
Epilepsy is one of the most common neurological disorders, affecting millions of people worldwide. It can start at any age and has various causes, ranging from genetic factors to brain injuries and infections. While some people experience only occasional seizures, others may have frequent episodes that impact their daily lives. Advances in medicine have significantly improved the management of epilepsy, helping individuals lead normal, fulfilling lives.
Understanding epilepsy is crucial not only for those diagnosed but also for caregivers and society. Let’s take a closer look at what epilepsy is and how it affects people. We will explore the epilepsy symptoms, types of epilepsy, epilepsy treatment options, and epilepsy triggers in the blog to understand the condition better.
Synopsis
What is Epilepsy?
Epilepsy is a chronic brain condition that causes seizures due to sudden electrical disturbances in the brain. These seizures can range from mild, where a person experiences brief confusion. In severe cases, a person diagnosed with epilepsy can lose consciousness and experience uncontrollable body movements.
Who Can Get Epilepsy?
Epilepsy can affect people of all ages, but it is more common in infants and children due to their developing neural structures. Adults and the elderly, especially due to strokes, brain infections, or tumours.
Is Epilepsy Inherited?
Some forms of epilepsy have a genetic link, meaning they can run in families. However, most cases are caused by brain injuries, infections, autoimmune conditions, or metabolic disorders.
What Causes Epilepsy?
Epilepsy occurs due to abnormal electrical activity in the brain, but the underlying reasons for this disruption can vary widely. Some individuals develop epilepsy due to structural brain abnormalities, while others may have a genetic predisposition. In some cases, no clear cause is identified, making it a condition with diverse origins. Let’s understand the factors from the below list:
Genetic Factors: Some people inherit mutations in genes that affect brain activity, making them more likely to develop epilepsy.
-
Brain Injuries: Head trauma from accidents, falls, or sports injuries can damage the brain and cause seizures.
-
Brain Tumours and Stroke: Structural issues in the brain, such as tumours, strokes, or aneurysms, can trigger epilepsy, especially in older adults.
-
Infections: Brain infections like meningitis, encephalitis, or neurocysticercosis can lead to epilepsy.
-
Autoimmune Disorders: Certain autoimmune conditions can cause brain inflammation, leading to seizures.
-
Developmental Disorders: Conditions like autism and cerebral palsy are associated with epilepsy.
-
Metabolic Imbalances: Issues like low blood sugar, sodium imbalances, or vitamin deficiencies can also contribute to epilepsy.
Types of Epilepsy
Epilepsy is classified based on the type of seizures a person experiences.
Generalised Epilepsy: Seizures affect both sides of the brain. Examples include:
-
Tonic-clonic seizures: Sudden loss of consciousness, stiffening, and jerking movements.
-
Absence seizures: Brief staring episodes, mostly in children.
-
Focal Epilepsy: Seizures originate from a specific part of the brain and may or may not affect consciousness.
-
Unknown-Onset Epilepsy: When the origin of seizures is unclear, it is classified as unknown-onset epilepsy.
