-
Centre of
Excellence
Centre of Excellence
Other Specialities
- Allergy and Immunology
- Andrology
- Anesthesiology
- Dental Medicine
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- Ear Nose Throat
- Electrophysiology
- Fetal Medicine
- General Medicine
- General Surgery
- Geriatric Medicine
- GI Surgery
- Growth and Hormone
- Gynaec Oncology
- Hand Surgery
- Hemato Oncology
- Hematology
- Hepatobiliary Surgery
- ICU and Critical Care
- Infectious Disease
- Internal Medicine
- Interventional Radiology
- Kidney Transplant
- Lifestyle Clinic
- Medical Gastro
- Medical Oncology
- Microbiology
- Minimal Access Surgery
- Neonatology & NICU
- Nuclear Medicine
- Nutrition And Dietetics
- Ophthalmology
- Oral Maxillo Facial Surgery
- Paediatric Urology
- Pain Medicine
- Parkinson Disease and Movement Disorder
- Pathology
- Pharmacy
- Physiotherapy
- Plastic And Cosmetic Surgery
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology (Respiratory and Sleep Medicine)
- Radiology
- Radiotherapy (Oncology Radiation)
- Renal Sciences
- Surgical Gastro
- Surgical Oncology
- Transfusion Medicine
- Vascular and Endovascular Surgery
Speciality Clinics
- Doctors
- Dhakuria
- International Patients



Clinics








- Self Registration
- Mars - Ambulance
- Corporate & PSU
- Insurance Helpdesk
- Awards And Achievements
- Careers
- Contact Us
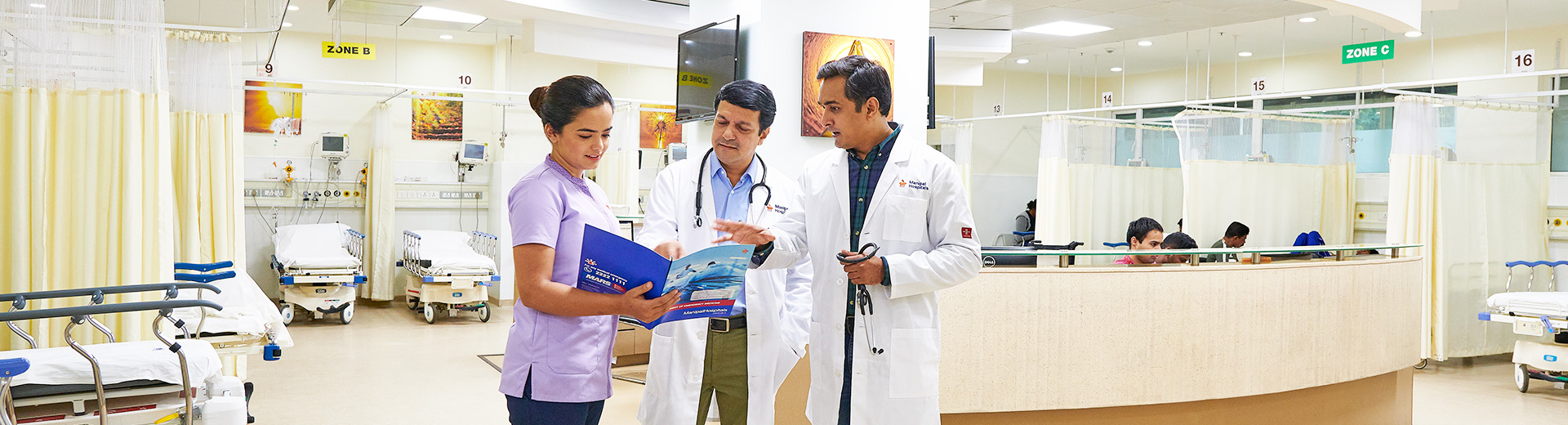

Coronary Artery Bypass Graft Surgery
Coronary Artery Bypass Graft Surgery in Dhakuria
Coronary Artery Bypass Graft (CABG) is a surgical procedure used to treat coronary artery disease (CAD), a condition where the blood vessels supplying the heart become narrowed or blocked, leading to reduced blood flow and heart complications.
During CABG, surgeons create new routes for blood flow to the heart by bypassing blocked or narrowed arteries using healthy blood vessels harvested from other parts of the body, typically the chest, leg, or arm.
In our pursuit of excellence, Manipal Hospitals is at the forefront of embracing the latest advancements in CABG treatment. Our approach includes:
- Minimally Invasive CABG
- Off-Pump CABG
- Hybrid CABG Procedures
FAQ's
CABG is performed to restore adequate blood flow to the heart muscle when coronary arteries become narrowed or blocked due to coronary artery disease (CAD). This narrowing or blockage restricts blood flow to the heart, leading to symptoms such as chest pain (angina) or shortness of breath. CABG is recommended in cases where medication or less invasive treatments have not adequately relieved symptoms or when the risk of a heart attack or other complications is high. By bypassing the blocked arteries with grafts taken from other parts of the body, CABG improves blood flow to the heart, relieves symptoms, and reduces the risk of heart attack and other cardiovascular events, ultimately improving the patient's quality of life and prognosis.
Yes, a person can survive with blocked arteries, but again, it increases life risk and the chances of heart attacks. So, a healthy diet intake, along with regular workouts and visiting a doctor frequently, may help in avoiding the CABG.
Artery Bypass Surgery can take anywhere between 3 to 6 hours, depending on the extent of the condition.
A surgeon may suggest you make minor lifestyle modifications, continue with regular exercise and diet changes, and quit smoking and alcohol to achieve the success of surgery.
For a procedure to be successful, a well-diagnostic pre-treatment procedure is essential to decide the condition of the patient. Initially, the surgeon discusses the patient's pre-existing health conditions or tries to understand the family history of other comorbidities to correlate the risks associated with the CABG procedure. Patients may be recommended to go ahead with some essential diagnostic procedures such as basic blood tests, electrocardiograms (ECG), stress tests, and chest X-rays. Further, to overcome complications, appropriate medication is administered before the surgery to control the blood loss or pressure, and for diabetic patients’ medication is continued during the surgery.
The patient is administered anaesthesia and connected to a machine that carries out the normal function of the heart and lungs until the surgery is completed. To use the bypass graft, the surgeon holds a functioning blood vessel either from the leg, arm, or chest. A small cut is made at the chest site, near the coronary arteries of the heart. They sew the graft to the main artery from the heart, and another sew is made beyond the area of the blocked region. Soon after the grafting is done, the surgeon ensures the smooth flow of blood to the heart, and the incision made near the heart is sewed successfully.
To achieve a standard recovery pace, a hospital stay is needed for a few days to 4 to 6 weeks, and later, depending on the patient’s condition, they are either made to stay or discharged.
Complications may occur with poor hygiene, living style, and bleeding issues, and if the patient is diabetic and wound healing is slow, the possibility of pneumonia may occur.
Yes, after discharge, the post-cardiac care unit advises the patient to seek cardiac rehabilitation sessions that psychologically strengthen the patient for a speedy recovery and educate him/her on heart-healthy lifestyle choices and the way to lead after the surgery.
Getting back to normal depends on the patient's capacity to manage the activities they hold, and many patients easily perform all their routine work.
In some situations, one may undergo repeat CABG if their lifestyle is not healthy, leading to new blockages, or if the previous graft is again blocked.
Yes, it reduces the chances of risk of a heart attack and improves quality of life.
Home Dhakuria Specialities Cardiology Coronary-artery-bypass-graft-surgery

You’re on Our Indian Website
Visit the Global site for International patient services
Your Feedback is Highly Valued!












