-
Centre of
Excellence
Centre of Excellence
Other Specialities
- Allergy and Immunology
- Andrology
- Anesthesiology
- Dental Medicine
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- Ear Nose Throat
- Electrophysiology
- Fetal Medicine
- General Medicine
- General Surgery
- Geriatric Medicine
- GI Surgery
- Growth and Hormone
- Gynaec Oncology
- Hand Surgery
- Hemato Oncology
- Hematology
- Hepatobiliary Surgery
- ICU and Critical Care
- Infectious Disease
- Internal Medicine
- Interventional Radiology
- Kidney Transplant
- Lifestyle Clinic
- Medical Gastro
- Medical Oncology
- Microbiology
- Minimal Access Surgery
- Neonatology & NICU
- Nuclear Medicine
- Nutrition And Dietetics
- Ophthalmology
- Oral Maxillo Facial Surgery
- Paediatric Urology
- Pain Medicine
- Parkinson Disease and Movement Disorder
- Pathology
- Pharmacy
- Physiotherapy
- Plastic And Cosmetic Surgery
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology (Respiratory and Sleep Medicine)
- Radiology
- Radiotherapy (Oncology Radiation)
- Renal Sciences
- Surgical Gastro
- Surgical Oncology
- Transfusion Medicine
- Vascular and Endovascular Surgery
Speciality Clinics
- Doctors
- Dhakuria
- International Patients



Clinics








- Self Registration
- Mars - Ambulance
- Corporate & PSU
- Insurance Helpdesk
- Awards And Achievements
- Careers
- Contact Us
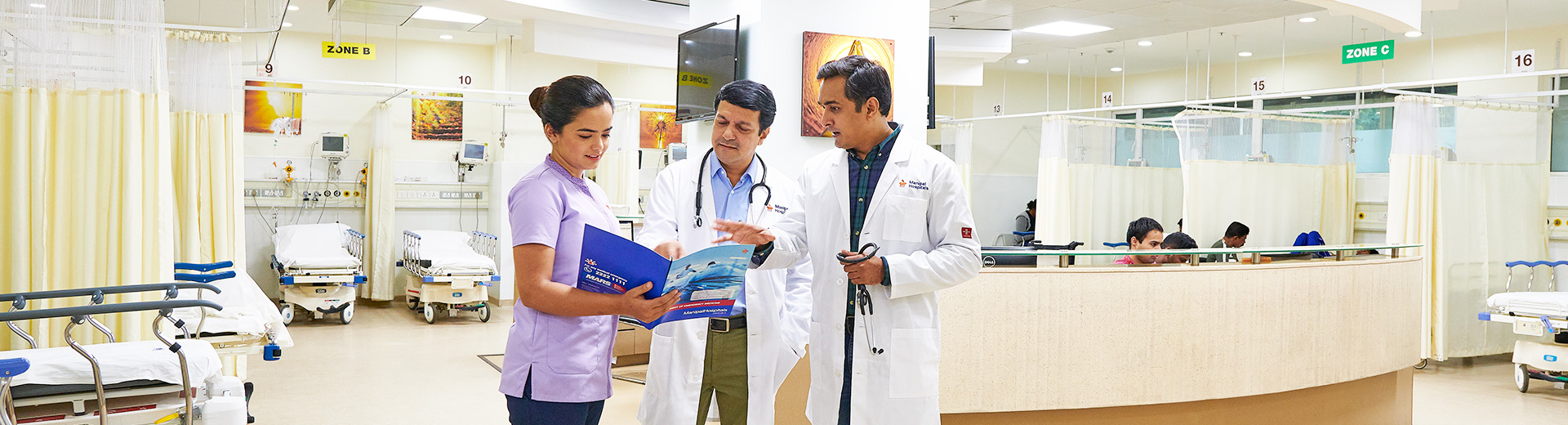

