-
Centre of
Excellence
Centre of Excellence
Other Specialities
- Allergy and Immunology
- Andrology
- Anesthesiology
- Dental Medicine
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- Ear Nose Throat
- Electrophysiology
- Fetal Medicine
- General Medicine
- General Surgery
- Geriatric Medicine
- GI Surgery
- Growth and Hormone
- Gynaec Oncology
- Hand Surgery
- Hemato Oncology
- Hematology
- Hepatobiliary Surgery
- ICU and Critical Care
- Infectious Disease
- Internal Medicine
- Interventional Radiology
- Kidney Transplant
- Lifestyle Clinic
- Medical Gastro
- Medical Oncology
- Microbiology
- Minimal Access Surgery
- Neonatology & NICU
- Nuclear Medicine
- Nutrition And Dietetics
- Ophthalmology
- Oral Maxillo Facial Surgery
- Paediatric Urology
- Pain Medicine
- Parkinson Disease and Movement Disorder
- Pathology
- Pharmacy
- Physiotherapy
- Plastic And Cosmetic Surgery
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology (Respiratory and Sleep Medicine)
- Radiology
- Radiotherapy (Oncology Radiation)
- Renal Sciences
- Surgical Gastro
- Surgical Oncology
- Transfusion Medicine
- Vascular and Endovascular Surgery
Speciality Clinics
- Doctors
- Dhakuria
-

Bengaluru

-
-

Bhubaneswar

-

Bhubaneswar
-
-

Delhi - NCR

-

Goa

-

Goa
-
-

Jaipur
-

Kolkata

-

Mangaluru
-

Mysuru
-

Patiala
-

Pune

-

Ranchi
-

Salem
-

Siliguri City

-

Vijayawada
- International Patients



Clinics







- Self Registration
- Mars - Ambulance
- Corporate & PSU
- Insurance Helpdesk
- Awards And Achievements
- Careers
- Contact Us
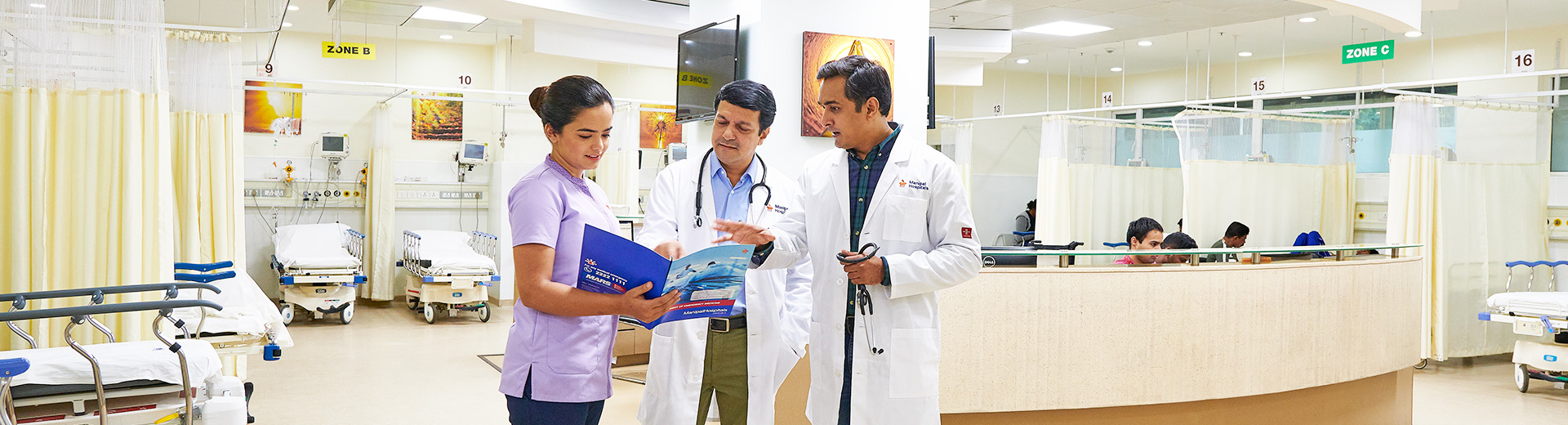

