For many years, Bone Marrow Transplants have been used to treat a variety of illnesses, including lymphomas, aplastic anaemia, immune system deficiencies, leukaemias, and some solid tumour malignancies. Bone Marrow Transplantation (BMT) facilities in India have grown gradually but steadily since early 1983. The results are positive, with 90% survival in thalassemia major and roughly 50% disease-free survival in acute myeloid leukaemia and aplastic anaemia. Even though great strides have been made in Bone Marrow Transplantation techniques, patients still experience complications. This blog post walks you through the benefits and risks of undergoing Bone Marrow Transplantation.
Synopsis
About the Bone Marrow Transplant
A Bone Marrow Transplant includes infusing your body with healthy blood-forming stem cells to replace bone marrow that isn't producing enough healthy blood cells. A Stem Cell Transplant is another term for a Bone Marrow Transplant. If your bone marrow fails to generate enough healthy blood cells or stops functioning altogether, you may require a Bone Marrow Transplant.
What is Bone Marrow?
The soft, fatty substance found inside bone cavities is called bone marrow. Your bone marrow is where red, white, and platelets, as well as other blood components, are formed. Almost all of the components of your blood are made in your bone marrow. Also, fat is stored in the bone marrow and converted to energy as needed.
Conditions That Require Bone Marrow Transplant
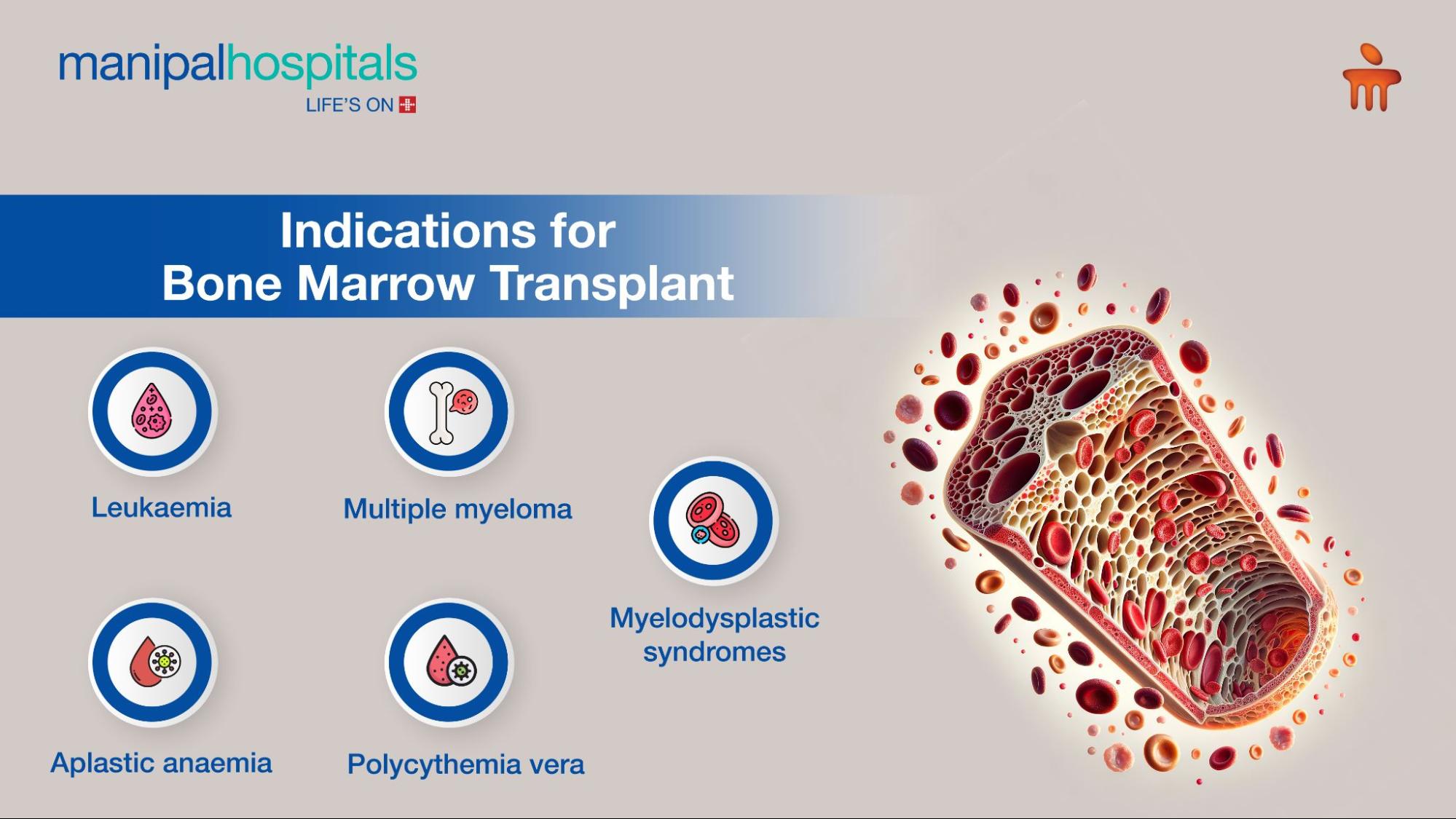
Blood-related disorders are frequently the consequence of aberrantly functioning bone marrow, as bone marrow serves as the building block for the production of red blood cells. Among these prerequisites are:
-
Leukaemia: A blood and bone marrow malignancy that directly targets the bone marrow. When a cell mutation happens in your bone marrow, the number of mutant cells multiplies uncontrollably, decreasing the number of healthy, normal cells produced.
