
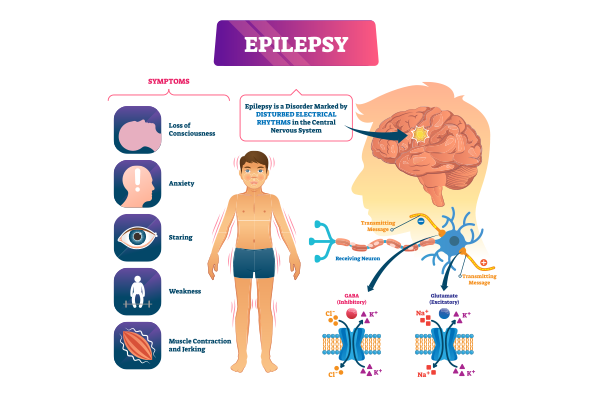
Epilepsy treatment in Delhi is crucial for individuals living with this neurological condition. Epilepsy is characterized by recurrent seizures, which are sudden bursts of electrical activity in the brain. While epilepsy can be challenging to live with, understanding its epilepsy causes, seizure triggers, and best epilepsy management practices can help individuals and their families navigate life with the condition more effectively. This guide will provide essential insights into types of epilepsy, seizure first aid, epilepsy medication tips, and how to support a loved one with epilepsy.
Synopsis
- Understanding Epilepsy: Seizure Types, Causes, Triggers, and Diagnosis
- Get Seizure Smart: First Aid for Seizures
- Management of Epilepsy: Treatment and Lifestyle Adjustments
- Seizure Medication Tips: How to Make the Most of Your Treatment
- Checklist to Manage Epilepsy Well: Key Steps for Everyday Life
- Helping Your Child with Epilepsy: Emotional and Practical Support
- Coming to Terms with Epilepsy: Emotional Coping and Adjustment
- Conclusion
Understanding Epilepsy: Seizure Types, Causes, Triggers, and Diagnosis
Epilepsy is not a singular disorder but rather a spectrum of brain conditions that cause seizures. There are different types of epilepsy, broadly categorized as focal onset seizures (which start in one part of the brain) and generalized onset seizures (which involve both hemispheres of the brain). Some people may also experience unknown onset seizures, where the origin is unclear.

Common Causes of Epilepsy:
|
Cause |
Description |
|
Genetic Factors |
Some forms of epilepsy are hereditary. |
|
Head Injuries |
Trauma from accidents falls, or sports injuries. |
|
Infections |
Conditions like meningitis, encephalitis, or neurocysticercosis. |
|
Stroke or Brain Tumors |
These can cause epilepsy in adults. |
|
Developmental Disorders |
Conditions like autism or cerebral palsy can be linked to epilepsy. |
Seizure Triggers:
-
Lack of sleep and stress
-
Flashing lights (photosensitive epilepsy)
-
Alcohol and drug use
-
Fever or illness
Diagnosis:
A doctor may use EEG (electroencephalogram), MRI scans, and blood tests to diagnose epilepsy and determine its cause. Understanding seizure patterns and triggers of epilepsy can help tailor treatment options.
More Reads: Symptoms of Epilepsy
Get Seizure Smart: First Aid for Seizures
Knowing how to help someone having a seizure can prevent injury and save lives. Follow these steps for seizure first aid:
-
Stay Calm and Keep Track of Time – If a seizure lasts more than 5 minutes, seek emergency help.
-
Protect the Person from Injury – Clear the area of sharp objects and cushion their head.
-
Turn Them on Their Side – Helps prevent choking.
-
Do Not Restrain or Put Anything in Their Mouth – A person having a seizure cannot swallow their tongue.
-
Stay with the Person – Comfort them as they regain consciousness and ensure they recover safely.
Seek immediate medical help if the seizure is prolonged, occurs repeatedly, or if the person is injured.
Management of Epilepsy: Treatment and Lifestyle Adjustments
Living with epilepsy requires a combination of medical treatment and lifestyle adjustments. Here’s how epilepsy treatment in Delhi can be managed effectively:
Medical Treatments:
-
Anti-epileptic drugs (AEDs): The most common treatment for epilepsy.
-
Surgery: For individuals with drug-resistant epilepsy.
-
Vagus Nerve Stimulation (VNS): A device that sends electrical impulses to the brain.
