-
Book Appointments & Health Checkup Packages
- Access Lab Reports
-
-
Book Appointments & Health Checkup Packages
-
Centre of
Excellence
Centre of Excellence
- Bariatric Surgery - MIBS
- Accident and Emergency Care
- Cardiology
- Cardiothoracic Vascular Surgery
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- Gastrointestinal Science
- General Surgery
- Laparoscopic Surgery
- Liver Transplantation Surgery
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Neurosurgery
- Obstetrics and Gynaecology
- Orthopaedics
- Renal Sciences
- Spine Care
- Urology
Other Specialities
- Anesthesiology
- Bariatric Surgery
- Cancer Care
- Dental Medicine
- Dermatology
- Ear Nose Throat
- Fetal Medicine
- Hemato Oncology
- ICU and Critical Care
- Internal Medicine
- Interventional Radiology
- IVF and Infertility
- Laboratory Medicine
- Microbiology
- Neonatology & NICU
- Nocturnal Dialysis
- Nutrition And Dietetics
- Ophthalmology
- Paediatric And Child Care
- Paediatric Surgery
- Pain Medicine
- Pathology
- Pharmacy
- Physiotherapy
- Plastic, Reconstructive And Cosmetic Surgery
- Podiatric Surgery
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology (Respiratory and Sleep Medicine)
- Radiology
- Reproductive Medicine
- Rheumatology
- Sports Medicine
- Vascular and Endovascular Surgery
Speciality Clinics
- Doctors
- Hebbal
- International Patients



Clinics








- Self Registration
- In-Patient Deposit
- Mars - Ambulance
- Home Care
- Organ Donation
- Corporate & PSU
- Insurance Helpdesk
- Awards And Achievements
- Manipal Insider
- Extended Clinical Arm
- Careers
- Contact Us
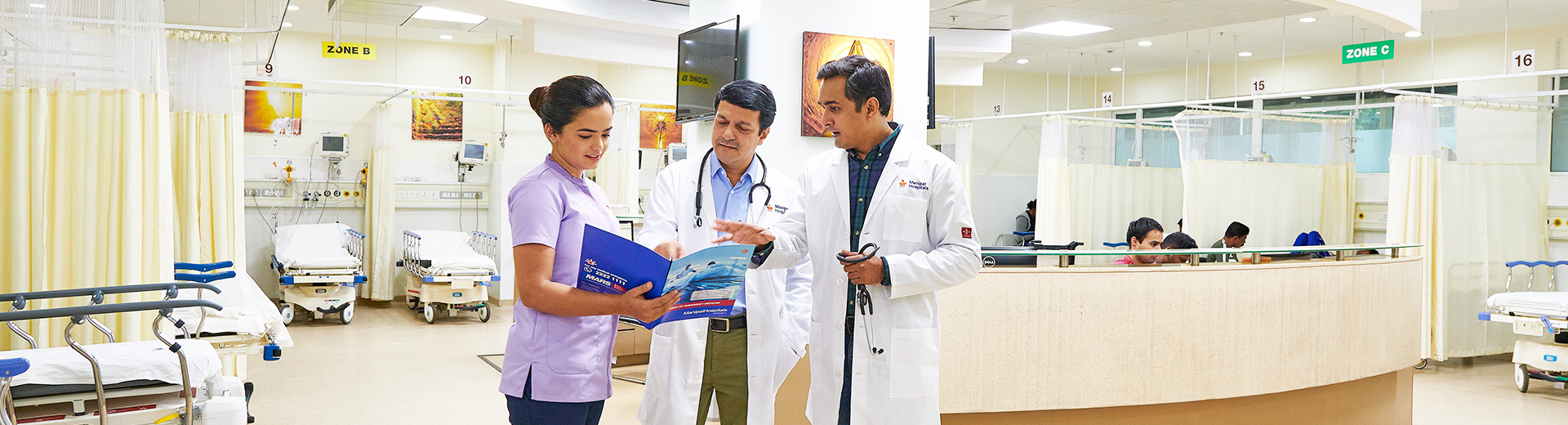

