-
Centre of
Excellence
Centre of Excellence
Other Specialities
- Allergy and Immunology
- Andrology
- Anesthesiology
- Dental Medicine
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- Ear Nose Throat
- Electrophysiology
- Fetal Medicine
- General Medicine
- General Surgery
- Geriatric Medicine
- GI Surgery
- Growth and Hormone
- Gynaec Oncology
- Hand Surgery
- Hemato Oncology
- Hematology
- Hepatobiliary Surgery
- ICU and Critical Care
- Infectious Disease
- Internal Medicine
- Interventional Radiology
- Kidney Transplant
- Lifestyle Clinic
- Medical Gastro
- Medical Oncology
- Microbiology
- Minimal Access Surgery
- Neonatology & NICU
- Nuclear Medicine
- Nutrition And Dietetics
- Ophthalmology
- Oral Maxillo Facial Surgery
- Paediatric Urology
- Pain Medicine
- Parkinson Disease and Movement Disorder
- Pathology
- Pharmacy
- Physiotherapy
- Plastic And Cosmetic Surgery
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology (Respiratory and Sleep Medicine)
- Radiology
- Radiotherapy (Oncology Radiation)
- Renal Sciences
- Surgical Gastro
- Surgical Oncology
- Transfusion Medicine
- Vascular and Endovascular Surgery
Speciality Clinics
- Doctors
- Dhakuria
- International Patients



Clinics








- Self Registration
- Mars - Ambulance
- Corporate & PSU
- Insurance Helpdesk
- Awards And Achievements
- Careers
- Contact Us
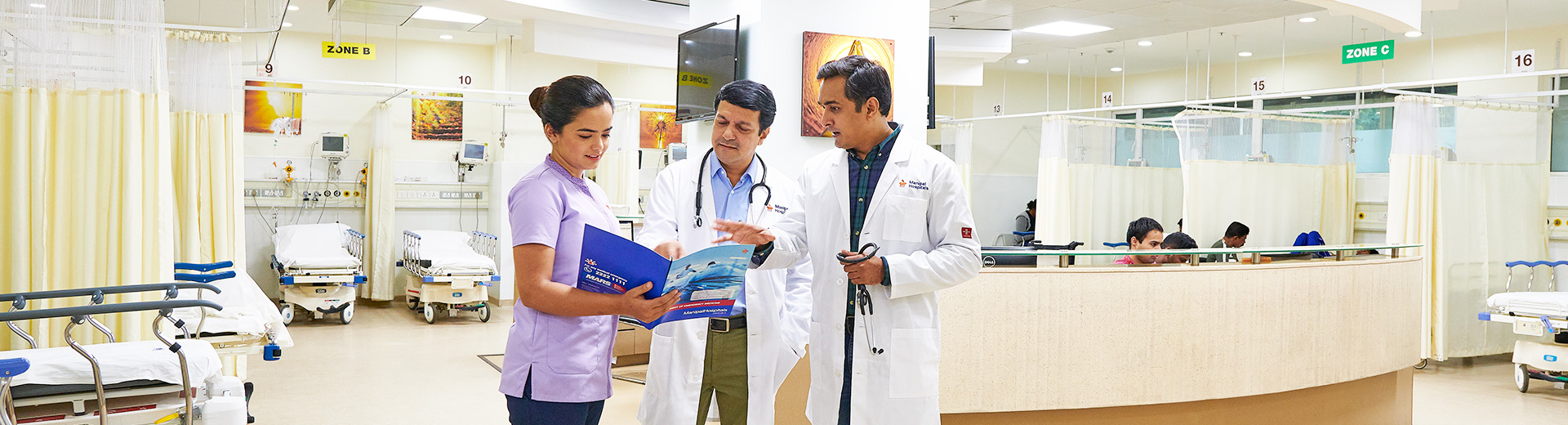

