-
Centre of
Excellence
Centre of Excellence
Other Specialities
- Allergy and Immunology
- Andrology
- Anesthesiology
- Dental Medicine
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- Ear Nose Throat
- Electrophysiology
- Fetal Medicine
- General Medicine
- General Surgery
- Geriatric Medicine
- GI Surgery
- Growth and Hormone
- Gynaec Oncology
- Hand Surgery
- Hemato Oncology
- Hematology
- Hepatobiliary Surgery
- ICU and Critical Care
- Infectious Disease
- Internal Medicine
- Interventional Radiology
- Kidney Transplant
- Lifestyle Clinic
- Medical Gastro
- Medical Oncology
- Microbiology
- Minimal Access Surgery
- Neonatology & NICU
- Nuclear Medicine
- Nutrition And Dietetics
- Ophthalmology
- Oral Maxillo Facial Surgery
- Paediatric Urology
- Pain Medicine
- Parkinson Disease and Movement Disorder
- Pathology
- Pharmacy
- Physiotherapy
- Plastic And Cosmetic Surgery
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology (Respiratory and Sleep Medicine)
- Radiology
- Radiotherapy (Oncology Radiation)
- Renal Sciences
- Surgical Gastro
- Surgical Oncology
- Transfusion Medicine
- Vascular and Endovascular Surgery
Speciality Clinics
- Doctors
- Dhakuria
- International Patients



Clinics








- Self Registration
- Mars - Ambulance
- Corporate & PSU
- Insurance Helpdesk
- Awards And Achievements
- Careers
- Contact Us
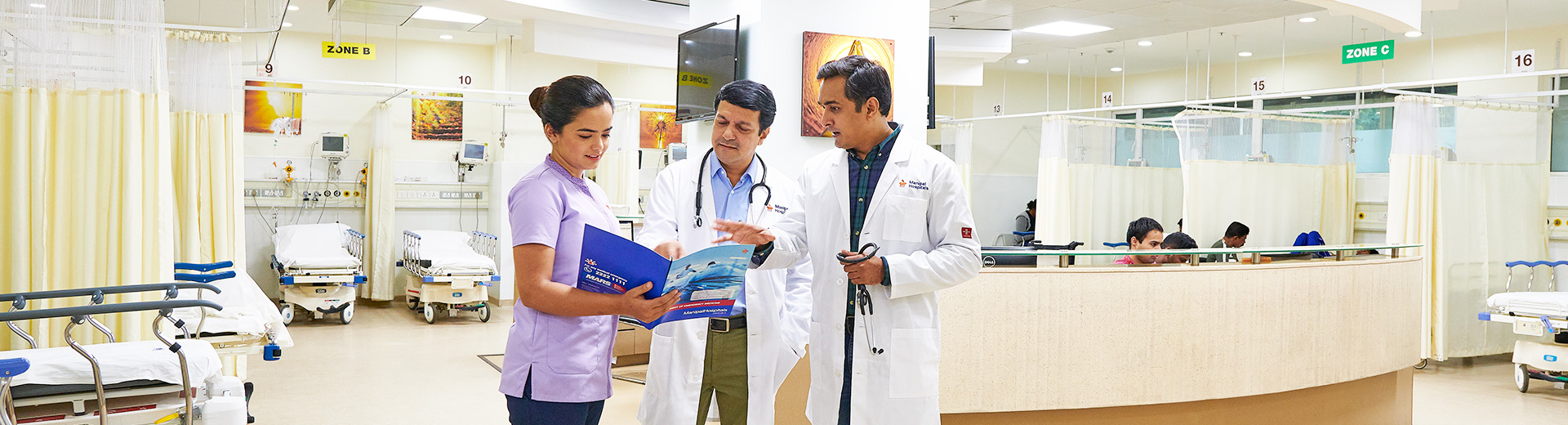

