
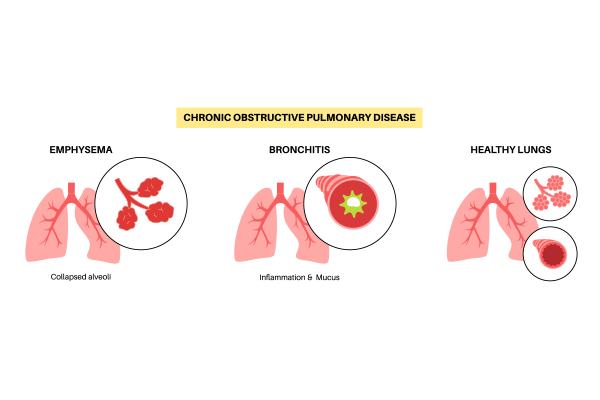
Emphysema is a chronic lung condition that falls under the umbrella of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD). It primarily affects the alveoli, the tiny air sacs in the lungs, leading to breathing difficulties and reduced oxygen intake. This blog will delve into the causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment options for emphysema, providing a comprehensive overview of this debilitating disease.
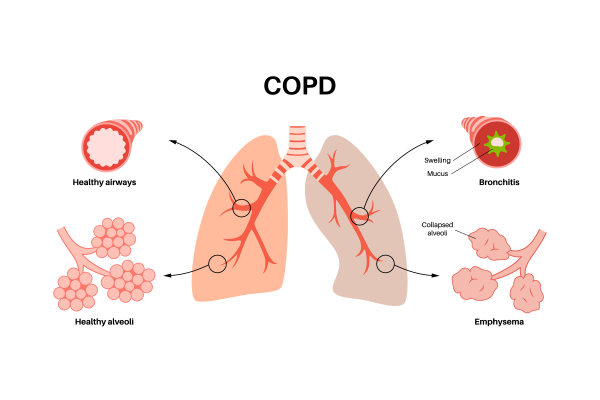
Synopsis
Causes of Emphysema
The primary cause of emphysema is long-term exposure to airborne irritants. The most significant risk factor is smoking, which accounts for the majority of emphysema cases. The harmful chemicals in tobacco smoke damage the alveoli and the small airways, leading to inflammation and destruction of lung tissue. Even secondhand smoke can contribute to the development of emphysema.
Other causes include:
-
Air Pollution: Prolonged exposure to air pollutants, such as industrial fumes, vehicle emissions, and dust, can damage the lungs.
-
Chemical Fumes: Occupational exposure to chemical fumes and dust can increase the risk of emphysema.
-
Genetic Factors: A rare genetic condition known as alpha-1 antitrypsin deficiency can lead to emphysema. Alpha-1 antitrypsin is a protein that protects the lungs from damage. A deficiency in this protein makes the lungs more susceptible to irritants.
-
Respiratory Infections: Frequent respiratory infections can contribute to lung damage and increase the risk of developing emphysema.
Symptoms of Emphysema
Emphysema symptoms typically develop gradually and worsen over time. Early symptoms may be mild and often go unnoticed. As the disease progresses, symptoms become more severe and can significantly impact daily life. Common symptoms include:
-
Shortness of Breath: Initially, shortness of breath may occur during physical activity. As the disease advances, it can happen even at rest.
-
Chronic Cough: A persistent cough, often accompanied by mucus production, is a common symptom.
-
Wheezing: A high-pitched whistling sound when breathing is another symptom of emphysema.
-
Fatigue: Reduced oxygen levels can lead to fatigue and decreased stamina.
-
Frequent Respiratory Infections: Emphysema patients are more prone to respiratory infections, such as bronchitis and pneumonia.
-
Cyanosis: A bluish tint to the lips and fingernails due to low oxygen levels in the blood.
Here's a table summarizing the key aspects of diagnosing emphysema:
|
Diagnosis of Emphysema |
Description |
|
Medical History and Physical Examination |
The healthcare provider reviews the patient's medical history, including smoking habits and exposure to lung irritants. A physical examination assesses breathing sounds and overall lung function. |
|
Spirometry/Diffusion Study |
This lung function test measures the amount of air a person can exhale and how quickly they can do it. It helps determine the severity of airflow obstruction; and assessment of lung volumes and capacities. |
|
Imaging Tests |
Chest X-rays and CT scans reveal changes in the lungs, such as enlarged air spaces and a flattened diaphragm, indicative of emphysema. |
|
Blood Tests |
Blood tests like ABG (Arterial blood gas analysis) measure oxygen and carbon dioxide levels in the blood and check for alpha-1 antitrypsin deficiency. |
|
Pulse Oximetry |
This non-invasive test measures the oxygen saturation level in the blood using a sensor placed on the finger. |
Treatment Options for Emphysema
As COPD/Emphysema is a persistent progressive disease, various treatments can help manage symptoms, improve quality of life, and slow disease progression. Treatment plans are tailored to the individual's needs and may include medications, therapies, and lifestyle changes.