-
Ketogenic Diet: A high-fat, low-carb diet beneficial for some epilepsy patients.
Lifestyle Adjustments:
-
Manage stress through relaxation techniques.
-
Avoid seizure triggers like flashing lights and excessive alcohol.
-
Wear a medical ID bracelet for emergencies.
Seizure Medication Tips: How to Make the Most of Your Treatment
Best epilepsy medication practices include:
-
Take Medications on Time – Set reminders to ensure consistency.
-
Do Not Skip Doses – Missing doses can increase seizure risk.
-
Discuss Side Effects with Your Doctor – Adjustments may be needed.
-
Avoid Drug Interactions – Check before taking new medications.
-
Monitor Your Seizures – Keeping a seizure diary helps track effectiveness.
Consistency is key when taking anti-seizure medication. Any changes should be done under neurologist supervision.
Checklist to Manage Epilepsy Well: Key Steps for Everyday Life
|
Checklist Item |
Importance |
|
Take medications as prescribed |
Ensures seizure control. |
|
Get enough sleep every night |
Reduces seizure frequency. |
|
Identify and avoid seizure triggers |
Helps prevent seizures. |
|
Wear a medical ID bracelet |
Provides emergency information. |
|
Keep emergency contacts handy |
Ensures quick response in case of seizures. |
|
Educate friends and family about seizure first aid |
Prepares others to assist. |
|
Maintain regular medical check-ups |
Helps monitor and adjust treatment. |
|
Keep a seizure diary to track patterns |
Identifies triggers and treatment effectiveness. |
Helping Your Child with Epilepsy: Emotional and Practical Support
Supporting a child with epilepsy goes beyond medical care. Here’s how parents can help:
-
Recognizing childhood epilepsy types can help with early diagnosis.
-
Emotional Support: Reassure them that epilepsy does not define them.
-
Education: Teach them about their condition in an age-appropriate way.
-
Advocacy: Work with schools for a safe and supportive learning environment.
-
Encouragement: Allow participation in activities with necessary precautions.
Coming to Terms with Epilepsy: Emotional Coping and Adjustment
A diagnosis of epilepsy can be overwhelming, but epilepsy support groups in Delhi can help. Here are some coping strategies:
-
Join epilepsy support groups to connect with others.
-
Stay Informed: Education empowers individuals and families.
-
Address Mental Health: Anxiety and depression in epilepsy are common; seek professional help if needed.
-
Understanding if epilepsy causes death can alleviate fears with the right information.
-
Focus on Strengths: Many people with epilepsy lead successful lives with the right support and management.
Conclusion
Epilepsy specialists in Delhi offer a range of treatment and management options to help individuals lead normal lives. Whether you are managing epilepsy yourself or caring for a loved one, being informed and proactive is essential. From understanding partial epilepsy types, ensuring medication adherence, and providing epilepsy first aid, every effort counts. If you or a loved one has epilepsy, work closely with a neurologist near you to develop a personalized epilepsy treatment plan and seek support when needed.
FAQ's
Epilepsy is classified into focal epilepsy (partial epilepsy types), generalized epilepsy, and unknown onset epilepsy. These categories help doctors determine the most effective treatment approach.
Causes of epilepsy in adults and causes of epilepsy in older adults may include brain injuries, strokes, tumours, infections, and neurodegenerative diseases like Alzheimer’s.
Causes of epilepsy in children often include genetic factors, brain development issues, perinatal injuries, or infections like meningitis.
While epilepsy itself is not fatal, severe or uncontrolled seizures can lead to Sudden Unexpected Death in Epilepsy (SUDEP) or complications like status epilepticus, which requires immediate medical intervention.
Some childhood epilepsy types include Benign Rolandic Epilepsy (BRE), Childhood Absence Epilepsy (CAE), and Lennox-Gastaut Syndrome (LGS). Early diagnosis and treatment are crucial for managing symptoms.
Management includes anti-epileptic medication (AEDs), dietary therapy (ketogenic diet), lifestyle adjustments, and in some cases, surgery. Identifying and avoiding seizure triggers is also key.
While epilepsy cannot always be cured, many people achieve seizure control through medications, therapy, and surgery. Some children may also outgrow epilepsy as they age.



















 6 Min Read
6 Min Read













