
Prostate surgery is a critical medical procedure aimed at addressing various conditions affecting the prostate gland, a small walnut-shaped gland in men that produces seminal fluid. This blog will explore the different types of prostate surgeries, their purposes, prostate removal surgery, and prostate surgery recovery time, providing a comprehensive understanding of how these surgeries help treat prostate conditions.
Synopsis
Understanding Prostate Conditions
The prostate gland can be affected by several conditions, including:
-
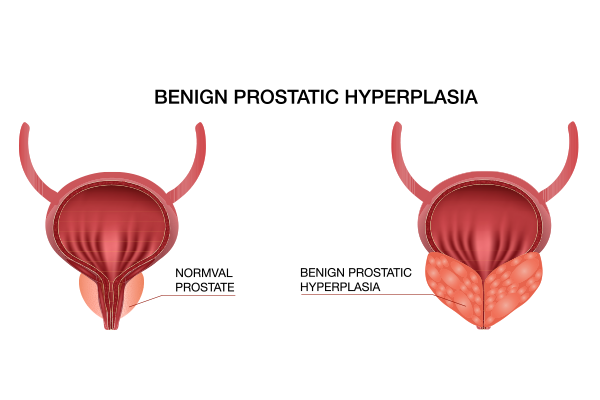
Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH): This is a non-cancerous enlargement of the prostate gland, common in older men. It can cause urinary problems such as difficulty starting urination, a weak urine stream, and frequent urination, especially at night.
-
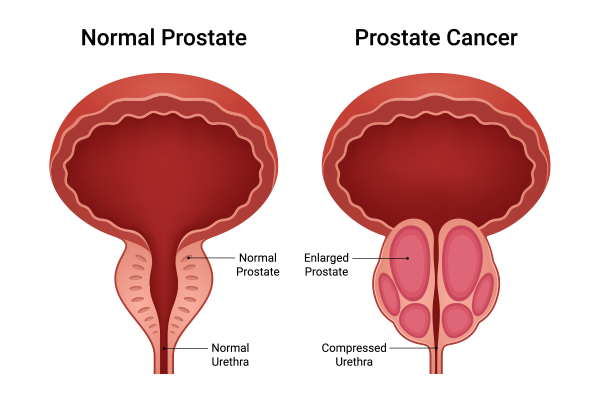
Prostate Cancer: One of the most common cancers in men, prostate cancer can range from slow-growing tumors that may not require immediate treatment to aggressive forms that need prompt intervention.
-
Prostatitis: This is an inflammation of the prostate gland, which can be either bacterial or non-bacterial. It can cause pain, urinary issues, and sexual dysfunction.
Types of Prostate Surgeries
Several surgical options are available to treat prostate conditions, each tailored to the specific condition and its severity.
Transurethral Resection of the Prostate (TURP):
-
Purpose: TURP is primarily used to treat BPH.
-
Procedure: During TURP, a resectoscope is inserted through the urethra to remove parts of the enlarged prostate that are obstructing urine flow.
-
Recovery: Patients typically stay in the hospital for one to two days. Full recovery can take a few weeks, during which patients may experience some urinary discomfort.
Prostatectomy:
- Purpose: This surgery is often performed to treat prostate cancer.
- Types:
-
Radical Prostatectomy: Removal of the entire prostate gland and some surrounding tissue.
-
Laparoscopic Prostatectomy: A minimally invasive procedure using small incisions and a camera to guide the surgery.
-
Robotic-Assisted Laparoscopic Prostatectomy: A more advanced form of laparoscopic surgery using robotic arms for greater precision.
- Recovery: Hospital stays can range from one to three days. Recovery involves managing pain, catheter care, and gradually resuming normal activities over several weeks.
Transurethral Incision of the Prostate (TUIP):
-
Purpose: TUIP is used to treat mild to moderate BPH.
-
Procedure: Small cuts are made in the prostate to relieve pressure on the urethra and improve urine flow.
-
Recovery: This procedure often requires a shorter hospital stay and recovery period compared to TURP.
Laser Surgery:
-
Purpose: Laser surgeries, such as Holmium Laser Enucleation of the Prostate (HoLEP) and Photoselective Vaporization of the Prostate (PVP), are used to treat BPH.
-
Procedure: A laser is used to remove or vaporize excess prostate tissue.
-
Recovery: These minimally invasive procedures typically result in less bleeding and quicker recovery times.
Here's a comparative analysis of different types of prostate surgeries, highlighting their pros and cons:
| Type of Surgery | Pros | Cons |
| Robotic-Assisted Surgery |
|
|
| Transurethral Resection of the Prostate (TURP) |
|
|
| Holmium Laser Enucleation of the Prostate (HoLEP) |
|
|
| Optilume BPH Catheter System |
|
|
| High-Intensity Focused Ultrasound (HIFU) |
|
|
| Immunotherapy |
|
|
| Proton Therapy |
|
|
Preparing for Prostate Surgery
Preparation for prostate surgery involves several steps to ensure the patient's safety and the procedure's success:
-
Medical Evaluation: A thorough medical evaluation, including blood tests, imaging studies, and sometimes a biopsy, is conducted to assess the patient's overall health and the extent of the prostate condition.