Cleft Lip and Palate Repair
Cleft Lip and Palate Repair Surgery treatment in Dhakuria
A cleft lip or cleft palate refers to a condition in which there are openings in a baby's upper lip or palate. These are referred to as birth defects or congenital anomalies that arise during the uterine development of a foetus. When the tissues of the upper lip and roof of the mouth don't fuse appropriately or there is some disturbance in fusion during foetal development, it can result in cleft palates and lips. Surgery is a common method for addressing these congenital abnormalities. Usually, the Cleft Lip and Palate Repair procedure is carried out during the first year of life. Cleft Lip Repair happens between three and six months of age, while Cleft Palate Repair happens between nine and eighteen months. To regain functionality and appearance, it is necessary to close the gap in the lip or palate during the treatment. Children may need speech therapy following surgery and further procedures as they get older. The objective is to enhance speaking, feeding, and general facial aesthetics. Manipal Hospitals, Dhakuria, has an experienced team skilled in performing Cleft Lip and Palate Repair Surgeries with precision, enhancing your child’s quality of life.
FAQ's
During the first 6 to 10 weeks of pregnancy, the bones and tissues of the upper jaw, nose, and mouth of a developing baby fuse to form the roof of the mouth and the upper lip. When portions of the lip and/or palate do not fully fuse, clefts result.
The cause of a baby's cleft is not usually known to medical professionals, while some cases may be linked to hereditary (inherited) causes. Additionally, a few environmental factors, such as the following, can increase the chance of a birth defect:
-
Using specific medications (like certain anti-seizure medications) while pregnant
-
Lacking adequate prenatal nutrition, specifically folate
-
Pregnant women being in contact with certain chemicals
-
Engaging in cigarette smoking, drug consumption, and/or alcohol consumption while pregnant
-
Cleft Lip Repair Surgery typically occurs within the first 2-3 months after birth, ideally around 10 weeks old
-
Surgeons often follow the "rule of 10s": the child is at least 10 weeks old, weighs at least 10 pounds, and has at least 10 g/dL haemoglobin
-
For bilateral and extensive clefts, two surgeries may be necessary, with each side repaired separately
-
Ralph Millard's innovative technique, known as the Millard procedure, is widely used for cleft lip repair.
-
Incomplete cleft lips often require the same surgery as complete clefts to restore muscle function and minimise scarring
-
Surgeons aim to align scars with natural lip lines and tuck stitches up the nose for a more natural appearance
There are various surgical techniques employed to repair the cleft lip
Millard Method (Advanced Rotation):
-
This procedure requires shifting the outer edge of the lip forward and tilting the inner edge downward to readjust the base of the nostril and regain the lip's vertical length.
-
Preserves structural characteristics such as the philtral ridge and Cupid's bow shape.
-
Prioritising individualised procedures based on markers' instructions is a key aspect of modern cleft lip repairs, which are continuously progressing.
The Tennison-Randall Method:
-
The Z-plasty technique is used to lengthen and straighten the red border
-
Usually employed for secondary cleft lip revisions or surgeries
-
Enhances symmetry and visual results
-
It can be used in conjunction with additional methods to provide thorough repair
The Mohler Method
-
This is to maintain the lip's natural symmetry and contour
-
Makes use of geometric concepts to decide where to make an incision
-
Emphasises the least amount of tissue disturbance possible
-
Aims for the best possible practical and aesthetic outcomes
Palatoplasty is a surgical procedure carried out to repair a cleft palate during infancy, as follows:
Timing: Typically, this is carried out when a child is between 9 and 18 months old.
Uses:
-
The Wardill-Veau-Kilner V-Y Pushback technique is commonly used for repairing soft palates.
-
The Furlow Double-Opposing Z-Plasty technique is a popular choice for restoring hard palates.
Goals:
-
Close the gap to facilitate adequate eating and talking
-
Reduce fluid accumulation to enhance middle ear function
-
Enhance dental positioning and facial aesthetics
Post-operative care:
-
Monitor for any adverse reactions, such as infection or fistula development.
-
To achieve optimal outcomes, it is important to undergo Speech Therapy and receive interdisciplinary follow-up.
Your doctor may recommend additional strategies or techniques to handle the complications arising from the treatments, which include:
-
Feeding techniques utilise feeders or bottle nipples
-
Speech Therapy to address difficulties with speaking
-
Orthodontic corrections, such as aligning teeth using braces
-
Consistent dental health monitoring by a paediatric dentist
-
Ear infection treatment, including the insertion of an ear tube
-
Assistance for hearing loss, such as hearing aids or other equipment
-
Psychological counselling to address psychological problems and stress
Compared to Cleft Lip Surgery, this procedure is typically more complex and may result in greater discomfort and pain for the child. The physician responsible for your child's care may recommend pain relief medication to help with this issue. Your child may have difficulty eating and drinking as usual due to the discomfort and positioning of the procedure.
Depending on the procedure, your child's doctor might approve cup, bottle, or nursing feedings. Following surgery, your child should be on a soft diet for seven to ten days. Age-appropriate soft meals for older babies and kids can include strained baby food, popsicles, yoghurt, mashed potatoes, and gelatin. It is important to remember that your child should avoid using a pacifier or straw, as it could potentially damage the surgical site.
Home Dhakuria Specialities Oral-maxillo-facial-surgery Cleft-lip-and-palate-repair

You’re on Our Indian Website
Visit the Global site for International patient services
Your Feedback is Highly Valued!