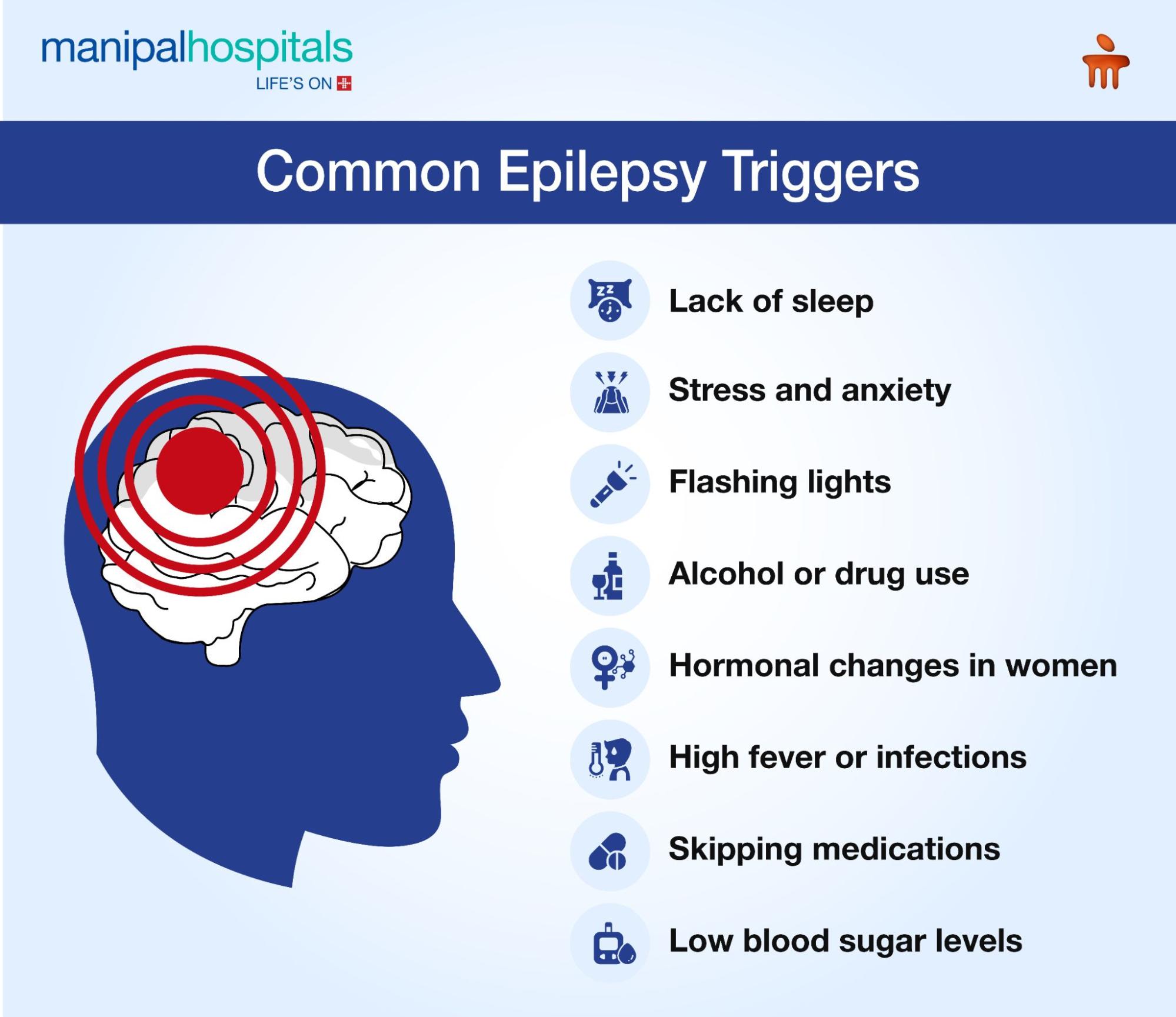
What are Epilepsy Triggers?
While epilepsy is a neurological condition, seizures are not always random. Certain factors, known as triggers, can increase the likelihood of a seizure in people with epilepsy. These triggers vary from person to person, and identifying them can help manage the conditions better.
Common epilepsy triggers include:
-
Lack of sleep - Sleep deprivation can disturb brain activity, making seizures more likely.
-
Stress and anxiety - Emotional stress can trigger seizures in some individuals.
-
Flashing lights - Bright or flickering lights may cause seizures, especially in photosensitive epilepsy.
-
Alcohol or drug use - These substances can affect brain function and lower the seizure threshold.
-
Hormonal changes in women - Menstrual cycles or hormonal fluctuations can sometimes increase seizure frequency.
-
High fever or infections - Illnesses that cause high body temperature can trigger seizures, especially in children.
-
Skipping medications - Missing epilepsy medication doses can lead to breakthrough seizures.
-
Low blood sugar levels - Hypoglycaemia can affect brain function, increasing seizure risk.
Is Epilepsy Curable?
