
Joint pain can be debilitating, affecting your ability to perform everyday activities and diminishing your quality of life. Intra-articular injections have emerged as a promising treatment option for managing joint pain, offering targeted relief and improving joint function. In this blog, we will explore the top five benefits of intra-articular injections for joint pain.
Synopsis
What is Intra-Articular?
The intra-articular injection procedure is used to deliver medication directly for joint pain relief and inflammation. These injections are commonly used to treat conditions such as osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, bursitis, and tendonitis.
Benefits of Intra-Articular Injections for Joint Pain
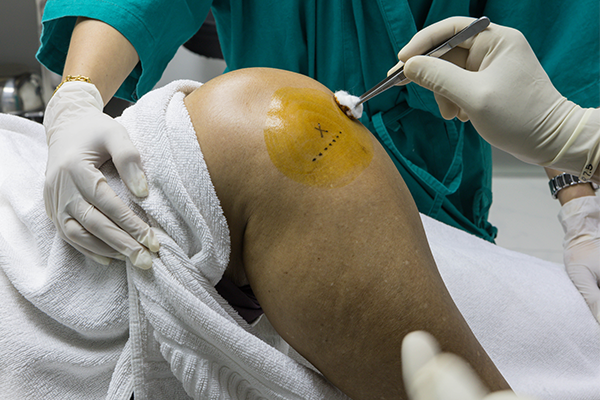
1. Targeted Pain Relief
One of the most significant advantages of intra-articular injections is their ability to deliver medication directly to the affected joint. This targeted approach ensures that the medication reaches the precise location where it is needed, providing localized and effective pain relief. Unlike oral medications, which must travel through the bloodstream and may cause systemic side effects, intra-articular injections focus solely on the problematic joint, minimizing the risk of adverse effects.
There are several types of intra-articular injections commonly used to treat joint-related conditions, each offering unique benefits for patients. The most common types include corticosteroid injections, which help reduce inflammation and pain; hyaluronic acid injections, used to lubricate the joint and improve mobility in conditions like osteoarthritis; platelet-rich plasma (PRP) injections, which promote healing by utilizing the body’s growth factors; and stem cell injections, which stimulate tissue regeneration and repair. These injections are tailored to address specific joint issues and provide relief for conditions such as arthritis, tendonitis, and joint stiffness.
2. Reduced Inflammation
Inflammation is a common cause of joint pain and stiffness. Intra-articular injections can help reduce inflammation in the affected joint, leading to improved comfort and mobility. Corticosteroids, one of the most frequently used medications in these injections, are potent anti-inflammatory agents that can quickly alleviate swelling and pain.
In addition to corticosteroids, other medications such as hyaluronic acid and platelet-rich plasma (PRP) can also be used to reduce inflammation. Hyaluronic acid injections, for example, help lubricate the joint, reducing friction and inflammation. PRP injections, derived from the patient's blood, contain growth factors that promote healing and reduce inflammation.
Here’s a short table of the Risks and Side Effects of intra-articular injections:
|
Type of Injection |
Common Risks and Side Effects |
|
Corticosteroid Injections |
Infection, joint damage, increased blood sugar, thinning of skin, allergic reactions |
|
Hyaluronic Acid Injections |
Mild pain or swelling at the injection site, allergic reactions, joint stiffness |
|
Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP) |
Swelling, pain, infection, bruising, rare nerve injury |
|
Stem Cell Injections |
Infection, allergic reactions, swelling, pain at the injection site |
3. Improved Mobility and Quality of Life
Joint pain can severely limit your ability to move and perform daily activities. Intra-articular injections can help improve joint mobility by reducing pain and inflammation. Patients often report an increased range of motion and greater ease in performing tasks such as walking, climbing stairs, and participating in physical activities.
Improved joint function can have a profound impact on your overall quality of life. By alleviating pain and enhancing mobility, intra-articular injections enable you to engage in activities you enjoy, maintain an active lifestyle, and reduce the risk of further joint damage.