Emergency Percutaneous Coronary Intervention (PCI)
Emergency Percutaneous Coronary Intervention (PCI) Dhakuria
The minimally invasive and non-surgical treatment for coronary artery disease is called Percutaneous Coronary Intervention, or PCI. Arteries are the blood vessels that are responsible for carrying oxygen-rich blood from your heart throughout your body. In coronary artery disease, blood flow to the heart is affected as the coronary artery is narrowed or blocked. PCI is used to treat these blockages in the coronary artery, which further avoids chest pain and a heart attack. It is performed in a cardiac catheterization laboratory (cath lab) by a specialised team of interventional cardiologists and support staff.
The PCI procedure involves three steps:
-
Angiography: A thin, flexible tube called a catheter is inserted into a blood vessel in the groyne or wrist and threaded up to the coronary arteries. Contrast dye is injected through the catheter, allowing the cardiologist to visualise any blockages or narrowing in the coronary arteries on X-ray images (angiograms).
-
Angioplasty: Once the blockage is identified, a small balloon attached to the tip of the catheter is inflated at the site of the blockage. This compresses the plaque against the artery wall, widening the artery and restoring blood flow to the heart.
-
Stenting: In many cases, a small metal mesh tube called a stent is placed in the artery to help keep it open and prevent re-narrowing (restenosis) of the artery. The stent is delivered to the blockage site on a balloon catheter and expanded into place once the balloon is inflated. The balloon is then deflated and removed, leaving the stent in place to support the artery.
FAQ's
You may need a PCI procedure to treat the following heart disorders:
- Coronary Artery Disease: In this condition, there is the presence of plaque (a thick, fatty substance) that accumulates along the walls of the artery.
- Atherosclerosis: Atherosclerosis occurs when the plaque hardens in the arteries, further contributing to blockages and restricted blood flow.
- Acute Coronary Syndrome: In this condition, the blood flow to the heart is reduced, and you may have a heart attack or chest pain.
You will be asked to follow some instructions by your healthcare professional:
- If PCI is carried out in a non-emergency situation, you will be asked to come on an empty stomach. You need to avoid eating and drinking for some hours prior to the surgery.
- You will be asked to quit some medications that can hinder the procedure and healing. These medicines may include anticoagulants (blood-thinning medicines).
- On your arrival at the hospital, you will be given a sedative to relax.
- If you have hair in the groyne area, a healthcare provider may shave it.
There are two types of PCI: Balloon Angioplasty and Angioplasty with a Stent. Your doctor will decide which type you will be treated with after analysing your heart condition.
- You will be given local anaesthesia in the skin, where a catheter will be inserted.
- A small incision will be made so that the catheter with a tipped balloon can be inserted.
- If you feel pain while the catheter is inserted into the blood vessels, the doctor may give you painkillers.
- Once the catheter reaches the target area, which is the heart, the contrast dye will be released, so the area where the blood vessel is narrowed can be identified.
- When the dye is released, you might taste metallic or have a temporary headache.
- Once the narrowed blood vessel is identified, the catheter will be removed.
- Pressure will be applied to the insertion site to control bleeding.
- A tight bandage will be placed on the insertion site to aid healing.
- You need to keep the area straight where the catheter was inserted (groyne or arm).
Following the PCI procedure, you may expect the following:
- Depending on your particular situation, you may be required to stay in bed for two to six hours.
- Painkillers may be given if you experience any discomfort.
- You will be asked to drink water and other fluids so that the contrast dye may get flushed from your body.
- You need to spend at least a day or two in the hospital after your surgery.
The procedure may last somewhere between 30 minutes and 2 hours. However, the exact time depends on various factors, which may include the extent of plaque buildup.
The recovery time after PCI may depend on various factors. But usually, you can resume your normal routine a week after your surgery. It is advised to avoid doing heavy exercises or lifting weights for some days after surgery.
The PCI procedure helps improve the blood flow of the heart, reducing the risk of stroke, and treating various heart disorders. A coronary artery can narrow or constrict again. In such cases, similar symptoms usually return, and another PCI or Coronary Bypass Surgery may be necessary.
Percutaneous Coronary Intervention is a safe procedure. However, some elderly people, heart patients, and diabetic patients may experience risks. The risks associated may include:
- Heart attack.
- Bleeding or infection at the catheter insertion site.
- Blood clots in the heart stent.
- Re-narrowing in the artery.
- Stroke.
You immediately need to contact your doctor if you feel the following unusual symptoms:
- Fever that doesn't improve with medicines
- Chest pain
- Bleeding and infection at the site of catheter insertion
- Pain or swelling
PCI is quite successful in increasing many patients' quality of life and reducing symptoms like chest discomfort. Additionally, it can lessen the chance of a heart attack and other coronary artery disease-related problems.
Home Dhakuria Specialities Cardiology Emergency-percutaneous-coronary-intervention

You’re on Our Indian Website
Visit the Global site for International patient services











