A permanent pacemaker is a small device implanted in the chest to help manage irregular heartbeats, known as arrhythmias. This life-saving device ensures that the heart beats at a regular pace, providing a steady flow of blood and oxygen to the body. Understanding the procedure, types, and benefits of permanent pacemaker implantation can help patients and their families make informed decisions about their cardiac care.
Permanent pacemaker implantation is a life-saving procedure for individuals with certain heart conditions. This blog will discuss potential risks and complications, highlight the latest developments in pacemaker technology, and provide practical advice for living with a pacemaker.
Synopsis
Permanent Pacemaker Implantation Procedure
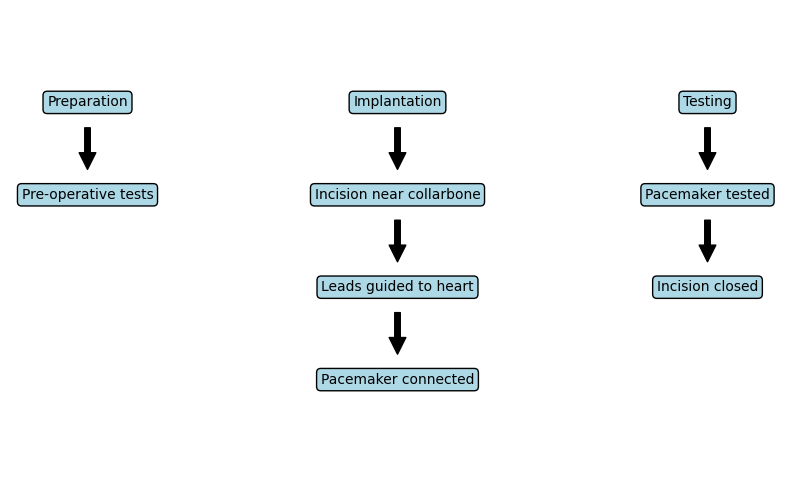
The permanent pacemaker implantation procedure involves placing a small device under the skin near the collarbone. This device helps regulate the heart's rhythm by sending electrical impulses to the heart muscles. The procedure typically takes a few hours and is performed under local anesthesia.
-
Preparation: Patients undergo pre-operative tests, including blood tests and imaging studies, to ensure they are fit for surgery.
-
Implantation: A small incision is made near the collarbone, and leads (wires) are guided through a vein to the heart. The pacemaker device is then connected to these leads and placed under the skin.
-
Testing: The pacemaker is tested to ensure it is working correctly, and the incision is closed with sutures.
Table Explaining the Procedure
|
Step |
Description |
|
Preparation |
Patients undergo pre-operative tests, including blood tests and imaging studies, to ensure they are fit for surgery. |
|
Implantation |
A small incision is made near the collarbone, and leads (wires) are guided through a vein to the heart. The pacemaker device is then connected to these leads and placed under the skin. |
|
Testing |
The pacemaker is tested to ensure it is working correctly, and the incision is closed with sutures. |
Types of Pacemaker Devices
There are several types of pacemakers, each designed to meet specific needs:
-
Single-chamber pacemakers: These have one lead placed in either the right atrium or right ventricle.
-
Dual-chamber pacemakers: These have two leads, one in the right atrium and one in the right ventricle, allowing for more coordinated heart rhythm control.
-
Biventricular pacemakers: Also known as cardiac resynchronization therapy (CRT) devices, these have three leads to help both ventricles contract simultaneously, improving heart function in patients with heart failure.
-
Leadless pacemakers: These are newer, minimally invasive devices implanted directly into the heart without the need for leads. They offer advantages such as reduced infection risk and quicker recovery times.
Benefits
Permanent pacemakers offer numerous benefits, including:
-
Improved quality of life: By regulating heart rhythm, pacemakers can alleviate symptoms like fatigue, dizziness, and fainting.
-
Increased lifespan: Pacemakers can prevent life-threatening arrhythmias, significantly improving survival rates.
-
Enhanced heart function: For patients with heart failure, biventricular pacemakers can improve the heart's pumping efficiency.
Risks and Complications
While pacemaker implantation is generally safe, there are potential risks and complications:
-
Infection: At the implantation site, which can be managed with antibiotics.
-
Bleeding or swelling: Around the implantation area.
-
Lead displacement or malfunction: This may require repositioning or replacement.
-
Device malfunction: Requiring reprogramming or replacement.
These risks are managed through careful monitoring and follow-up care.
Latest Developments in Pacemaker Technology
Recent advancements in pacemaker technology include:
-
Leadless pacemakers: These devices are smaller and implanted directly into the heart, reducing the risk of complications associated with leads.
-
Remote monitoring: Modern pacemakers can transmit data to healthcare providers, allowing for continuous monitoring and timely interventions.
-
Bluetooth connectivity: Some pacemakers can connect to smartphones, enabling patients to track their heart health and receive alerts.
Consult our cardiology hospital in Gurugram if you need Permanent Pacemaker Implantation.
Recovery and Long-Term Care
Post-procedure recovery involves several stages:
-
First week: Patients may experience mild discomfort and are advised to avoid strenuous activities.
-
Long-term considerations: Regular follow-up appointments are essential to monitor the pacemaker's function and battery life. Patients should contact their doctor if they notice signs of infection or device-related discomfort.
Managing battery life is crucial, as pacemakers typically need battery replacement every 5-15 years, depending on usage.
Living with a Pacemaker
Practical advice for daily life includes:
-
Physical activities: Patients can engage in most activities but should avoid contact sports and heavy lifting.
-
Household appliances: Most appliances, including microwaves and smartphones, are safe to use. However, patients should avoid strong magnetic fields.
-
Travel tips: Pacemaker patients can travel and go through airport security. It's advisable to carry a pacemaker identification card and inform security personnel.
Lifestyle and Dietary Tips
Maintaining a heart-healthy lifestyle is important:
-
Diet: A balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins supports heart health.
-
Exercise: Regular, moderate exercise helps maintain cardiovascular fitness.
-
Avoiding smoking and excessive alcohol: These habits can negatively impact heart health.
Myths and Facts about Pacemakers
Common misconceptions include:
-
"Pacemakers cure heart disease": Pacemakers manage symptoms but do not cure underlying heart conditions.
-
"You cannot lead an active life with a pacemaker": Many pacemaker patients lead active, fulfilling lives.
Pacemakers and Pregnancy
Women with pacemakers can have healthy pregnancies. It's important to work closely with a cardiologist and obstetrician to manage heart health during pregnancy and delivery.
Conclusion
Permanent pacemaker implantation is a vital procedure for many patients with heart conditions. Understanding the procedure, types, benefits, and potential risks can help patients make informed decisions and lead healthy lives with their pacemakers.
For expert care and advanced treatment options, consider visiting Manipal Hospitals Gurugram. Their team of experienced cardiologists and state-of-the-art facilities ensure the best possible outcomes for patients requiring pacemaker implantation and other cardiac procedures.
FAQ's
Yes, you can travel and go through airport security. Inform security personnel about your pacemaker and carry an identification card.
Signs of malfunction include dizziness, fatigue, and irregular heartbeats. Contact your doctor if you experience these symptoms.
Avoid contact sports, heavy lifting, and activities that involve strong magnetic fields.
The procedure involves making a small incision in the chest, inserting leads through a vein to the heart, and connecting them to the pacemaker device, which is placed under the skin.
Benefits include regulated heart rhythm, improved quality of life, reduced risk of complications like stroke and heart failure, and enhanced cardiac function.



















 4 Min Read
4 Min Read