Statistics Related to Hearing Loss in The Elderly
Hearing loss impacts over 1.5 billion people worldwide, around 20% of the global population. Around 430 million of the affected have disabling hearing loss. People between 20 and 69 years of age often get affected by hearing loss; it is twice as likely in men. 60 to 69 years of age are more likely to lose their hearing.
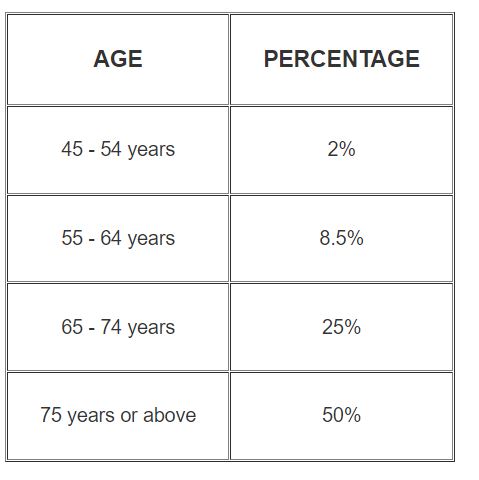
These statistics become even more striking with the elderly population. Here is a list of the age and the percentage of adults who have disabling hearing loss:
What Is Presbyacusis?
Presbyacusis essentially means age-related hearing loss. According to WHO, around 6.3% (63 million) of the Indian populace suffers from significant auditory impairment. Presbyacusis affects approximately 25% to 40% of those aged 65, 40% to 60% of people above 75, and 80% of individuals older than 85.
Causes of Hearing Loss In the Elderly
Understanding the causes of hearing loss in the elderly is essential to address and prevent it effectively. Here are some key factors contributing to this issue:
Ageing Nerves: Our nerves, including those responsible for hearing, can weaken as we age. This natural process often results in impaired hearing or loss of hearing in old age. Book an appointment with the top specialists at the best ENT hospital in Bangalore.
-
Diabetes: Diabetics have a higher risk of hearing loss, making regular check-ups vital.
-
Occupational Exposure: Some people who were exposed to loud noise in their younger years may experience high-frequency hearing loss, especially in older age.
-
Modern Technology: The increased use of headphones and earphones in the modern era can cause nerve damage over time.
What Are the Signs of Hearing Loss?
Knowing the signs of hearing loss will help you detect the issue faster. Look for the following symptoms to take early measures:
-
Difficulty in Conversations: Seeing a person constantly asking others to repeat them can be a sign.
-
Volume Increase: Pay attention if an individual consistently turns up the volume level on the TV or radio that others find uncomfortably loud.
-
Tinnitus: It is also called ringing in the ears. So, a buzzing sound in your ears can be a sign of hearing loss.
What Are the Health Effects of Hearing Loss?
It may seem that hearing loss is not a very big deal, but this issue has several health effects.
-
Cognitive Decline: Hearing loss has a link with cognitive decline. So, it may raise the risks of dementia and Alzheimer's.
-
Depression and Isolation: Hearing loss can lead to feelings of depression and isolation. Difficulty in communication can limit social interactions.
-
Increased Risk of Falls: Hearing loss can affect balance and spatial awareness, increasing the risk of falls among the elderly.
-
Reduced Quality of Life: Untreated hearing loss can diminish one's quality of life, impacting emotional well-being and daily activities.
How to Prevent Hearing Loss and Protect the Nerves?
While hearing loss is common in the elderly, there are precautions you can take to preserve your hearing and protect those precious nerves:
-
Avoid Loud Noise: Protect your ears from excessive noise, especially in occupational settings. Ear protection can go a long way in preventing hearing damage.
-
Limit Earphone Usage: If you love your music, be mindful of volume levels when using earphones. Keep it at a reasonable level to avoid nerve damage.
-
Control Blood Sugar: If you are suffering from diabetes, maintaining healthy blood sugar levels can reduce your risk of hearing loss.
-
Take Supplements: Consider taking multivitamins or vitamin B12 supplements, as they can support overall ear health.
-
Regular Hearing Tests: Get a hearing test (audiometry) done annually to catch any issues early and take steps to address them.
-
Safe Listening: When enjoying recreational activities with loud sounds, practise safe listening by wearing ear protection to reduce exposure.
-
Avoid Ototoxic Drugs: Some medications can harm your hearing. Consult your doctor to explore alternative treatments or medications.
-
Treat Ear Infections: Promptly treat ear infections, such as chronic otitis media, to prevent nerve damage.
Try to be mindful when talking to a person suffering from hearing loss. You can use hand gestures or talk slowly to make them understand what you are saying. It is best if there is no or less background noise. Most importantly, be patient with the person because they are already frustrated in their heads.
Hearing loss in the elderly is a prevalent issue. It can hugely impact our quality of life. Understanding the causes and taking precautions can help maintain good hearing health as you age. If you or any of your dear ones are experiencing symptoms of loss of hearing get a hearing test (audiometry) done at Manipal Hospitals, Hebbal for appropriate diagnosis and treatment. Ensure you are connected to the world of sounds by starting to protect your hearing.
FAQs
-
Is hearing loss a normal part of ageing?
Hearing loss, known as presbyacusis, is a common part of ageing, affecting a significant portion of the elderly population.
-
Can hearing loss in the elderly be reversed?
Not all of them, but hearing aids or medical interventions can improve some forms of hearing loss. Early detection and treatment can manage hearing loss effectively. You can visit Manipal Hospitals, Hebbal and consult the best ENT specialist in Hebbal.
-
When should I consider hearing aids?
Consult an ear specialist or an audiologist if you notice signs of hearing loss. They can analyse and tell you if it is necessary to get a hearing aid or not.





















 3 Min Read
3 Min Read

.png)