Epilepsy is a manageable condition, but whether it can be completely cured or not depends on the underlying cause. A seizure is a manifestation of a disturbed electrical circuit formed by certain neurons. Identifying the underlying cause is the most important step in management. Seizures can be controlled by appropriate anti-seizure medications. Usually, treating underlying conditions, proper adjustment of anti-seizure medication, and slow tapering of medications will give satisfactory results. Certain genetic epileptic disorders, epilepsy with developmental problems or epilepsy associated with other genetic diseases may need long-term treatment with suitable anti-seizure medications.
Epilepsy Treatment Options
In recent years, epilepsy management has seen remarkable progress, improving patient outcomes and reducing complications. With newer treatments and technologies, people with epilepsy now have better options for seizure control and overall well-being.
-
New medications – Modern anti-seizure drugs offer better efficacy with fewer side effects. This makes long-term management easier.
-
Surgical advancements – Epilepsy surgeries for drug-resistant cases have shown higher success rates, providing relief for many patients.
-
Neuromodulation therapies – Treatments like Vagus Nerve Stimulation (VNS) and Deep Brain Stimulation (DBS) help reduce seizure frequency, lowering dependence on medication.
-
Dietary approaches – The ketogenic diet and high-dose pyridoxine (vitamin B6) have proven effective for specific types of epilepsy, particularly in children with genetic mutations.
-
Advanced monitoring – Improvements in EEG technology and wearable seizure detection devices allow for early diagnosis and better seizure tracking, enhancing patient safety.
-
Research and genetic studies – Advances in genetic testing, including whole genome and exome sequencing with next-generation sequencing, have improved diagnosis and personalised treatment approaches.
-
Autoimmune and paraneoplastic encephalitis treatment – Patients with identified antibodies, such as anti-NMDA receptor encephalitis, have shown good seizure control and recovery with targeted immune therapies.
Common Myths About Epilepsy
|
Myth |
Fact |
|
Epilepsy is a Mental Illness |
Epilepsy is a neurological disorder, not a mental illness. |
|
People with Epilepsy Cannot Lead Normal Lives |
With proper treatment, most people with epilepsy can live full, active lives |
|
Seizures Are Always Violent |
Some seizures involve brief staring spells, confusion, or numbness, not just convulsions |
|
You Should Put Something in a Person’s Mouth During a Seizure |
This is dangerous and can cause choking. The best way to help is to move sharp objects away and turn the person on their side |
|
Epilepsy is Contagious |
Epilepsy is not contagious and cannot be passed from one person to another |
Conclusion
Epilepsy is a manageable condition with the right treatment. While some types are curable, others require lifelong management. With advancements in medicine, improved awareness, and early diagnosis, people with epilepsy can lead healthy, fulfilling lives. If you or a loved one experiences epilepsy symptoms, consult a doctor for early intervention and proper management. You can also connect to Manipal Hospitals, Goa, for any further assistance.
FAQ's
Yes, epilepsy can sometimes impact memory, concentration, and cognitive function, especially if seizures occur frequently or affect areas of the brain responsible for memory. Certain anti-seizure medications may also cause temporary cognitive side effects.
Yes, regular exercise can be beneficial for people with epilepsy, as it helps reduce stress and improve overall well-being. However, high-risk activities like swimming alone, climbing, or contact sports should be approached with caution.
Women with epilepsy can have healthy pregnancies, but it's essential to plan with a doctor. Some anti-seizure medications may pose risks to the baby, so medication adjustments might be needed. Seizure control during pregnancy is also crucial for both the mother's and baby’s safety.
For some, epilepsy remains stable, while in others, seizures may become more frequent or severe due to factors like ageing, stress, or other medical conditions. Proper treatment and lifestyle management can help prevent the worsening of symptoms.
Yes, epilepsy is sometimes misdiagnosed, as other conditions like migraine, fainting (syncope), sleep disorders, or anxiety attacks can mimic seizures. EEG monitoring and thorough medical evaluation help ensure an accurate diagnosis.



















 7 Min Read
7 Min Read