-
Multiple myeloma: The bone marrow of your body creates malignant plasma cells.
-
Aplastic anaemia: Your bone marrow fails to produce enough blood cells.
-
Polycythemia vera: It occurs when your blood thickens because your body produces an excessive amount of red blood cells.
-
Myelodysplastic syndromes: They are typified by anaemia, or the bone marrow's insufficient production of healthy red blood cells.
Types of Bone Marrow Transplants
There are mainly two types of Bone Marrow Transplants, including:
-
Allogeneic Stem Cell Transplant: In an Allogeneic Stem Cell Transplant, bone marrow that isn't making enough healthy blood cells is replaced with healthy blood stem cells from a donor. The donor could either be a family member, a friend, or a stranger willing to donate the bone marrow.
-
Autologous Stem Cell Transplant: With an Autologous Stem Cell Transplant, healthy blood stem cells from within your body are used to replace damaged bone marrow.
Consult our Hematology Doctor at Manipal Dhakuria to find your ideal bone marrow transplantation treatment.
Bone Marrow Transplant: Risks vs. Benefits
Understanding the risks and benefits before a Bone Marrow Transplant procedure can improve the chances of successful outcomes.
Risks Involved in Bone Marrow Transplant
A Bone Marrow Transplant involves a few risks, such as:
-
Graft vs. Host Disease: This condition arises when the donor cells attack the patient's healthy cells. When the patient's tissue does not match the donor's exactly, this can occur.
-
Infection: Patients undergoing Bone Marrow Transplants are susceptible to infection due to weakened immune systems. Antibiotics or other drugs may be required to treat or prevent infections in them.
-
Bleeding: One of the most frequent side effects of Bone Marrow Transplants is bleeding. To stop bleeding, patients can require blood transfusions or other medical procedures.
-
Rejection: The donor cells may be rejected by the patient's body. This may occur if the patient does not match the donor cells well or if the patient has an underlying illness that makes it challenging for the body to receive fresh cells.
Benefits of a Bone Marrow Transplant
A Bone Marrow Transplant provides long-term benefits, including:
-
Cure for some diseases: Leukaemia and lymphoma are two conditions that can be successfully treated with Bone Marrow Transplants but are otherwise incurable.
-
Replaces diseased marrow: A transplant can enhance immunological response and general health by substituting healthy marrow for sick or damaged marrow.
-
Long-term survival: Patients who have a Bone Marrow Transplant may be able to resume their regular activities and have a better likelihood of long-term survival.
Conclusion
Often, the purpose of a Bone Marrow Transplant is to cure cancer. Certain malignancies, including some forms of leukaemia and lymphoma, may be curable. The best outcome for other conditions is cancer remission. Before having a Bone Marrow Transplant, it's crucial to go over the advantages and disadvantages of the process with a trained medical expert, a bone marrow transplant specialist. We at Manipal Hospitals have a fully functional, cutting-edge Bone Marrow Transplant (BMT) unit with the most advanced equipment and a highly skilled interdisciplinary staff with a proven successful track record of Bone Marrow Transplants. Book an appointment at our Hematology Hospital in Dhakuria to learn more about bone marrow transplants.
FAQ's
Physicians search for a donor whose tissue type, especially the patient's human leukocyte antigen (HLA) tissue type, matches the donor’s tissue type. For the benefit of the patient, the HLA markers should match as closely as possible.
The majority of the cells in your body include proteins called HLAs, which act as markers. These indicators help your immune system distinguish between cells that belong in your body and those that don't.
If you are receiving an Autologous Stem Cell Transplant, you will likely spend three weeks in the hospital; if you are receiving an Allogeneic Stem Cell Transplant, you may spend four weeks.
Regaining strength and endurance after a Bone Marrow Transplant is crucial. You should also stay away from crowds and wait six to twelve months for allogeneic transplants and three to six months for autologous transplants.
For individuals suffering from leukaemia, lymphoma, sickle cell anaemia, and many other illnesses, a bone marrow or cord blood transplant may be the best course of action or their last chance for recovery. New illnesses are being treated with transplants as the research behind them advances.
To schedule an appointment at Manipal Hospitals, contact our hospital or visit our website.



















 5 Min Read
5 Min Read










