-
Centre of
Excellence
Centre of Excellence
Other Specialities
- Allergy and Immunology
- Andrology
- Anesthesiology
- Dental Medicine
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- Ear Nose Throat
- Electrophysiology
- Fetal Medicine
- General Medicine
- General Surgery
- Geriatric Medicine
- GI Surgery
- Growth and Hormone
- Gynaec Oncology
- Hand Surgery
- Hemato Oncology
- Hematology
- Hepatobiliary Surgery
- ICU and Critical Care
- Infectious Disease
- Internal Medicine
- Interventional Radiology
- Kidney Transplant
- Lifestyle Clinic
- Medical Gastro
- Medical Oncology
- Microbiology
- Minimal Access Surgery
- Neonatology & NICU
- Nuclear Medicine
- Nutrition And Dietetics
- Ophthalmology
- Oral Maxillo Facial Surgery
- Paediatric Urology
- Pain Medicine
- Parkinson Disease and Movement Disorder
- Pathology
- Pharmacy
- Physiotherapy
- Plastic And Cosmetic Surgery
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology (Respiratory and Sleep Medicine)
- Radiology
- Radiotherapy (Oncology Radiation)
- Renal Sciences
- Surgical Gastro
- Surgical Oncology
- Transfusion Medicine
- Vascular and Endovascular Surgery
Speciality Clinics
- Doctors
- Dhakuria
- International Patients



Clinics








- Self Registration
- Mars - Ambulance
- Corporate & PSU
- Insurance Helpdesk
- Awards And Achievements
- Careers
- Contact Us
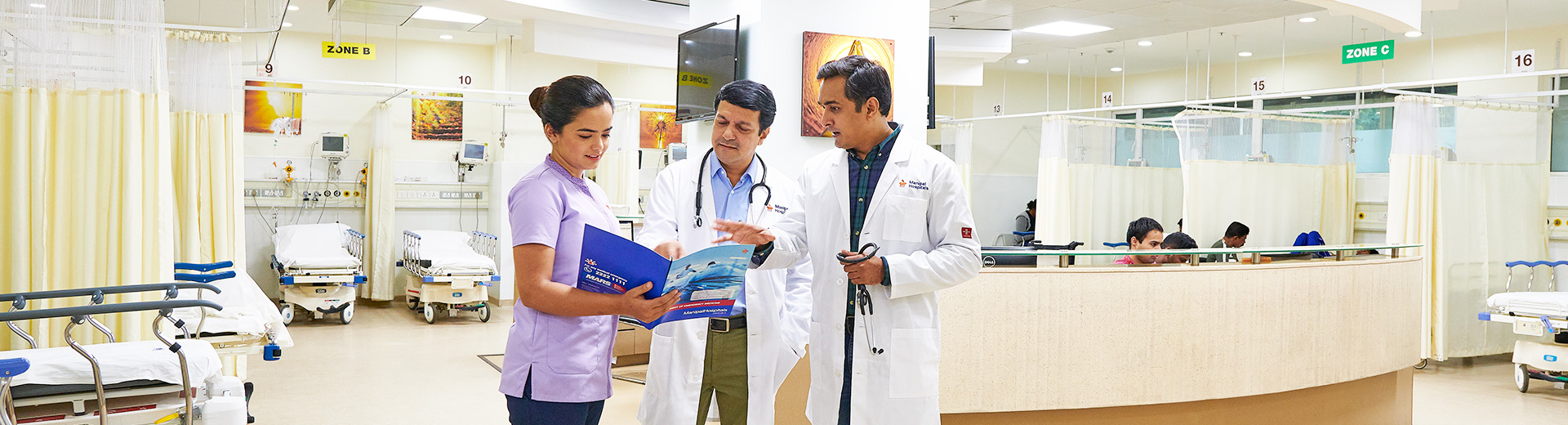

