
Listen to article
Loading audio...
Angioplasty is an intervention performed to blockages or constrictions in blood vessels. Usually arteries. In order to enhance the circulation of blood in the body. This process plays a role in treating individuals dealing with ailments such as artery disease which hinders the flow of blood to the heart due to the accumulation of plaque.
Imagine waking up one day, feeling a tightness in your chest, and realizing that your heart's lifeline is at risk. This scenario is a stark reality for many, but thanks to modern medical advancements, there are life-saving techniques that can restore the flow of life itself. Today, we'll explore these groundbreaking procedures, focusing on balloon angioplasty and the insertion of stents in arteries or veins. We'll also delve into the different types of stents, such as bare metal stents and drug-eluting stents, that play a crucial role in these interventions. Join us as we uncover how these innovations are transforming lives and offering hope to countless patients.
Synopsis
Balloon Angioplasty
Balloon angioplasty, also known as PTA, is a simple, minimally invasive procedure. A small catheter with a balloon tip is inserted into the blocked artery. The balloon is then inflated to push the plaque against the artery walls, widening the artery and restoring blood flow.
Procedure
-
Preparation: The patient is usually given a local anaesthetic to numb the area where the catheter will be inserted, typically in the groin or wrist. Sometimes, a mild sedative is also administered to help the patient relax.
-
Insertion: A thin, flexible tube called a catheter is inserted into the artery and guided to the site of the blockage using X-ray imaging.
-
Inflation: The balloon at the tip of the catheter is inflated, compressing the plaque and widening the artery. This process may be repeated several times to ensure the artery is sufficiently widened.
-
Deflation and Removal: Afterward, the balloon is deflated, and the catheter is removed. In some instances, a stent is placed to ensure the artery remains open.
Stent Placement
Stent placement is frequently done alongside balloon angioplasty. A stent, which is a small mesh-like tube, is inserted into the artery to keep it open after the balloon is deflated and removed. There are two main types of stents: bare-metal stents and drug-eluting stents.
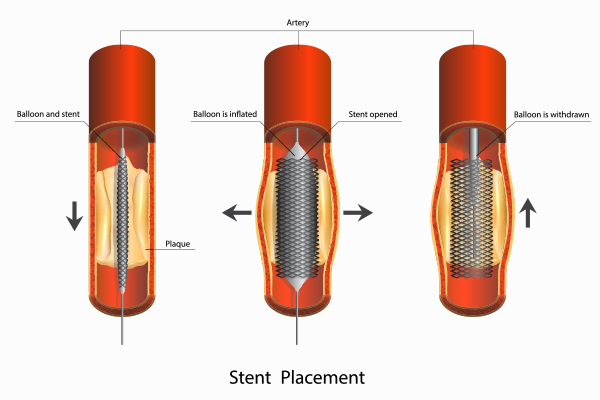
Bare-Metal Stents
Bare-metal stents are straightforward metal mesh tubes that offer structural support to the artery. They effectively prevent the artery from collapsing post-angioplasty. However, there is a risk of restenosis, where the artery may narrow again due to tissue growth over the stent.
Drug-Eluting Stents
Drug-eluting stents are coated with medication that is gradually released to prevent tissue growth, which can cause restenosis. These stents have proven to reduce the risk of restenosis more effectively than bare-metal stents. The medication helps keep the artery open longer by inhibiting scar tissue formation.
Leading Cardiac Treatments in Ghaziabad
Manipal Hospitals Ghaziabad is a leader in cardiac treatments, offering balloon angioplasty and stent placement to improve heart health. Learn more here.
RELATED - What Should You Know About Coronary Angiography?
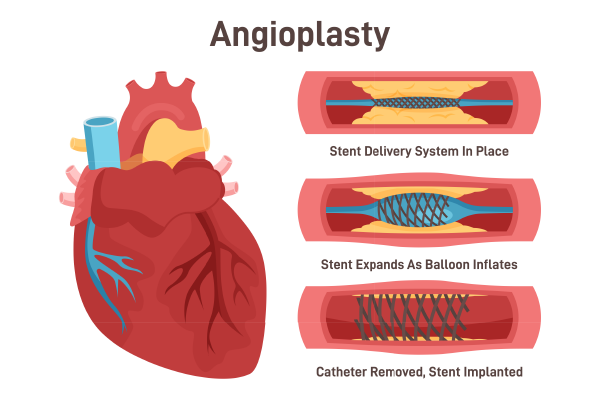
Procedure
-
Preparation: Similar to balloon angioplasty, the patient is given a local anaesthetic. The area where the catheter will be inserted is cleaned and sterilized.
-
Insertion: A catheter with a stent mounted on a balloon is inserted into the artery. The catheter is carefully guided to the site of the blockage.
-
Inflation: The balloon is inflated, expanding the stent and pressing it against the artery walls. This ensures that the stent is properly positioned and the artery is kept open.