1. Medications:
-
Inhaled Bronchodilators: These medications relax the muscles around the airways, making breathing easier.
-
Inhaled Steroids: Corticosteroids reduce inflammation in the airways, helping to relieve symptoms.
-
Antibiotics: These are prescribed to treat respiratory infections that can exacerbate emphysema symptoms.
-
Phosphodiesterase-4 Inhibitors: These medications reduce inflammation and relax the airways.
2. Pulmonary Rehabilitation:
-
Pulmonary rehabilitation programs combine exercise training, nutritional counselling, and education to help patients manage their symptoms and improve their overall health. These programs are designed to enhance the patient's ability to perform daily activities and improve their quality of life.
3. Oxygen Therapy:
-
For patients with severe emphysema and low blood oxygen levels, supplemental oxygen can help improve breathing and reduce symptoms. Oxygen therapy can be administered at home using portable oxygen tanks or concentrators.
4. Surgical Options:
-
Lung Volume Reduction Surgery (LVRS): This procedure involves removing damaged lung tissue to improve the function of the remaining healthy tissue. LVRS can help reduce symptoms and improve breathing in selected patients.
-
Bullectomy: In this surgery, large air spaces (bullae) that form in the lungs due to emphysema are removed. This can help improve lung function and reduce shortness of breath.
-
Lung Transplant: In severe cases where other treatments are ineffective, a lung transplant may be considered. This procedure involves replacing the damaged lung with a healthy lung from a donor.
5. Lifestyle Changes:
-
Smoking Cessation: Quitting smoking is the most crucial step in managing emphysema. It can slow disease progression and improve overall lung health.
-
Avoiding Lung Irritants: Patients should avoid exposure to air pollution, chemical fumes, and other lung irritants.
-
Healthy Diet: A balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins can support overall health and improve energy levels.
-
Regular Exercise: Engaging in regular physical activity can help improve lung function, reduce symptoms, and enhance overall well-being.
|
Coping and Support |
Description |
|
Living with Emphysema |
Living with emphysema can be challenging, both physically and emotionally. Patients need to have a strong support system and access to resources that can help them manage their condition. |
|
Mental Health and Emotional Well-being |
Emphysema can lead to anxiety, depression, and stress. Seeking support from mental health professionals, joining support groups, and practising relaxation techniques can help manage these emotional challenges. |
|
Support Groups |
Joining a support group for individuals with emphysema or COPD can provide a sense of community and shared experiences. These groups offer emotional support, practical advice, and encouragement. |
|
Caregiver Support |
Caregivers play a vital role in helping patients manage their condition. Providing education, resources, and support for caregivers is essential for the well-being of both the patient and the caregiver. |
Innovations and Research
Ongoing research and advancements in medical science continue to improve the understanding and treatment of emphysema. Some areas of focus include:
-
New Medications: Researchers are developing new drugs that target specific pathways involved in emphysema to provide more effective treatments with fewer side effects.
-
Stem Cell Therapy: Investigating the potential of stem cell therapy to repair damaged lung tissue and improve lung function.
-
Gene Therapy: Exploring gene therapy approaches to address genetic factors, such as alpha-1 antitrypsin deficiency, that contribute to emphysema.
-
Advanced Imaging Techniques: Developing more precise imaging techniques to diagnose emphysema earlier and monitor disease progression more accurately.
Conclusion
Emphysema is a chronic and progressive lung disease that significantly impacts the quality of life. Early diagnosis and appropriate treatment can help manage symptoms, slow disease progression, and improve overall well-being. By understanding the causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment options for emphysema, patients and their caregivers can take proactive steps to manage the condition and enhance their quality of life. Ongoing research and advancements in medical science continue to offer hope for better treatments and improved outcomes for individuals living with emphysema.
With a team of highly skilled and internationally acclaimed doctors, state-of-the-art facilities, and a patient-centric approach, Manipal Hospital Delhi ensures that every patient receives the highest standard of care. The hospital's commitment to innovation, research, and continuous improvement further enhances its reputation as a leader in the healthcare industry.
Whether you need routine medical care or specialized treatment, Manipal Hospital Delhi is dedicated to providing exceptional healthcare services, making it the trusted choice for patients seeking quality medical care. Choose Manipal Hospital for a healthier, brighter future.



















 6 Min Read
6 Min Read
















