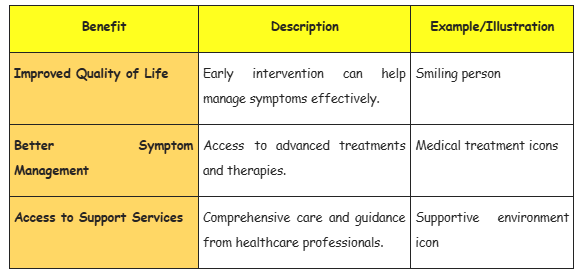
At Manipal Hospitals Dwarka, we are committed to providing the highest quality care for patients with Parkinson's disease. Our team of experienced neurologists and healthcare professionals uses state-of-the-art technology and personalized treatment plans to ensure the best possible outcomes. We offer a supportive environment where patients and their families can receive comprehensive care and guidance.
For more information and to book an appointment, visit our website or contact us directly.





















 6 Min Read
6 Min Read









_Early_Detection.png)