-
Placement: The balloon is deflated and removed, leaving the stent in place to keep the artery open. The stent remains in the artery permanently to provide continuous support.
Comparing Balloon Angioplasty and Stent Placement
Effectiveness
-
Balloon Angioplasty: Effective in temporarily widening the artery but has a higher risk of restenosis. It is often used as a preliminary step before stent placement.
-
Stent Placement: Provides longer-term results by keeping the artery open and reducing the risk of restenosis, especially with drug-eluting stents. Stents are particularly beneficial for patients with complex or multiple blockages.
Risks and Complications
-
Balloon Angioplasty: Risks include artery damage, bleeding, and restenosis. There is also a small risk of blood clots forming at the site of the procedure.
-
Stent Placement: Similar risks as balloon angioplasty, with additional risks of blood clots forming on the stent (stent thrombosis). Patients may need to take blood-thinning medications to prevent this complication.
Recovery
-
Balloon Angioplasty: Typically, this procedure has a shorter recovery period, though additional treatments may be necessary if restenosis (re-narrowing of the artery) occurs. Most patients can resume normal activities within a few days.
-
Stent Placement: This procedure generally requires a longer recovery time because patients need to take blood-thinning medications to prevent stent thrombosis. Patients are usually advised to avoid strenuous activities for several weeks.
| Aspect | Bare-Metal Stents (BMS) | Drug-Eluting Stents (DLS) |
| Advantages |
|
|
| Disadvantages |
|
|
| Preferred Situations |
|
|
| Cost Implications |
|
|
| Outcomes |
|
|
Conclusion
Both balloon angioplasty and stent placement are vital procedures in the treatment of blocked arteries. While balloon angioplasty is effective in the short term, stent placement, particularly with drug-eluting stents, offers a more durable solution by reducing the risk of restenosis. Patients in Ghaziabad and other regions can benefit from these advanced procedures, which significantly improve blood flow and reduce the risk of heart attacks and other complications.
Regular follow-ups are crucial for anyone who has undergone stent placement. These routine check-ups play a vital role in monitoring the health of the stent and ensuring that it continues to function properly. They help in detecting any early signs of complications, such as re-narrowing of the artery or new blockages, allowing for timely intervention and preventing more serious issues down the line.
At Manipal Hospitals, follow-up care plans are designed to provide comprehensive support to patients. These plans typically include:
-
Scheduled Appointments: Regular visits to the cardiologist to assess the stent's condition and overall heart health.
-
Imaging Tests: Periodic imaging tests like angiograms or ultrasounds to visualize the stent and surrounding blood vessels.
-
Medication Management: Monitoring and adjusting medications to prevent blood clots and manage other risk factors.
-
Lifestyle Guidance: Advice on diet, exercise, and other lifestyle changes to support heart health.
-
Emergency Support: Access to emergency care if any urgent issues arise.
By adhering to these follow-up care plans, patients can significantly reduce the risk of future blockages and maintain optimal heart health.
Top Cardiologists in Ghaziabad
Our team at Manipal Hospitals Ghaziabad specializes in balloon angioplasty and stent placement, offering the best care for your heart. Learn more here.
FAQ's
There are two primary types of angioplasty. The first is balloon angioplasty, where an inflating balloon is used to apply pressure and clear plaque from a blocked artery. This method is seldom used on its own, except when doctors cannot place a stent in the necessary position.
Both procedures typically have short recovery times. However, stent placement may require a slightly longer recovery period due to the need for blood-thinning medications to prevent blood clots.
Local anaesthesia is typically used to numb the area where the catheter is inserted, usually in the groin or wrist.
To reduce your risk, maintain a healthy weight, eat a balanced diet, exercise regularly, quit smoking, manage stress, and get regular check-ups.
Risk factors include high blood pressure, high cholesterol, smoking, diabetes, obesity, and family history.



















 6 Min Read
6 Min Read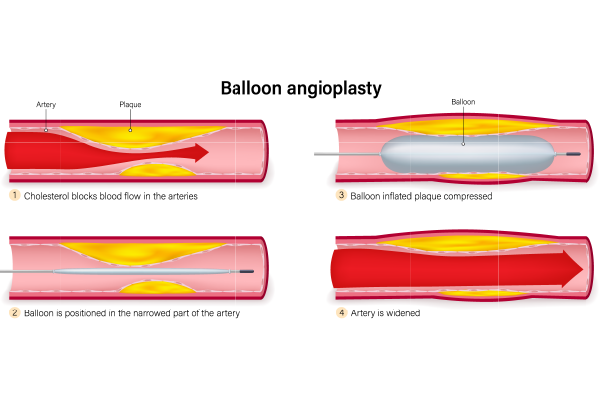






.png)








