-
Centre of
Excellence
Centre of Excellence
Other Specialities
- Allergy and Immunology
- Andrology
- Anesthesiology
- Dental Medicine
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- Ear Nose Throat
- Electrophysiology
- Fetal Medicine
- General Medicine
- General Surgery
- Geriatric Medicine
- GI Surgery
- Growth and Hormone
- Gynaec Oncology
- Hand Surgery
- Hemato Oncology
- Hematology
- Hepatobiliary Surgery
- ICU and Critical Care
- Infectious Disease
- Internal Medicine
- Interventional Radiology
- Kidney Transplant
- Lifestyle Clinic
- Medical Gastro
- Medical Oncology
- Microbiology
- Minimal Access Surgery
- Neonatology & NICU
- Nuclear Medicine
- Nutrition And Dietetics
- Ophthalmology
- Oral Maxillo Facial Surgery
- Paediatric Urology
- Pain Medicine
- Parkinson Disease and Movement Disorder
- Pathology
- Pharmacy
- Physiotherapy
- Plastic And Cosmetic Surgery
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology (Respiratory and Sleep Medicine)
- Radiology
- Radiotherapy (Oncology Radiation)
- Renal Sciences
- Surgical Gastro
- Surgical Oncology
- Transfusion Medicine
- Vascular and Endovascular Surgery
Speciality Clinics
- Doctors
- Dhakuria
- International Patients



Clinics








- Self Registration
- Mars - Ambulance
- Corporate & PSU
- Insurance Helpdesk
- Awards And Achievements
- Careers
- Contact Us


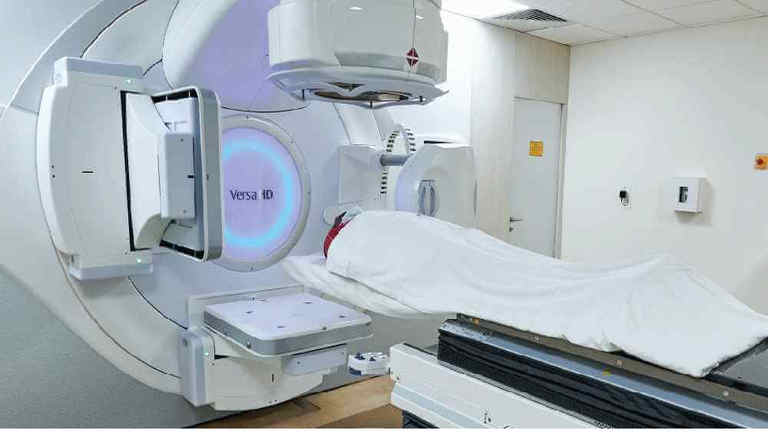
Radiology
Best Radiology/X-ray Hospital in Dhakuria
Radiology is a cornerstone of modern medical diagnostics, enabling accurate detection and management of various health conditions. At Manipal Hospitals, Dhakuria, our radiology department is equipped with advanced imaging technology to deliver precise, efficient, and reliable diagnostic solutions. We offer a comprehensive range of services, including MRI scans, CT scans, X-rays, ultrasounds, and more, tailored to meet the diverse healthcare needs of our patients.

OUR STORY
Know About Us
Why Manipal?
At Manipal Hospitals, we redefine the radiology experience by offering cutting-edge imaging services, quick results, and exceptional patient care for Kolkata. Our advanced technology, combined with a team of expert radiologists, ensures the most accurate and reliable diagnostics for a wide range of medical conditions. We provide MRI scans, CT scans, X-rays, ultrasounds, and more, with a commitment to patient comfort, safety, and convenience. Our focus on same-day reporting, flexible appointments, and compassionate care sets us apart, making Manipal Hospitals a trusted leader in radiology in Dhakuria.
Treatment & Procedures
CT Scans
CT scans, or Computed Tomography scans, are a powerful imaging tool that combines X-ray technology with advanced computer processing to generate detailed cross-sectional images of the body.
