
Listen to article
Loading audio...
The brain is one of the most vital organs in our body. It is responsible for controlling every function from movement to thought. A blood clot in the brain, also known as a thrombus, can disrupt the blood supply to this delicate organ. If not identified and treated promptly, it can lead to potentially life-threatening complications. Recognising the early symptoms of a blood clot in the brain is crucial, as it can prevent severe damage and improve the chances of recovery.
A blood clot can lead to a stroke, which may result in permanent disability or even death. Let's explore the symptoms, causes, and treatments for blood clots in the brain, as well as the importance of seeking immediate medical attention.
Synopsis
What is a Blood Clot in the Brain?
A blood clot in the brain occurs when a blood vessel in the brain becomes blocked. This leads to a lack of blood flow in the brain. This blockage can cause brain cells to be deprived of oxygen and nutrients, resulting in brain damage. There are two main types of blood clots in the brain: thrombotic and embolic.
-
Thrombotic Clots: These form in the arteries of the brain and are often caused by the build-up of fatty deposits or plaque, which restricts blood flow.
-
Embolic Clots: These clots form elsewhere in the body, often in the heart, and travel through the bloodstream to the brain.
Causes of Blood Clot
Common causes of blood clots in the brain include: medical conditions such as atrial fibrillation (a heart rhythm disorder), and high cholesterol or high blood pressure and diabetes, smoking, alcohol consumption. Blood clots form when the blood thickens and clumps together, potentially obstructing vital blood vessels in the brain, thereby disrupting normal brain function.
What are the Signs and Symptoms of Blood Clots in the Brain?
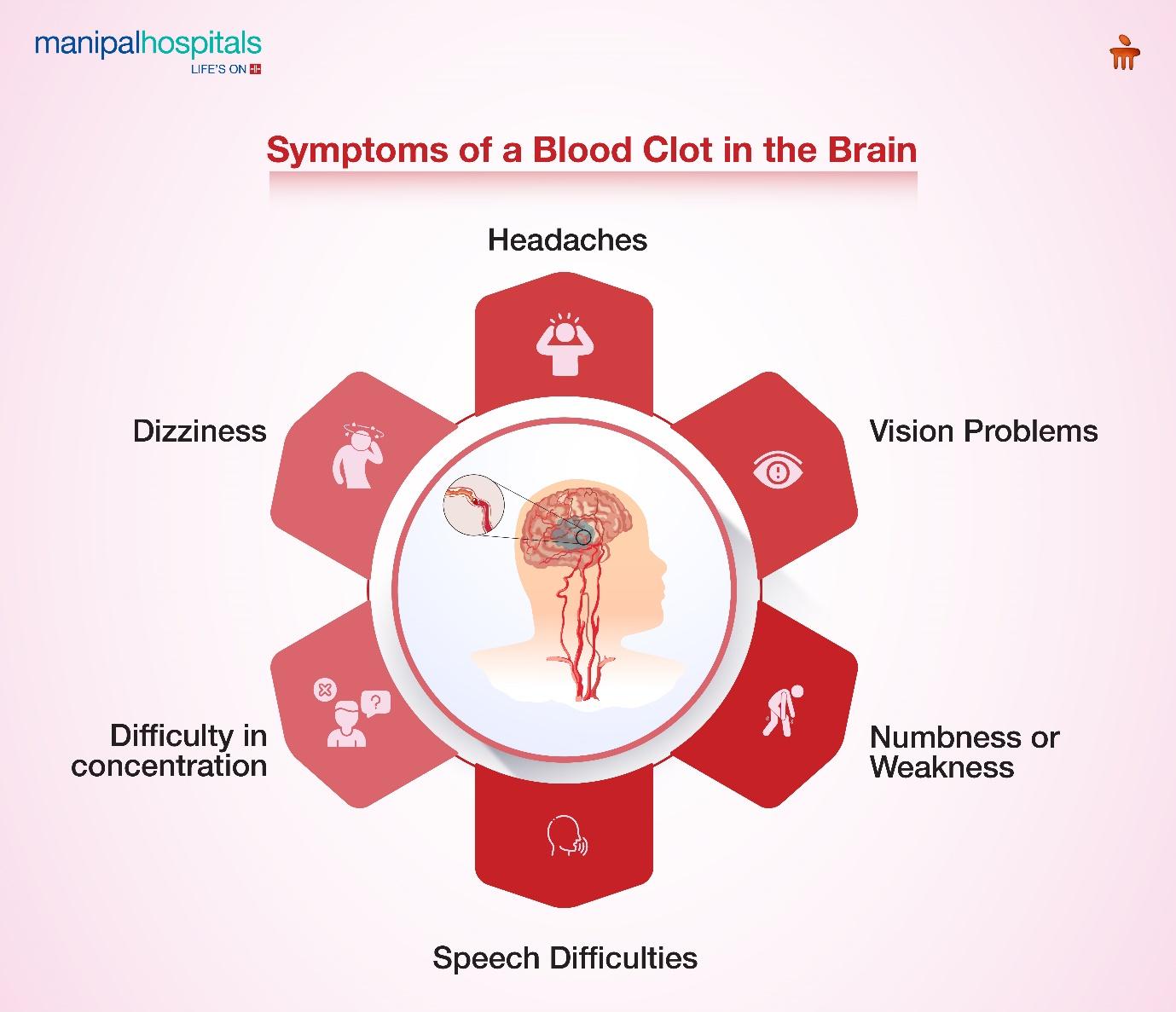
Identifying the signs and symptoms of blood clots in the brain early can be life-saving. Following are some of the key symptoms:
Initial symptoms of stroke can be remembered as BEFAST:
B: Balance related problem
E: Eyesight /Vision loss
F: Facial asymmetry
A: Arm or Lep weakness
S: Speech problem
T: Act on time and visit the nearest centre
-
Numbness or Weakness: One-sided numbness or paralysis in the face, arm, or leg is a major warning sign of a blood clot in the brain. Difficulty moving or feeling specific body parts may indicate that the clot is blocking important signals to the brain.