Treatment of infectious diseases like tuberculosis, typhoid and gastroenteritis
Infectious disease treatment in Hebbal, Bangalore
A potentially severe infectious disease, tuberculosis primarily affects the lungs. By coughing and sneezing, tiny droplets of tuberculosis-causing bacteria pass into the air.
In 1985, tuberculosis infections began to increase in developed countries, partly due to the emergence of HIV, the virus that is responsible for AIDS. HIV impairs a person's immunity, making him unable to fight TB germs.
Most tuberculosis strains are resistant to drugs commonly used to treat the disease. People suffering from active tuberculosis require various treatments for months to successfully eliminate the infection and prevent the occurrence of antibiotic resistance.
Treatment
Your doctor during infectious disease treatment in Hebbal, Bangalore may recommend treatment with medication if you are at high risk of developing active TB if you have latent TB. You should take antibiotics for at least six to nine months in the case of active tuberculosis.
Drugs and length of therapy are influenced by your age, health status, potential drug resistance, and the severity of the disease in your body.
TB drugs are most commonly prescribed. You may only require one or two types of TB medications if you have latent tuberculosis. The treatment of active tuberculosis will require administering several drugs at once, mainly if the strain is drug-resistant. To treat tuberculosis, the following medications are often prescribed,
-
The isoniazid
-
The drug rifampin
-
The drug ethambutol
-
It is pyrazinamide
The treatment of drug-resistant TB typically consists of a mixture of antibiotics referred to as fluoroquinolones and drugs administered via injection, such as amikacin or capreomycin. These medications are also becoming less resistant to certain strains of tuberculosis.
There is a wide range of medications that can be added to therapy to counter drug resistance, including,
-
The drug bedaquiline
-
The drug linezolid
Choosing the right time to see a physician
When you are experiencing a fever, unexplained weight loss, drenching night sweats, or a persistent cough, it is essential to see your physician. As a result, they are often indicative of tuberculosis, but other conditions can also cause them. Moreover, if you believe that you have been exposed to TB, you should consult your physician if you think you have been exposed.
By the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, people at an increased risk of tuberculosis should be screened for latent tuberculosis infections as soon as possible.
Causes
Tuberculosis is caused by bacteria due to the release of microscopic droplets into the air due to the release of tiny droplets. People with the untreated, active form of tuberculosis can experience a reaction like this when they cough, speak, sneeze, spit, laugh, or sing while suffering from the disease.
Although tuberculosis is contagious, it is not a manageable disease to contract, although it is contagious. It is much more likely to contract tuberculosis from someone you live or work with than from someone who is a stranger. There is a high level of contagiousness among people with active TB as long as they have received appropriate drug treatment for at least two weeks.
Take your medication to the end
The most important thing you can do to prevent yourself and others from contracting tuberculosis is to take this step as soon as possible. As a result of stopping treatment for TB early or skipping doses, TB bacteria may develop mutations that enable them to survive the most potent TB drugs. It is much more difficult and dangerous to treat drug-resistant strains of bacteria that result from this process.
Treatment of Typhoid
Salmonella typhi is the bacteria that causes Typhoid fever. It is relatively uncommon to contract typhoid fever in advanced countries. The disease continues to pose a severe health threat in the developing world, especially among children.
Most people with typhoid fever recover after receiving antibiotic treatment within a few days; however, a small percentage may suffer fatal complications. Vaccines against typhoid fever are only marginally effective. Vaccinations are recommended for individuals who may be exposed to the disease or are travelling to areas where typhoid fever is prevalent.
A physician should be consulted when necessary
You should seek medical attention immediately as soon as you suspect you are suffering from typhoid fever. If you become ill while travelling abroad, you should contact the American Consulate for a list of available physicians in the area.
You should consider consulting a physician specialising in international travel medicine or infectious diseases if you experience symptoms after returning home. If you see a doctor who is familiar with these areas, they may be able to diagnose and treat your illness more quickly than someone who isn't.
Causes
A bacteria called Salmonella typhi is responsible for transmitting typhoid fever to humans. There is a relationship between Salmonella typhi and salmonellosis, another severe intestinal infection, but the two bacteria do not belong to the same family.
Faecal-oral transmission route
Travelling is the most common way for people in developed countries to acquire typhoid bacteria. Infected individuals can spread the disease through faeces and oral fluids.
Infected individuals pass Salmonella typhi through their faeces and their urine. You can become infected if you eat food handled by someone with typhoid fever and who has not washed their hands thoroughly after using the toilet.
In developing countries where typhoid fever is established, most people contract the disease by drinking contaminated water. Bacteria may also be transmitted through contaminated food and contact with an infected individual.
The Treatment
The only effective treatment for typhoid fever is antibiotic therapy.
Antibiotics commonly prescribed by physicians
Physicians commonly prescribe the following antibiotics,
-
Ciprofloxacin. In the United States, doctors often recommend this medication to adults who are not pregnant. Ofloxacin is an alternative drug that may also be used. Salmonella typhi bacteria, especially those found in Southeast Asia, are no longer susceptible to antibiotics suitable for this type.
-
Azithromycin. If a patient cannot take ciprofloxacin or the bacteria are resistant to ciprofloxacin, this medication could be effective.
-
Ceftriaxone. This drug may be a suitable alternative in cases of more complicated or severe infections or for patients who may not be candidates for ciprofloxacin, such as children.
Consult with the internal medicine experts in Hebbal to know more about treatments at Manipal Hospitals.
Home Hebbal Specialities Internal-medicine Infectious-disease-treatment

You’re on Our Indian Website
Visit the Global site for International patient services