Family Planning
Family Planning in Dhakuria, West Bengal
According to the World Health Organisation (WHO), family planning involves empowering individuals and couples to anticipate and realise their desired family size and regulate the spacing and timing of their pregnancies. This is achieved through the use of various contraceptive methods and addressing issues related to involuntary infertility. Family planning serves crucial purposes: firstly, it enables couples to prevent unintended pregnancies; secondly, it plays a pivotal role in curbing the transmission of sexually transmitted diseases (STDs); and thirdly, by addressing STDs, it helps mitigate the incidence of infertility.
The capacity for individuals to determine the size of their families and the timing and spacing of their children has resulted in significant improvements in health, social, and economic well-being. Decreased family sizes and improved intervals between childbirths have contributed to reductions in infant and child mortality rates, improved the socio-economic circumstances of women and their families, and elevated maternal healthcare standards.
Manipal Hospitals, one of the best Family Planning hospitals in Dhakuria is contributing by offering complete family planning services, including education, counselling, and access to various contraceptive methods. These services empower people to make decisions about the size and health of their family and reproductive system.
FAQ's
Unmet need for family planning refers to the proportion of sexually active women aged 15 to 49 who desire to postpone or avoid pregnancy but are not utilising contraception. This need is particularly pronounced among adolescents and women following a recent pregnancy, as well as in urban, migrant, and refugee communities. In 2019, out of the 923 million women in low- and middle-income nations wishing to prevent pregnancy, 218 million did not have access to modern contraception, highlighting the significance of addressing this gap.
You can conceive during ovulation, which typically occurs around the middle of your menstrual cycle. Following ovulation, an egg can remain viable in the fallopian tube for about 12 to 24 hours, while sperm from a man can survive inside a woman's body for up to 3 to 5 days following intercourse. This means that conception can happen if you engage in sexual activity anywhere from about 5 days before ovulation to 1 day after ovulation. The likelihood of conception is highest when live sperm are present in the fallopian tubes during ovulation.
There are several contraceptive methods available, such as:
-
Birth control pills: These include hormones that stop ovulation and are used daily.
-
Implants for contraception: Tiny rods placed beneath the skin that deliver hormones to stop ovulation for some years.
-
Contraceptive patches: These are applied topically and function by secreting hormones that stop ovulation.
-
Vaginal rings: These are placed within the vagina and kept there for several weeks in order to release hormones and stop ovulation.
-
Male and female condoms are available, and they act as a barrier to prevent sperm from reaching the egg.
-
IUDs, or intrauterine devices, are tiny, T-shaped devices that are inserted within the uterus to prevent conception. They can last for several years and be either non-hormonal or hormonal.
-
Hormonal injections given every few months to stop ovulation are known as contraceptive injections.
Family planning is for all people, regardless of gender, who are capable of becoming parents. To avoid unplanned births, both men and women can actively engage in family planning decisions and assume responsibility for contraception. Open communication and decision-making regarding the optimal kind of contraception for each partner's needs and objectives are crucial. Couples can successfully prepare for their future reproductive endeavours and assure mutual understanding and support by cooperating.
There is a chance that using some contraception can have negative effects, including mood swings, headaches, nausea, or changes in menstrual bleeding. It is crucial to remember that the frequency and intensity of these adverse effects can differ greatly across individuals and depend on the particular kind of contraception that is being taken. Thus, it's essential to have an honest conversation with a healthcare professional to address any worries or enquiries about possible side effects and, if needed, look into other possibilities.
Depending on the technique and how consistently and effectively it is used, contraception can have varying effects. When used properly, certain techniques—such as IUDs and birth control pills—can be quite successful; nevertheless, other methods, like condoms, may have greater failure rates if they are not worn regularly or if they break or fall off.
Family planning offers numerous advantages, both for individuals and society as a whole:
-
Control over reproductive health: It gives the ability to plan pregnancies following their objectives and personal circumstances, enabling them to make educated decisions about when to start a family.
-
Better health outcomes: Spacing out pregnancies and making plans for them may maximise the health of both the mother and the child.
-
Enhanced economic stability: Planning a pregnancy can help families better manage their money by ensuring that a family is both emotionally and financially ready to have a child.
-
Preventing sexually transmitted infections: Certain contraceptive techniques, like condoms, give protection against STIs in addition to preventing pregnancy, which promotes sexual health and lowers the spread of STIs.
-
Environmental sustainability: Family planning helps relieve demand for natural resources, lessen environmental deterioration, and promote sustainability by regulating population growth.
-
Reduction of maternal mortality and morbidity: Family planning helps women postpone having children until they are emotionally and physically prepared, which lowers the chance of difficulties during pregnancy and delivery.
The optimal time between pregnancies can vary based on several variables, such as the mother's health, the health of the prior child, and individual conditions. To give the next baby the best chance of being healthy and the mother's body time to recover, doctors often advise waiting at least 18 to 24 months between pregnancies. This time helps the mother and the unborn child heal from childbirth, restore vital nutrients, and lower the chance of problems.
Home Dhakuria Specialities Obstetrics-and-gynaecology Family-planning

You’re on Our Indian Website
Visit the Global site for International patient services