Here’s a table for the section on Medications Utilized in Intra-Articular Injections:
|
Medication |
Primary Use |
Benefits |
Common Conditions Treated |
|
Corticosteroids (e.g., Methylprednisolone) |
Reduces inflammation and pain |
Provides fast relief from pain and inflammation |
Osteoarthritis, Rheumatoid Arthritis, Bursitis, Tendonitis |
|
Hyaluronic Acid (e.g., Synvisc, Hyalgan) |
Lubricates the joint and improves mobility |
Helps restore normal joint function and reduces pain by lubricating the joint |
Osteoarthritis, Joint Stiffness, Synovitis |
|
Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP) |
Stimulates tissue repair and regeneration |
Promotes healing by utilizing the body's growth factors |
Chronic Tendonitis, Ligament Injuries, Arthritis |
|
Stem Cell Therapy |
Promotes regeneration of joint tissues |
Accelerates healing and tissue repair |
Osteoarthritis, Cartilage Defects, Joint Degeneration |
|
Local Anesthetics (e.g., Lidocaine) |
Provides immediate pain relief |
Relieves acute pain and discomfort in the joint |
Joint Injuries, Post-Surgical Pain, Inflammation |
|
Biologic Therapies (e.g., Prolotherapy) |
Stimulates tissue healing |
Enhances natural healing processes and tissue regeneration |
Chronic Ligament or Tendon Injury, Arthritis |
These medications are commonly used in intra-articular injections to treat various joint-related conditions and are proven to be effective in reducing pain, inflammation, and promoting healing. Each medication offers unique benefits depending on the condition being treated.
4. Minimally Invasive Procedure
Intra-articular injections are minimally invasive, meaning they can be performed in an outpatient setting with minimal recovery time. The procedure involves using a fine needle to inject medication directly into the joint space, guided by imaging techniques such as ultrasound or fluoroscopy to ensure accuracy.
The minimally invasive nature of intra-articular injections means that patients can often return to their normal activities shortly after the procedure. There is no need for extensive downtime or prolonged recovery periods, making these injections a convenient option for managing joint pain.
5. Variety of Medications Used
Intra-articular injections offer versatility in terms of the medications that can be used, allowing for personalized treatment plans tailored to the specific needs of each patient. Some of the most commonly used medications include:
-
Corticosteroids: These powerful anti-inflammatory agents provide rapid relief from pain and swelling. They are particularly effective for treating acute flare-ups of inflammatory joint conditions.
-
Hyaluronic Acid: This naturally occurring substance helps lubricate and cushion the joint, reducing friction and improving joint function. Hyaluronic acid injections are often used for osteoarthritis patients to enhance joint lubrication and reduce pain.
-
Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP): PRP injections utilize the patient's blood, which is processed to concentrate platelets and growth factors. These injections promote healing, reduce inflammation, and stimulate tissue regeneration, making them a valuable option for patients with chronic joint pain.
-
Biologic Agents: In some cases, biologic agents such as tumour necrosis factor (TNF) inhibitors or interleukin inhibitors may be used to target specific inflammatory pathways. These medications can be particularly beneficial for patients with autoimmune joint conditions like rheumatoid arthritis.
Consult our Orthopaedics Experts in Jaipur if you are experiencing pain and get treatment.
Procedure and Technique: Step-by-Step Overview of Intra-Articular Injections
Intra-articular injections are a minimally invasive procedure used to deliver medication directly into a joint to relieve pain and inflammation. Here is a step-by-step overview of the injection procedure, including preparation, imaging guidance, and post-injection care:
1. Preparation
-
Patient Assessment: The healthcare provider will review the patient's medical history, current medications, and any allergies. A physical examination of the affected joint will also be conducted.
-
Informed Consent: The patient will be informed about the procedure, its benefits, potential risks, and alternatives. Informed consent will be obtained.
-
Sterilization: The injection site will be cleaned and sterilized to reduce the risk of infection. This typically involves using an antiseptic solution to cleanse the skin around the joint.
2. Imaging Guidance
-
Positioning: The patient will be positioned comfortably to allow easy access to the joint. Depending on the joint being treated, the patient may be lying down, sitting, or standing.
-
Imaging Techniques: To ensure accurate needle placement, imaging techniques such as ultrasound or fluoroscopy may be used. These imaging methods provide real-time visualization of the joint and guide the healthcare provider during the injection.
-
Ultrasound: A handheld device called a transducer is used to produce images of the joint. The transducer is placed on the skin, and the images are displayed on a monitor.
-
Fluoroscopy: This technique uses X-rays to create live images of the joint. A contrast dye may be injected to enhance the visibility of the joint structures.