Electrophysiological Radio Ablation ERA including 3D ablation
Electrophysiological Radio Ablation ERA including 3D ablation in Dhakuria
An Electrophysiological Study (EPS) is a diagnostic test that is done to measure the electrical activity of the heart and to diagnose irregular heart rhythms (arrhythmias).
Radioablation is a non-surgical procedure performed to treat different types of arrhythmias. This procedure is also known as Catheter Ablation, Cardiac Ablation, or Radiofrequency Ablation. In most cases, Radiotherapy is done after an Electrophysiological Study in the same sitting. EPS is done to diagnose the problem, and Radioablation is done to treat it. Electrophysiological Radio Ablation has a good success rate and a very low risk of complications associated with this procedure.
FAQ's
Electrophysiological Radioablation may be beneficial in the following conditions:
- A person is suffering from irregular heart rhythms (arrhythmias)
- Despite having medications, arrhythmias do not get treated
- Medicines for arrhythmias are causing side effects
- A heart attack could happen
Your healthcare provider will provide you with all the instructions that you need to follow before arriving for the procedure.
- Your healthcare provider will take your complete medical history, including any previous disorders, medications you consume daily, any known allergies, etc
- You will be asked to avoid eating or drinking anything for some hours before the surgery.
- You will be asked to stop some medications, like the ones that affect blood clotting and the antiarrhythmic medications that you take.
- Shaving the target area—the catheter insertion site—will make the process easier. If not, medical professionals will take that action.
During the Electrophysiological Radioablation, you can expect the following:
When you get to the hospital, examinations such as blood tests, X-rays, and Echocardiograms might be performed.
- You will be given a sedative before the surgery begins.
- A local anaesthetic will be administered to you at the groyne catheter insertion site.
- The catheter's sensors, or electrodes, record the electrical activity of the heart and transmit electrical impulses. With the use of the data transmitted by the sensors, your physician will identify the region that results in arrhythmia.
- An electrophysiology investigation is the process of gathering data regarding the electrical activity of your heart.
- A catheter is then positioned near the heart cells during Radioablation, which produces aberrant electrical signals and irregular heartbeats. The catheter's tip transmits radiofrequency energy to destroy the abnormal cells in that area. This will bring the heart back to a normal state. You may feel a slight discomfort when the energy is used on the cells in your heart.
- After the procedure, the catheter is removed, and a dressing is applied to the insertion area.
The duration of the procedure may depend on various factors and your condition. However, on average, Electrophysiological Radioablation may take somewhere around 3 to 6 hours. The process is carried out in an Electrophysiology lab under strict observation.
No, the procedure does not hurt. Most patients experience no pain at all during the process. You may feel uncomfortable during the Electrophysiological Radio Ablation procedure from the injection of the local anaesthetic or numbing medicine where catheters are placed, or intermittently when doctors induce an abnormal heart rhythm. To reduce your discomfort, you may be given sedative agents, depending on the type of procedure you receive and the type of arrhythmia you have.
The risks associated with Electrophysiological Radio Ablation are very low and depend on the type of ablation and why it is done. Possible risks may include:
- Infection at the site of the catheter insertion
- Blood vessel damage
- Heart valve damage
- A new irregular heartbeat or worsening of the existing irregular heartbeat
- Slow heartbeat
- Blood clots in the legs or lungs
- Stroke or heart attack
- Pulmonary vein stenosis (a condition in which there is a narrowing of the veins that carry blood between the lungs and heart)
- Allergic reaction from contrast dye
- Damage to the kidneys due to the contrast dye used
In most cases, people can return to their normal routine activities within a couple of days. But you should avoid lifting heavy objects or doing heavy workouts for at least two weeks. You also need to avoid driving for at least a week after the procedure.
Contact your doctor immediately if you have
- Unusual pain or swelling
- Excessive bleeding
- Fever that does not improve with medicines
- Shortness of breath
- There are continuous irregularities in your heartbeat
Although everyone's experience with Radiofrequency Ablation pain relief differs, many patients report pain alleviation that lasts for several months to a year or more. For ongoing pain alleviation, some people could require recurrent treatments regularly.
Alternative treatments for Electrophysiological Radioablation include management with medications or the insertion of implantable devices.
Home Dhakuria Specialities Cardiology Electrophysiological-radio-ablation-era-including-3d-ablation

You’re on Our Indian Website
Visit the Global site for International patient services