Advanced Diagnostics
Advanced Diagnostics in Dhakuria, West Bengal
Increasing outbreaks of infectious diseases such as COVID-19, flu, and H1N1 have boosted the demand for advanced diagnostic tests. Rapid testing methods, which are easily available, are in great demand. Recent innovations in diagnostic technologies have changed the landscape for diagnostic disease detection. Novel technologies like Mass Spectroscopy and Next-generation Sequencing offer rapid diagnostic and antimicrobial resistance detection methods.
Whether testing for an individual patient with an infectious disease or a global pandemic, determining the accurate case for the outbreak is vital to providing quality care. The availability of these advanced diagnostic tools for infectious diseases could mean a difference between life and death for patients.
The Infectious Diseases Department at Manipal Hospitals, Dhakuria, West Bengal, is equipped with the latest diagnostic tools, which give access to results on the same day rather than several days or weeks, empowering the patients with greater therapeutic potential. We provide the best Advanced Diagnostics in Dhakuria.
FAQ's
Infectious diseases are illnesses caused by pathogens (bacteria, viruses, fungi, and parasites) entering the body. Infectious diseases can spread through contaminated food, water, and bug bites. Many symptoms can be based on the organ affected, but generally include fever and fatigue.
The conventional testing methods for infectious diseases are:
-
Microscopic examination: The microorganisms can be directly visualised.
-
Antigen detection: The test involves identifying substances in microorganisms that trigger an immune response.
-
Antibody test: The test involves identifying antibodies produced by the immune system against the microorganisms. They help determine past or current infections and the person’s immune response.
-
Culture and sensitivity tests: The obtained samples are placed in an environment that is favourable for microbial growth.
-
Genetic testing: The DNA or RNA from the microorganism is separated and tested.
-
Blood testing: Indicators of infection can be identified with blood tests. The testing involves the measurement of white blood cell count (WBC), C-reactive protein (CRP), and erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR).
-
Imaging: If the infectious disease is affecting organs or deeper tissues, imaging techniques like X-rays, computed tomography, and magnetic resonance imaging may be employed to visualise the extent of damage.
These testing methods are still in use and are essential for determining the cause of infectious diseases. However, these have a longer turn-around time and are not an ideal testing method for emerging infectious diseases.
Advanced diagnostic tools for infectious diseases are:
-
Nucleic-acid Amplification: Analysing the sequence of the amplified microbial DNA or RNA enables the identification and characterisation of pathogens. For example, techniques like Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) help with rapid detection of fastidious organisms without the need for cultures.
-
Mass Spectrometry: This technique has been widely used for microbial identification as it produces rapid and accurate results.
-
Next-generation Sequencing: The testing method is a platform for sequencing millions of DNA and RNA molecules in parallel. This method allows for a rapid and accurate diagnosis of infectious diseases at a lower cost.
-
CRISPR-based diagnostics: These are the most cost-effective diagnostic methods for identifying infectious diseases caused by bacteria, viruses, fungi, or parasites.
-
Point-of-care diagnosis devices: These are portable testing devices that allow rapid testing of infectious diseases. Some of the point-of-care diagnostics are:
-
LIAT analyzer for HIV detection
-
Truelab Uno for malaria detection
-
GenePoC for influenza virus detection
These advanced methods offer a rapid and robust diagnosis.
Point-of-care testing (POC) is a form of medical testing performed with a patient outside of a laboratory or hospital setting. POC testing has several advantages, which include faster diagnosis, better sensitivity and specificity, lower cost, and the ability to detect on-site.
The sample is taken from a body part containing microorganisms that are suspected of causing infection. The usual samples taken are:
-
Blood
-
Urine
-
Sputum
-
Stool
-
Mucous
-
Cerebrospinal fluid
You must get an infectious disease test if you suspect being exposed to one. Even though you have no symptoms or mild symptoms, you will be able to spread the infection. Certain infectious infections, especially in those with impaired immune systems, can result in serious health problems or even death.
Doctors will take a detailed medical history and analyse your risks. If the suspect has an infectious disease, diagnostic tests will be prescribed. The doctors may ask you about your signs and symptoms to determine the most appropriate testing method.
Testing for infectious disease may be performed in a laboratory, clinic, or hospital setting. However, you must know that if the testing is carried out soon after the initial infection, the result will not be accurate and may have to be repeated after some time.
You will probably receive the test results on your phone. During the follow-up appointment, your doctor will discuss the test results, guide you through treatment, and help you manage the risks associated with infection.
If the test results are positive, you must begin the treatment immediately to reduce the risk of complications. At the end of the treatment, retesting for the presence of infection may be suggested.
Infectious disease testing can help prevent the spread of the disease in the following ways:
-
Early diagnosis: Infectious disease specialists can identify the infections at an early stage and administer adequate treatment.
-
Isolation: If the infectious disease is found to be highly contagious, appropriate measures are taken to prevent its spread.
-
Contact tracing: Infectious disease testing also helps health authorities trace the contacts of people who tested positive.
-
Outbreak investigation: In cases of cluster infections or outbreaks, testing is crucial for finding the source of the illness or its mode of transmission.
-
Vaccine development: Infectious disease testing plays an important role in the development or evaluation of vaccines.
-
Health education: Awareness can be created among the general public about employing suitable preventive measures against infectious diseases.
Home Dhakuria Specialities Infectious-disease Advanced-diagnostics

You’re on Our Indian Website
Visit the Global site for International patient services











