-
Centre of
Excellence
Centre of Excellence
Other Specialities
- Allergy and Immunology
- Andrology
- Anesthesiology
- Dental Medicine
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- Ear Nose Throat
- Electrophysiology
- Fetal Medicine
- General Medicine
- General Surgery
- Geriatric Medicine
- GI Surgery
- Growth and Hormone
- Gynaec Oncology
- Hand Surgery
- Hemato Oncology
- Hematology
- Hepatobiliary Surgery
- ICU and Critical Care
- Infectious Disease
- Internal Medicine
- Interventional Radiology
- Kidney Transplant
- Lifestyle Clinic
- Medical Gastro
- Medical Oncology
- Microbiology
- Minimal Access Surgery
- Neonatology & NICU
- Nuclear Medicine
- Nutrition And Dietetics
- Ophthalmology
- Oral Maxillo Facial Surgery
- Paediatric Urology
- Pain Medicine
- Parkinson Disease and Movement Disorder
- Pathology
- Pharmacy
- Physiotherapy
- Plastic And Cosmetic Surgery
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology (Respiratory and Sleep Medicine)
- Radiology
- Radiotherapy (Oncology Radiation)
- Renal Sciences
- Surgical Gastro
- Surgical Oncology
- Transfusion Medicine
- Vascular and Endovascular Surgery
Speciality Clinics
- Doctors
- Dhakuria
- International Patients



Clinics








- Self Registration
- Mars - Ambulance
- Corporate & PSU
- Insurance Helpdesk
- Awards And Achievements
- Careers
- Contact Us
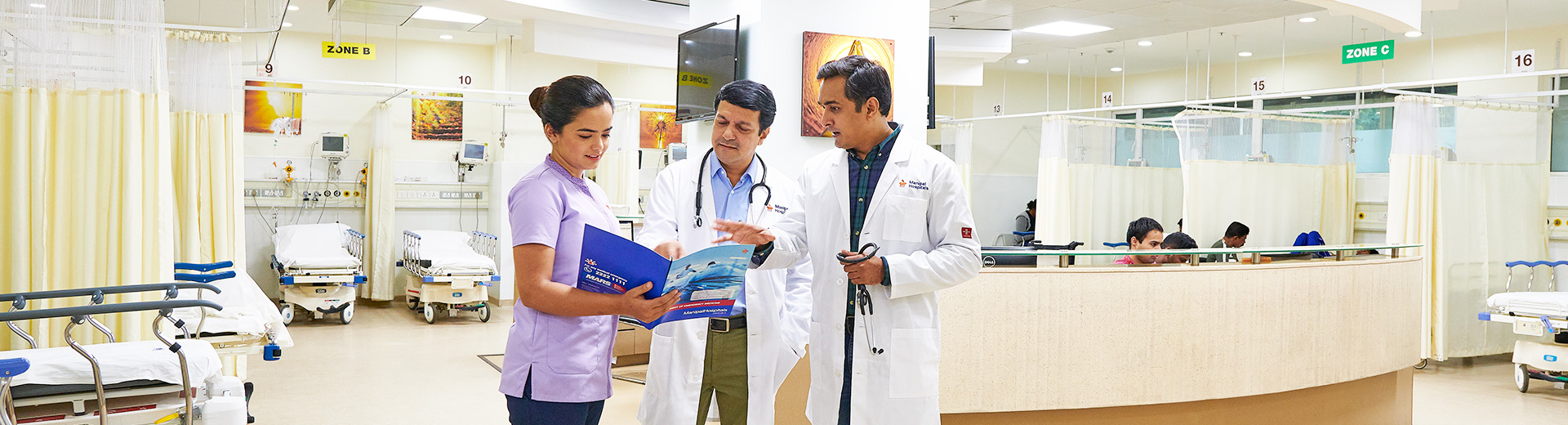

General Anesthesia
General Anesthesia Procedure in Dhakuria
General anaesthesia is a medical procedure used to induce a reversible state of unconsciousness and loss of sensation throughout the entire body. It allows patients to undergo surgeries or medical procedures without feeling pain or being aware of what's happening during the process.
General anaesthesia is administered by an anesthesiologist or a certified nurse anaesthetist. It can be given through inhalation (breathing in gases) or intravenously (through an IV line).
General anaesthesia is used for various surgical procedures ranging from minor outpatient surgeries to complex open-heart surgeries. During anaesthesia, vital signs such as heart rate, blood pressure, oxygen levels, and breathing are closely monitored to ensure the patient's safety throughout the procedure.
FAQ's
General anaesthesia is generally safe when administered by trained professionals in a controlled medical setting. However, there are possible risks and complications with any medical procedure. Your anesthesiologist will discuss these risks with you before the procedure.
Side effects of general anaesthesia can include nausea, vomiting, sore throat, confusion, dizziness, and shivering. Some patients may experience temporary memory loss or cognitive changes. Serious complications are rare but can include allergic reactions, breathing problems, and anaesthesia awareness (consciousness during surgery).
While rare, risks can include allergic reactions, breathing problems, postoperative cognitive dysfunction, and adverse reactions to medications. Your anesthesiologist will discuss these risks with you before surgery.
Before receiving general anaesthesia, patients are advised not to eat or drink anything for at least 8 hours prior to surgery. This fasting period helps reduce the risk of aspiration, where stomach contents are inhaled into the lungs during anaesthesia induction or surgery, causing serious complications. Patients should follow fasting instructions provided by their healthcare provider closely to ensure a safe surgical experience. Discuss any concerns or questions about fasting and pre-operative instructions with your healthcare provider before the scheduled procedure.
The effects of general anaesthesia wear off gradually after surgery. You may feel drowsy for several hours and should not drive or operate machinery until fully recovered.
No, you will not feel pain during surgery as you will be completely unconscious and unable to perceive sensations.
Inform your healthcare team about any previous reactions or allergies to anaesthesia medications. Your anesthesiologist will take this information into account when planning your anaesthesia regimen.
While the effects of general anaesthesia on memory and cognitive function are usually temporary, some patients may experience short-term memory loss or cognitive changes immediately after waking up. These effects typically resolve within a few hours or days.
After undergoing a procedure involving anaesthesia or sedation, it's generally not safe to drive yourself home from the hospital. Arrange for a designated driver or alternative transportation, as the effects of anaesthesia can impair your ability to drive safely.
To prepare for general anaesthesia, follow your healthcare provider's instructions regarding fasting, medication management, and preoperative testing. Inform your healthcare team about any medical conditions, allergies, or medications you are taking, and ask any questions or express concerns you may have before the procedure.
After a procedure with general anaesthesia, you can expect to feel groggy, possibly experience nausea or a sore throat, and may have some pain or discomfort at the surgical site. You will be monitored until you are fully awake and stable, and our healthcare team will provide instructions for your recovery, including pain management and follow-up appointments.
Anaesthesia typically poses minimal risk to breastfeeding individuals and their infants. Medications utilised in various types of anaesthesia, including general anaesthesia, are swiftly metabolised by the body. Your healthcare provider may suggest expressing your initial breast milk following general anaesthesia.
Home Dhakuria Specialities Anesthesiology General-anesthesia

You’re on Our Indian Website
Visit the Global site for International patient services