-
Vision Problems: Blurred or double vision or sudden loss of vision in one or both eyes. These are the signs of having a blood clot in the areas of the brain responsible for vision. These issues may appear suddenly and require prompt attention.
-
Speech Difficulties: Slurred speech, trouble finding words, or an inability to comprehend speech are serious symptoms. A blood clot may interfere with the brain's ability to process and articulate speech. This makes communication challenging.
-
Dizziness and Confusion: Difficulty maintaining balance and a sense of disorientation are common early symptoms. People with blood clots in the brain may also experience confusion, trouble concentrating, or an inability to process simple information.
Consult our neurologist in Goa if you are experiencing brain clot symptoms
Risk Factors and Causes
Certain conditions and lifestyle factors can increase the risk of developing a blood clot in the brain:
-
Medical Conditions: High cholesterol, hypertension, atrial fibrillation, and diabetes are some of the underlying health conditions that contribute to the formation of blood clots in the brain.
-
Lifestyle Factors: Smoking, obesity, and a lack of physical activity can also raise the risk of blood clots. These factors contribute to poor circulation and increased plaque build-up in the arteries.
-
Genetics: A family history of blood clots, stroke, or other cardiovascular diseases can increase the likelihood of experiencing a blood clot in the brain.
What to Do if You Suspect a Blood Clot in the Brain?
If you or someone you know is experiencing symptoms of a blood clot in the brain, it’s crucial to seek immediate medical attention. A CT scan or MRI can help diagnose the presence of a blood clot and determine its size and location. Emergency treatments like thrombolysis (clot-busting medication) or surgery for blood clots in the brain may be required to remove the clot and restore blood flow to the brain. Prompt intervention can significantly improve the chances of recovery and reduce the risk of long-term damage.
Consult our neurology hospital in Goa if you need treatment for blood clots in the brain.
Preventive Measures and Long-term Management
Preventing blood clots in the brain begins with adopting a healthy lifestyle. Here are some key steps:
-
Balanced Diet and Exercise: A diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains, along with regular exercise, can improve circulation and reduce the risk of clot formation.
-
Managing Underlying Conditions: Keeping blood pressure, cholesterol, and blood sugar levels in check is essential for preventing blood clots. Regular check-ups with a healthcare provider can help manage these conditions.
-
Medications: Anticoagulants or blood thinners may be prescribed to prevent blood clots in individuals at high risk. These medications help prevent the formation of clots and improve blood flow.
Conclusion
A blood clot (brain thrombus) in the brain is a serious medical emergency, and early detection is key to saving lives. Recognising the symptoms of a blood clot in the brain, such as Balance issues, Eyesight loss, Face weakness Arm or step weakness, and Speech Problems is crucial because reaching the hospital on time can reverse symptoms. This can help you seek timely treatment. If left untreated, a blood clot can lead to a stroke, causing permanent damage or even death. By understanding the symptoms and taking preventive measures, you can reduce your risk of blood clots and protect your brain health. Early intervention is the key to a positive outcome, so don’t hesitate to seek medical help if you suspect a blood clot Remember the Pneumonic BE- FAST.
FAQ's
A headache caused by a blood clot is usually severe, sudden, and unlike any headache you've experienced before. It may be accompanied by other symptoms such as nausea, vomiting, vision changes, or difficulty speaking.
Yes, a blood clot in the brain can obstruct blood flow, leading to an ischemic stroke. Immediate medical help is crucial to prevent damage
Early warning signs may include transient episodes of confusion, mild speech difficulties, brief vision disturbances, or sudden weakness in an arm or leg. These symptoms should not be ignored.
Risk factors include high blood pressure, smoking, obesity, a sedentary lifestyle, certain medical conditions like atrial fibrillation, and a family history of blood clots or strokes.
Yes, imaging tests such as CT scans, MRIs, and angiograms are commonly used to diagnose blood clots in the brain. Blood tests may also help identify underlying conditions that contribute to clot formation.



















 6 Min Read
6 Min Read