-
Preoperative Instructions: Patients are given specific instructions regarding diet, medications, and activities to follow before surgery. This may include fasting and stopping certain medications.
-
Informed Consent: The surgeon will explain the procedure, potential risks, and benefits, and obtain the patient's informed consent.
The Surgical Experience
On the day of surgery, patients can expect the following:
-
Anesthesia: Depending on the type of surgery, general or spinal anaesthesia will be administered to ensure the patient is comfortable and pain-free during the procedure.
-
Surgery Duration: The length of the surgery varies based on the type of procedure but generally ranges from one to four hours.
-
Postoperative Care: After surgery, patients are monitored in a recovery room before being transferred to a hospital room. Pain management, catheter care, and monitoring for complications are essential aspects of postoperative care.
Robotic-Assisted Surgery
Robotic systems like the da Vinci robot enhance precision in prostate surgeries, leading to:
-
Shorter recovery times
-
Greater precision
-
Reduced side effects such as less bleeding and fewer complications.
Minimally Invasive Procedures
These techniques reduce risks and improve outcomes:
-
TURP: Refined to minimize complications.
-
Laser therapies: Like HoLEP, offering faster recovery and fewer side effects.
-
Optilume BPH catheter system: Improves urinary flow with minimal invasiveness.
Non-Surgical Treatments
Innovative non-surgical options include:
-
HIFU: Uses ultrasound waves to destroy prostate tissue.
-
Immunotherapy: Utilizes the immune system to fight prostate cancer.
-
Proton Therapy: Targets cancer cells precisely, sparing healthy tissue.
These advancements make prostate treatments more effective and less burdensome. If you have any specific questions, feel free to ask!
Recovery and Aftercare
Recovery from prostate surgery involves several stages:
-
Immediate Postoperative Period: Patients may experience some pain and discomfort, which can be managed with medications. A catheter is usually placed to help with urination.
-
Hospital Stay: The length of the hospital stay depends on the type of surgery and the patient's overall health. Most patients are discharged within a few days.
-
Home Recovery: At home, patients should follow their surgeon's instructions regarding activity levels, diet, and wound care. Gradual resumption of normal activities is encouraged, but heavy lifting and strenuous activities should be avoided for several weeks.
-
Follow-Up Appointments: Regular follow-up appointments are crucial to monitor the patient's recovery, manage any complications, and assess the effectiveness of the surgery.
Potential Risks and Complications
As with any surgery, prostate surgery carries potential risks and complications, including:
-
Infection: Postoperative infections can occur, requiring antibiotics and sometimes additional treatment.
-
Bleeding: Some bleeding is expected, but excessive bleeding may require intervention.
-
Urinary Incontinence: Temporary or, in rare cases, permanent urinary incontinence can occur.
-
Erectile Dysfunction: Depending on the type of surgery and the patient's condition, there may be a risk of erectile dysfunction.
Bladder Neck Contracture: Scar tissue can form at the bladder neck, causing obstruction and requiring further treatment.
Conclusion
Prostate surgery is a vital option for treating various prostate conditions, offering relief from symptoms and, in the case of cancer, potentially life-saving intervention. Understanding the different types of prostate surgeries, their purposes, procedures, and recovery processes can help patients make informed decisions about their treatment options. With advancements in surgical techniques and postoperative care, the outcomes of prostate surgeries continue to improve, enhancing the quality of life for many men.
For those seeking expert care and advanced treatment options, Manipal Hospital Ghaziabad stands out as a premier healthcare facility. With a team of highly skilled surgeons, state-of-the-art technology, and a patient-centric approach, Manipal Hospital Ghaziabad ensures the best possible outcomes for prostate surgeries and other medical treatments. Trust your health to the experts at Manipal Hospital Ghaziabad, where your well-being is our top priority.
FAQ's
Common types include Transurethral Resection of the Prostate (TURP), prostatectomy (including radical, laparoscopic, and robotic-assisted), Transurethral Incision of the Prostate (TUIP), and laser surgeries like HoLEP and PVP.
Potential risks include infection, bleeding, urinary incontinence, erectile dysfunction, and bladder neck contracture. It's important to discuss these with your surgeon before the procedure.
Yes, there is a risk of erectile dysfunction following prostate surgery, especially with procedures like radical prostatectomy. However, many men recover sexual function over time, and treatments are available to help.
Pain levels vary, but anesthesia is used during the procedure to ensure comfort. Postoperative pain can be managed with medications, and discomfort typically decreases over time.



















 7 Min Read
7 Min Read




5.png)
_का_प्रबंधन.png)