MRI Scans
MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging) is a highly advanced imaging technique that uses powerful magnets, radio waves, and computer technology to create detailed images of the body’s internal structures. Unlike X-rays or CT scans, MRI does not use radiation, making it a safe and effective option for diagnosing a wide range of conditions involving soft tissues,…
X-Rays
X-rays are one of the most commonly used diagnostic tools in medicine, providing quick and detailed images of the inside of the body. They are especially effective for visualizing bones, joints, and certain soft tissues, helping to identify fractures, infections, tumours, or lung conditions like pneumonia. X-rays use a controlled amount of radiation…
Fluoroscopy Procedures
Fluoroscopy is an advanced imaging technique that provides real-time, moving images of the inside of the body using X-rays. It allows doctors to observe the motion of organs and the flow of fluids in the body, making it particularly useful for diagnosing and guiding various medical procedures. Unlike traditional X-rays, which provide static images,…
Ultrasound and Doppler
Ultrasound is a non-invasive, safe imaging technique that uses sound waves to create real-time images of soft tissues, organs, and blood vessels, with no radiation exposure. It’s commonly used for monitoring pregnancies, diagnosing abdominal or pelvic conditions, and assessing organ health. Doppler ultrasound, a specialized form of ultrasound, helps…
Interventional Radiology
Interventional radiology is a specialized branch of radiology that uses minimally invasive techniques to diagnose and treat various medical conditions, often as an alternative to traditional surgery. By guiding instruments such as catheters, needles, and wires through the body using imaging technologies like CT scans and X-rays, interventional radiologists…
DEXA Scans
DEXA (Dual-Energy X-ray Absorptiometry) scans are a non-invasive, highly accurate method for measuring bone mineral density (BMD). This simple procedure uses low-dose X-rays to assess bone strength and detect conditions like osteoporosis, a disease that weakens bones and increases the risk of fractures. By focusing on areas such as the spine, hips,…
Radiotherapy Planning CT/MRI
Radiotherapy planning is a crucial step in the treatment of cancer, ensuring that radiation is delivered precisely to the tumor while minimizing damage to surrounding healthy tissues. Radiotherapy Planning CT/MRI combines advanced CT or MRI imaging techniques to create detailed 3D maps of the tumor and nearby structures. These images are used to develop…
MR Urography
MR Urography is a specialized MRI technique used to visualize the urinary tract, including the kidneys, ureters, and bladder. This non-invasive procedure helps in the evaluation of various conditions such as kidney stones, urinary tract tumors, structural abnormalities, or blockages. By providing detailed images, MR Urography allows for a comprehensive…

The Radiology Department at Manipal Hospitals Dhakuria is committed to delivering high-precision diagnostic imaging with the latest advancements in medical technology. Our expert team of radiologists and highly trained technicians utilise state-of-the-art equipment to provide accurate and timely diagnoses, helping patients receive the best possible treatment. Our department is equipped with cutting-edge imaging technology, including 3T MRI, 128-slice Multidetector CT, Digital X-ray, Orthopantomogram (OPG), and Bone Mineral Densitometry (DEXA) machines. These advanced diagnostic tools allow us to perform high-resolution imaging with minimal radiation exposure, ensuring safer and more effective diagnosis.
We cater to patients of all age groups, including infants, elderly patients, ambulatory patients, and inpatients, ensuring comprehensive imaging services tailored to individual needs. Whether for routine screenings, emergency evaluations, or specialised imaging for complex conditions, our department offers precise diagnostic solutions with a patient-centric approach. At Manipal Hospitals Dhakuria, we continuously strive for excellence in radiology through ongoing research and technological advancements. By integrating innovation with clinical expertise, we not only provide advanced technology imaging services but also contribute to the future of medical diagnostics, enhancing patient outcomes and healthcare efficiency.
