
Managing blood sugar is crucial for individuals with diabetes, and one key factor influencing blood sugar levels is the Glycemic Index (GI). Understanding how different foods affect glucose levels can help in making informed dietary choices. In this article, we will explore the Glycemic Index, how it impacts blood sugar, and how it plays a role in glycemic index diabetes management. We will also discuss practical dietary strategies, including low glycemic index foods for diabetics, to help maintain stable glucose levels.
Synopsis
- What is the Glycemic Index (GI)?
- How the Glycemic Index Affects Blood Sugar?
- Glycemic Index vs. Glycemic Load: What’s the Difference?
- Why the Glycemic Index Matters for Diabetes Management
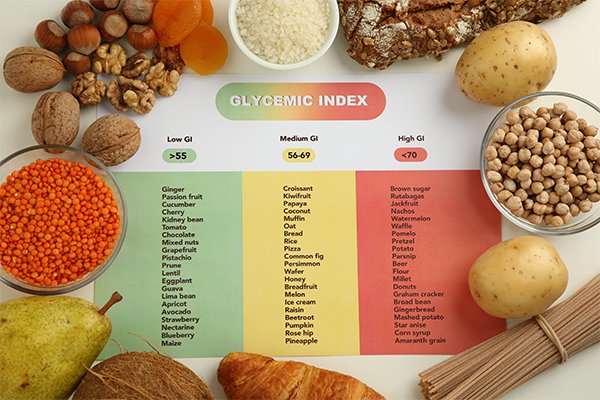
- List of Low, Medium, and High GI Foods
- Factors That Influence a Food’s GI
- Practical Tips for a Low-GI Diet
- Myths and Misconceptions About GI
- The Role of GI in Weight Management and Overall Health
- Balancing GI with a Holistic Approach to Health
What is the Glycemic Index (GI)?
The Glycemic Index is a ranking system that measures how quickly carbohydrate-containing foods raise blood glucose levels. Foods are classified into three categories based on their GI score:
|
GI Category |
GI Range |
Examples |
|
Low GI |
55 or less |
Whole grains, lentils, most vegetables |
|
Medium GI |
56-69 |
Brown rice, sweet potatoes, whole wheat bread |
|
High GI |
70 or more |
White bread, sugary cereals, processed snacks |
How the Glycemic Index Affects Blood Sugar?
When we eat carbohydrates, they are broken down into glucose, which enters the bloodstream. High-GI foods are digested and absorbed quickly, leading to a sharp increase in blood sugar and insulin levels. In contrast, low-GI foods provide a more gradual release of glucose, helping to maintain stable energy levels and reducing the risk of blood sugar spikes and crashes.
For individuals with diabetes, choosing low glycemic index foods for diabetics can help improve blood sugar control and insulin sensitivity.
Glycemic Index vs. Glycemic Load: What’s the Difference?
While the Glycemic Index indicates how quickly a food raises blood sugar, Glycemic Load (GL) considers both the GI and the amount of carbohydrates in a serving. This distinction is important because some foods with a high GI, such as watermelon, have a low GL due to their low carbohydrate content per serving. Understanding both GI and GL can help in making more balanced dietary choices.
Why the Glycemic Index Matters for Diabetes Management
The diabetes glycemic index is a valuable tool for managing blood sugar levels. Consuming low-GI foods can offer several benefits, including:
-
Better blood sugar control: Prevents sudden glucose spikes and crashes.
-
Improved insulin sensitivity: Reduces the body's need for excess insulin.
-
Reduced risk of complications: Helps prevent long-term issues like heart disease and nerve damage.
-
Increased satiety: Keeps you fuller for longer, aiding in weight management.
More Reads: Spreading Awareness and Offering Access to Diabetes Care
List of Low, Medium, and High GI Foods
Low GI Foods (Best Choices)
-
Whole grains (quinoa, barley, oats)
-
Legumes (lentils, chickpeas, black beans)
-
Vegetables (broccoli, spinach, bell peppers)
-
Fruits (apples, pears, berries)
-
Nuts and seeds
Medium GI Foods
-
Brown rice
-
Sweet potatoes
-
Whole wheat pasta
-
Corn
-
Bananas
High GI Foods (Limit These)
-
White bread
-
White rice
-
Sugary cereals
-
Soft drinks
-
Processed snacks
More Reads: Top Ways to Boost Your Immune System
Factors That Influence a Food’s GI
Several factors affect the Glycemic Index of a food, including:
|
Factor |
Impact on GI |
|
Cooking Methods |
Boiling lowers GI, while frying or roasting raises it |
|
Processing |
Highly processed foods generally have a higher GI |
|
Fiber Content |
High-fiber foods slow digestion, reducing GI |
|
Ripeness |
Riper fruits tend to have a higher GI |
|
Food Combinations |
Pairing with proteins or fats lowers overall GI |
Practical Tips for a Low-GI Diet
Adopting a low-GI diet can be simple with these strategies:
-
Choose whole grains over refined grains: Opt for quinoa, brown rice, and whole wheat bread instead of white bread and white rice.
-
Incorporate more fiber-rich foods: Fiber slows down digestion and stabilizes blood sugar levels.
-
Pair carbs with protein or healthy fats: Adding nuts, seeds, or lean proteins to a meal can lower the GI effect.
-
Eat more non-starchy vegetables: Vegetables like spinach, kale, and cucumbers have a minimal impact on blood sugar.
-
Avoid sugary drinks and processed foods: These often have high GI values and can cause rapid spikes in blood sugar.
-
Monitor portion sizes: Even low-GI foods can cause blood sugar spikes if consumed in large quantities.
Myths and Misconceptions About GI
Despite its usefulness, the diabetes glycemic index is often misunderstood. Here are some common myths:
-
Myth 1: GI is the only factor that matters in a healthy diet. In reality, factors like overall nutrition, portion control, and meal balance also play crucial roles.
-
Myth 2: All high-GI foods should be avoided. Some high-GI foods, such as carrots and watermelon, can still be part of a balanced diet when eaten in moderation.
-
Myth 3: Low-GI foods are always healthy. Some low-GI foods, like chocolate and ice cream, contain unhealthy fats and sugars.
The Role of GI in Weight Management and Overall Health
A low glycemic index diet is not only beneficial for diabetes management but also supports overall health by:
-
Reducing the risk of heart disease
-
Supporting weight loss and weight maintenance
-
Enhancing energy levels throughout the day
-
Lowering cholesterol levels
Balancing GI with a Holistic Approach to Health
While the Glycemic Index is a useful tool for managing diabetes, it should be combined with other healthy habits such as regular exercise, balanced nutrition, and portion control. Consulting an endocrinologist or a dietitian can provide personalized guidance for glycemic index diabetes management.
Expert Diabetes Care at Manipal Hospital Jaipur
For expert diabetes care and personalised dietary guidance, visit Manipal Hospital Jaipur. Our team of experienced endocrinologists and nutritionists provide comprehensive diabetes management solutions, including meal planning with low glycemic index foods for diabetics. Whether you are newly diagnosed or looking for better blood sugar control, we are here to support your health journey. Schedule a consultation today and take charge of your diabetes management with confidence!



















 6 Min Read
6 Min Read