3. Injection Procedure
-
Local Anesthesia: A local anaesthetic may be administered to numb the injection site and minimize discomfort during the procedure.
-
Needle Insertion: Using the imaging guidance, the healthcare provider will insert a fine needle into the joint space. The needle is carefully advanced to the precise location within the joint.
-
Medication Injection: Once the needle is in place, the medication is injected into the joint. The type of medication used will depend on the patient's condition and treatment plan. Common medications include corticosteroids, hyaluronic acid, and platelet-rich plasma (PRP).
-
Needle Removal: After the medication is injected, the needle is carefully removed. Pressure may be applied to the injection site to prevent bleeding.
4. Post-Injection Care
-
Observation: The patient may be observed for a short period to ensure there are no immediate adverse reactions to the injection.
-
Activity Restrictions: Patients are usually advised to avoid strenuous activities and heavy lifting for 24-48 hours after the injection. Gentle movement and light activities are generally encouraged to maintain joint mobility.
-
Pain Management: Mild pain or discomfort at the injection site is common and can be managed with over-the-counter pain relievers, such as acetaminophen or ibuprofen. Applying an ice pack to the area can also help reduce swelling and pain.
-
Follow-Up: The healthcare provider will schedule a follow-up appointment to assess the patient's response to the injection and determine if additional treatments are needed. Patients should report any unusual symptoms, such as increased pain, swelling, or signs of infection, to their healthcare provider immediately.
By following these steps, intra-articular injections can be performed safely and effectively, providing significant relief from joint pain and improving overall joint function.
Here's a table comparing the effectiveness and benefits of intra-articular injections with other joint pain treatments, such as oral medications, physical therapy, and surgery:
|
Treatment |
Effectiveness |
Benefits |
Considerations |
|
Intra-Articular Injections |
- Provides targeted pain relief |
- Minimally invasive |
- Temporary relief |
|
Oral Medications |
- Effective for mild to moderate pain |
- Easy to administer |
- Systemic side effects (e.g., gastrointestinal issues) |
|
Physical Therapy |
- Improves joint function |
- Non-invasive |
- Requires regular sessions |
|
Surgery |
- Effective for severe joint damage |
- Can provide significant pain relief |
- Invasive procedure |
Conclusion
Intra-articular injections offer a range of benefits for individuals suffering from joint pain. By providing targeted pain relief, reducing inflammation, improving mobility, and offering a minimally invasive treatment option, these injections can significantly enhance your quality of life. With a variety of medications available, healthcare providers can tailor treatment plans to meet the unique needs of each patient, ensuring optimal outcomes.
If you are experiencing joint pain and are considering intra-articular injections, consult with the expert orthopaedic doctors at Manipal Hospital Jaipur. Renowned for their advanced medical care and patient-centric approach, the orthopaedic specialists at Manipal Hospital Jaipur are dedicated to helping you regain control of your joint health and enjoy a more active, pain-free life.
FAQ's
Intra-articular injections are a procedure used to deliver medication directly into a joint to relieve pain and inflammation. They are commonly used to treat conditions like osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, and tendonitis. By targeting the specific joint, these injections provide localized pain relief without the systemic side effects often associated with oral medications.
The primary benefits include targeted pain relief, reduced inflammation, improved mobility, a minimally invasive procedure, and the use of a variety of medications that can be tailored to the patient's needs. These injections help reduce pain and stiffness, allowing patients to regain mobility and improve their quality of life.
Common medications used in intra-articular injections include corticosteroids (for inflammation), hyaluronic acid (for lubrication), platelet-rich plasma (PRP) (to promote healing), and stem cell injections (to regenerate joint tissue). Each medication serves a unique purpose and is chosen based on the patient's specific condition.
While generally safe, intra-articular injections can carry risks such as infection, joint damage, increased blood sugar (with corticosteroids), allergic reactions, and localized pain or swelling at the injection site. It is important to discuss these potential risks with your healthcare provider before undergoing the procedure.
Intra-articular injections are minimally invasive, meaning recovery time is usually quick. Patients can often return to normal activities shortly after the procedure, with only minor discomfort at the injection site. It is recommended to avoid strenuous activities for 24-48 hours following the injection to ensure proper healing.



















 10 Min Read
10 Min Read


















