-
Centre of
Excellence
Centre of Excellence
Other Specialities
- Allergy and Immunology
- Andrology
- Anesthesiology
- Dental Medicine
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- Ear Nose Throat
- Electrophysiology
- Fetal Medicine
- General Medicine
- General Surgery
- Geriatric Medicine
- GI Surgery
- Growth and Hormone
- Gynaec Oncology
- Hand Surgery
- Hemato Oncology
- Hematology
- Hepatobiliary Surgery
- ICU and Critical Care
- Infectious Disease
- Internal Medicine
- Interventional Radiology
- Kidney Transplant
- Lifestyle Clinic
- Medical Gastro
- Medical Oncology
- Microbiology
- Minimal Access Surgery
- Neonatology & NICU
- Nuclear Medicine
- Nutrition And Dietetics
- Ophthalmology
- Oral Maxillo Facial Surgery
- Paediatric Urology
- Pain Medicine
- Parkinson Disease and Movement Disorder
- Pathology
- Pharmacy
- Physiotherapy
- Plastic And Cosmetic Surgery
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology (Respiratory and Sleep Medicine)
- Radiology
- Radiotherapy (Oncology Radiation)
- Renal Sciences
- Surgical Gastro
- Surgical Oncology
- Transfusion Medicine
- Vascular and Endovascular Surgery
Speciality Clinics
- Doctors
- Dhakuria
- International Patients



Clinics








- Self Registration
- Mars - Ambulance
- Corporate & PSU
- Insurance Helpdesk
- Awards And Achievements
- Careers
- Contact Us
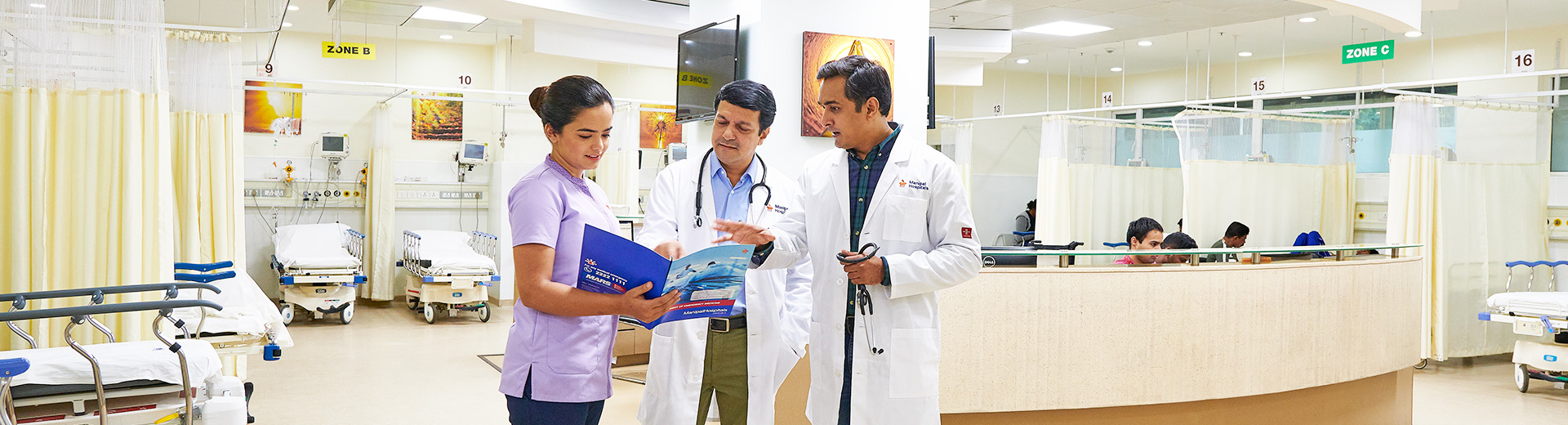