Facilities & Services
At Manipal Hospitals Dhakuria, we offer a wide range of advanced radiology services to meet diverse diagnostic needs:
1. CT Scans
-
CT Brain: For neurological conditions like strokes or brain injuries.
-
CT Angiography: Imaging of blood vessels in the neck, thorax, and renal arteries.
-
CT Pulmonary Angio: Detailed evaluation of pulmonary embolism and lung conditions.
-
CT Abdomen: For diagnosing abdominal issues like infections or tumours.
-
CT Triphase Liver: For a detailed assessment of liver lesions and diseases.
-
CT Spine (Cervical, Dorsal, Lumbar): For spinal injuries and disc-related problems.
-
High-Resolution CT Thorax: For detecting lung infections and interstitial lung diseases.
-
CT Bronchial Angio: Specialized imaging for bronchial artery conditions.
-
CT-Guided Biopsy/Drainage: Interventional procedure for tissue sampling or fluid removal.
2. MRI Scans
-
MRI Brain: For detecting strokes, tumours, or neurological disorders.
-
MRI Spine (Cervical, Dorsal, Lumbar): For spinal injuries and nerve-related issues.
-
Whole Body MRI: For cancer staging and oncological workups.
-
MRCP: Imaging of bile ducts and pancreas for diagnosing blockages or inflammation.
-
MRI Breast: For identifying breast tumours or abnormalities.
-
MRI Joints (Knee, Shoulder, Wrist, etc.): For soft tissue and joint assessments.
-
Cardiac MRI: For detailed imaging of the heart.
-
Multiparametric Prostate MRI: For accurate prostate cancer diagnosis.
-
MRI Angiography: For assessing blood vessels in the neck, renal arteries, and thorax.
3. Ultrasound and Doppler
-
Ultrasound Abdomen/Pelvis: For evaluating internal organs like the liver and kidneys.
-
Obstetric Ultrasound: Monitoring early pregnancy and fetal growth.
-
Doppler Studies: Blood flow assessments for arteries, veins, and renal arteries.
-
Liver Elastography: For diagnosing liver fibrosis or cirrhosis.
-
Transvaginal/Transrectal Ultrasound: For detailed pelvic imaging.
4. X-Rays
-
X-ray chest: For diagnosing lung conditions like pneumonia or TB.
-
X-Ray Spine and Joints: For injuries, fractures, or degenerative changes.
-
Fluoroscopic X-rays: Dynamic imaging for procedures like Barium Meal, HSG, and MCU.
5. Interventional Radiology
-
CT-Guided Biopsies and Drainage: For minimally invasive tissue sampling or fluid removal.
-
Percutaneous Nephrostomy: For kidney drainage.
-
Biliary Stenting: For managing bile duct blockages.
-
Bronchial Artery Embolization: To control bleeding in the lungs.
-
Radiofrequency Ablation: For destroying cancerous or abnormal tissue.
6. DEXA Scans
-
Bone Density Scans: For detecting osteoporosis and measuring bone strength in the hips and spine.
-
Whole-Body DEXA Scans: Comprehensive evaluation of bone health.
7. Fluoroscopy Procedures
-
Barium Swallow and Enema: For diagnosing gastrointestinal conditions.
-
HSG (Hysterosalpingography): For assessing fallopian tubes and uterine abnormalities.
-
MCU (Micturating Cystourethrogram): For urinary bladder and urethra evaluation.
-
Sinograms: For tracking abnormal tracts or fistulas.
8. Specialized Radiology Services
-
Radiotherapy Planning CT/MRI: For precise cancer treatment planning.
-
MR Urography: For detailed imaging of the urinary tract to detect abnormalities or blockages.
FAQ's
Patients visit the Radiology department at Manipal Hospitals Dhakuria for expert diagnosis, advanced treatment, and personalized care. The department specializes in managing CT Scans, MRI Scans, X-Rays, Fluoroscopy Procedures, Ultrasound and Doppler, Interventional Radiology, DEXA Scans, Radiotherapy Planning CT/MRI, MR Urography, ensuring world-class medical support for patients.