Coronary lesion physiological assessment and imaging
Coronary Lesion Physiological Assessment and Imaging in Dhakuria
Coronary physiology assessment and imaging are used as diagnostic indexes based on coronary pressure and flow. These diagnostic results are taken from direct measurements of coronary vessels or derived from image-based results. This way, doctors investigate the presence of obstructions and no obstructions in vessels. This assessment is helpful in the diagnosis of heart disease and its strategic management. Over the last two decades, the advancements in this test strongly recommend using it in all practice guidelines.
FAQ's
To confirm the type of coronary heart disease, several different tests are performed to diagnose the specific heart-related problem.
- Electrocardiogram
- Exercise Stress Test
- X-ray
- Echocardiogram
- Blood tests
- Coronary Angiography
- MRI scan
- CT scan
- Myocardial Perfusion scan
Cardiac CT Angiography, which is a test to check for clogged heart arteries, is considered a first-line diagnostic option for people with suspected heart disease. Angiography is a technique that allows surgeons to see the heart’s arteries. It can be done in two ways: first, the method is called Coronary Angiography, which has been in use for more than a half-century. It involves using a catheter through a leg, arm, or wrist artery up to the heart, and a special dye is injected that is visible under an X-ray.
The second way is Cardiac CT Angiography which was developed recently. The advantage of this test is that it does not require a catheter; rather, a special dye is sufficient, which is injected into the vein in the arm or hand. The scanner used is a CT scan, which takes multiple rapid X-rays that are merged to create a detailed, three-dimensional view of the heart artery.
This test measures the levels of cardiac biomarkers present in your blood. These include enzymes, hormones, and proteins. These markers become more visible when your heart undergoes stress and becomes injured because of a lack of oxygen supply to it. This condition leads to a heart attack. These biomarkers help to find out the cause and size of a heart attack and how seriously your heart is affected.
The cardiac biomarkers are:
- Cardiac Troponin: This is a protein used as a biomarker. It is highly sensitive. It enters your bloodstream right after your heart attack. It is considered the best biomarker for finding a heart attack.
- Creatinine Kinase: This is an enzyme also measured several times over 24 24-hour period. Its concentration doubles if you have had a heart attack previously.
- Myoglobin: It is a small and important protein that stores oxygen. It is measured occasionally.
Symptoms of coronary blockage include:
- Chest pain that lasts for a few minutes
- Pain or discomfort in your shoulders, neck, arm, and jaw
- Severe chest pain
- Sweating, paleness
- Shortness of breath
- Nausea or vomiting
- Dizziness or fainting
- Extreme tiredness
- Irregular pulse
This, also called cardiovascular (heart) imaging, is a broad term that includes many ways to take pictures of your heart and surrounding area. The main types of imaging are:
- Echocardiogram
- Cardiac Computed Tomography
- A Nuclear Cardiac Stress Test
- Single-Photon Emission Tomography
- Cardiac Positron Emission Tomography
- Coronary Angiogram
Some of the cardiac imaging procedures may be combined as CT scans with Coronary Angiograms for detailed imaging and better understanding.
An Echocardiogram is a test that uses ultrasound-frequency waves to produce images. It creates videos of your heart chambers, heart valves, walls, and blood vessels. It is used to measure the blood flow in your heart chambers. It helps to measure your heart’s pumping action and the severity of your heart condition. It determines any active defect in your valve, infection, blood clots, or hole in your heart.
A Coronary Angiogram is a special type of X-ray that is performed during Cardiac Catheterization. This process is done where a long, thin tube known as a catheter is inserted through an artery in your wrist or arm that reaches your heart, and then a dye is injected through the catheter into your bloodstream. The X-ray machine takes videos as the dye moves through the blood vessels around your heart. The test is used to locate the clogged blood vessels in your heart.
A Computerised Tomography (CT) Coronary Angiogram is an imaging test that gives clear and best results for diagnosis. This test is used to diagnose a variety of heart conditions.
MRI is a test that gives accurate information about the large sections of your coronary arteries, but it misses the smaller sections in your heart.
Home Dhakuria Specialities Cardiology Coronary-lesion-physiological-assessment-and-imaging

You’re on Our Indian Website
Visit the Global site for International patient services