The Radiology department at Manipal Hospitals Dhakuria provides a wide range of treatments, including:
- CT Scans
- MRI Scans
- X-Rays
- Fluoroscopy Procedures
- Ultrasound and Doppler
To book an appointment with a Radiology expert at Manipal Hospitals Dhakuria, please call 033 6907 0001. Our dedicated team will assist you in scheduling a convenient consultation.
The Radiology department is led by highly qualified specialists, including:
For your initial consultation at Manipal Hospitals Dhakuria, please bring:
- Medical Records – Previous reports, imaging scans, and lab results.
- Medication List – Details of current and past prescriptions.
- Insurance Details – Health insurance card and referral documents (if applicable).
- Personal ID Proof – For registration purposes.
Providing these documents will help our specialists ensure a comprehensive diagnosis and personalized treatment plan.
Manipal Hospitals Dhakuria is a preferred choice for Radiology due to:
- Highly experienced specialists.
- State-of-the-art medical infrastructure.
- Comprehensive treatment plans with a multidisciplinary approach.
- Advanced diagnostic & surgical facilities.
- Patient-centric care with personalized treatment options.
We are committed to providing world-class healthcare with compassionate service.
At Manipal Hospitals Dhakuria, we offer facilities such as:
At Manipal Hospitals Dhakuria, we offer a wide range of advanced radiology services to meet diverse diagnostic needs:
1. CT Scans
-
CT Brain: For neurological conditions like strokes or brain injuries.
-
CT Angiography: Imaging of blood vessels in the neck, thorax, and renal arteries.
-
CT Pulmonary Angio: Detailed evaluation of pulmonary embolism and lung conditions.
-
CT Abdomen: For diagnosing abdominal issues like infections or tumours.
-
CT Triphase Liver: For a detailed assessment of liver lesions and diseases.
-
CT Spine (Cervical, Dorsal, Lumbar): For spinal injuries and disc-related problems.
-
High-Resolution CT Thorax: For detecting lung infections and interstitial lung diseases.
-
CT Bronchial Angio: Specialized imaging for bronchial artery conditions.
-
CT-Guided Biopsy/Drainage: Interventional procedure for tissue sampling or fluid removal.
2. MRI Scans
-
MRI Brain: For detecting strokes, tumours, or neurological disorders.
-
MRI Spine (Cervical, Dorsal, Lumbar): For spinal injuries and nerve-related issues.
-
Whole Body MRI: For cancer staging and oncological workups.
-
MRCP: Imaging of bile ducts and pancreas for diagnosing blockages or inflammation.
-
MRI Breast: For identifying breast tumours or abnormalities.
-
MRI Joints (Knee, Shoulder, Wrist, etc.): For soft tissue and joint assessments.
-
Cardiac MRI: For detailed imaging of the heart.
-
Multiparametric Prostate MRI: For accurate prostate cancer diagnosis.
-
MRI Angiography: For assessing blood vessels in the neck, renal arteries, and thorax.
3. Ultrasound and Doppler
-
Ultrasound Abdomen/Pelvis: For evaluating internal organs like the liver and kidneys.
-
Obstetric Ultrasound: Monitoring early pregnancy and fetal growth.
-
Doppler Studies: Blood flow assessments for arteries, veins, and renal arteries.
-
Liver Elastography: For diagnosing liver fibrosis or cirrhosis.
-
Transvaginal/Transrectal Ultrasound: For detailed pelvic imaging.
4. X-Rays
-
X-ray chest: For diagnosing lung conditions like pneumonia or TB.
-
X-Ray Spine and Joints: For injuries, fractures, or degenerative changes.
-
Fluoroscopic X-rays: Dynamic imaging for procedures like Barium Meal, HSG, and MCU.
5. Interventional Radiology
-
CT-Guided Biopsies and Drainage: For minimally invasive tissue sampling or fluid removal.
-
Percutaneous Nephrostomy: For kidney drainage.
-
Biliary Stenting: For managing bile duct blockages.
-
Bronchial Artery Embolization: To control bleeding in the lungs.
-
Radiofrequency Ablation: For destroying cancerous or abnormal tissue.
6. DEXA Scans
-
Bone Density Scans: For detecting osteoporosis and measuring bone strength in the hips and spine.
-
Whole-Body DEXA Scans: Comprehensive evaluation of bone health.
7. Fluoroscopy Procedures
-
Barium Swallow and Enema: For diagnosing gastrointestinal conditions.
-
HSG (Hysterosalpingography): For assessing fallopian tubes and uterine abnormalities.
-
MCU (Micturating Cystourethrogram): For urinary bladder and urethra evaluation.
-
Sinograms: For tracking abnormal tracts or fistulas.
8. Specialized Radiology Services
-
Radiotherapy Planning CT/MRI: For precise cancer treatment planning.
-
MR Urography: For detailed imaging of the urinary tract to detect abnormalities or blockages.
Our team ensures precise diagnosis and treatment planning for each patient.
At Manipal Hospitals, we redefine the radiology experience by offering cutting-edge imaging services, quick results, and exceptional patient care for Kolkata. Our advanced technology, combined with a team of expert radiologists, ensures the most accurate and reliable diagnostics for a wide range of medical conditions. We provide MRI scans, CT scans, X-rays, ultrasounds, and more, with a commitment to patient comfort, safety, and convenience. Our focus on same-day reporting, flexible appointments, and compassionate care sets us apart, making Manipal Hospitals a trusted leader in radiology in Dhakuria.
Radiology uses imaging techniques to diagnose and treat diseases, helping doctors visualize the inside of the body and detect conditions like fractures, tumours, and infections.
We offer X-rays, CT scans, MRI, Ultrasound, Mammography, and Fluoroscopy for diagnosing and monitoring various conditions.
Scheduling an appointment is easy. You can call our dedicated radiology department at 033 6907 0000 or use our online appointment booking system on the website. Our staff will assist you in finding a convenient time for your procedure.
A DEXA scan measures bone density and is commonly used to diagnose osteoporosis. It is recommended for postmenopausal women, men over 70, individuals with a history of fractures, or those on specific medications that affect bone health.
X-ray is a basic imaging technique that uses radiation to create images of bones and some tissues, whereas a CT scan (or computed tomography) provides detailed cross-sectional images of bones, organs, and tissues, offering more comprehensive information about internal structures.
Yes, radiology is safe. We use low levels of radiation in procedures like X-rays and CT scans, ensuring minimal exposure.
You will lie still while the machine takes images. MRI is slightly noisy, and CT scans are quick and painless.
-
X-rays: A few minutes.
-
CT scans: 10-20 minutes.
-
MRI: 20-45 minutes.
-
Ultrasounds: 20-30 minutes.
Preparation varies. For some tests like CT scans or MRI, you may need to fast or follow specific instructions.
Results are typically available within 24-48 hours, and your doctor will discuss the findings with you.
The frequency depends on your health condition and doctor’s recommendations. Some tests may be part of routine screenings, while others are needed for diagnosis or monitoring.
Yes, we offer 24/7 radiology services for emergency cases, helping diagnose conditions quickly in urgent situations.
At Manipal Hospitals Dhakuria, we’re not just about advanced radiology – we’re about providing you with precise, personalized care that makes a difference. Our expert radiologists are here to ensure you get the most accurate results, supporting you every step of the way. Ready for clearer insights into your health? Reach out now to learn more about our radiology services in Kolkata and book your appointment today!
Manipal Hospitals Dhakuria is dedicated to providing high-quality, personalised care and building long-term partnerships with its patients. Our Radiology department and its patients are a testament to this. Contact us to know more about radiological testing and book an appointment with one of our radiologists today.
Explore Stories
Home Dhakuria Specialities Radiology

You’re on Our Indian Website
Visit the Global site for International patient services