
Vitamin A is a vital nutrient that plays a crucial role in maintaining good vision, a strong immune system, and healthy skin. However, vitamin A deficiency diseases are still prevalent, affecting millions worldwide. A lack of Vitamin A can lead to severe health issues, including vision problems, skin disorders, and weakened immunity. In this blog, we will explore the deficiency of vitamin A, which causes disease, symptoms, risks, and treatment options to ensure you are getting enough of this essential nutrient.
Synopsis
- Why Is Vitamin A Essential?
- Types of Vitamin A: Retinol vs. Beta-Carotene
- Symptoms of Vitamin A Deficiency
- Diseases Caused by Vitamin A Deficiency
- How Much Vitamin A Do You Need? (Daily Recommended Intake)
- Best Food Sources of Vitamin A
- Can You Get Too Much Vitamin A? (Toxicity Risks)
- Who Is Most at Risk for Vitamin A Deficiency?
- Vitamin A Deficiency Treatment
- Conclusion
Why Is Vitamin A Essential?
Vitamin A is a fat-soluble vitamin that supports various bodily functions, including:
-
Vision Health: It helps maintain the retina and prevents night blindness.
-
Immune System Boost: Strengthens the body’s defense against infections.
-
Skin and Cell Growth: Promotes healthy skin, wound healing, and reproduction.
-
Organ Function: Supports the heart, lungs, and kidney function.
A deficiency of Vitamin A can lead to serious health complications, making it essential to consume adequate amounts daily.
Types of Vitamin A: Retinol vs. Beta-Carotene
There are two primary forms of Vitamin A:
-
Retinol (Preformed Vitamin A): Found in animal products like liver, eggs, and dairy.
-
Beta-Carotene (Provitamin A): Found in plant-based sources like carrots, spinach, and sweet potatoes. The body converts beta-carotene into Vitamin A as needed.
Understanding these sources can help in maintaining a well-balanced diet to prevent vitamin A deficiency diseases.
Symptoms of Vitamin A Deficiency
Early detection of vitamin A deficiency diseases symptoms can help prevent serious health issues. Some common signs include:
-
Night Blindness: Difficulty seeing in low light conditions.
-
Dry Eyes (Xerophthalmia): Lack of tear production leading to corneal damage.
-
Rough and Dry Skin: Skin becomes flaky, rough, and prone to infections.
-
Weakened Immunity: Frequent infections due to a compromised immune system.
-
Delayed Growth: In children, Vitamin A deficiency can lead to stunted growth and developmental delays.
If you experience any of these symptoms, it’s important to seek medical advice and increase your intake of Vitamin A-rich foods.
Diseases Caused by Vitamin A Deficiency
The deficiency of vitamin A causes disease conditions that can severely impact health. Some of the major diseases include:
1. Xerophthalmia (Severe Dry Eye Disorder)
-
One of the leading causes of preventable blindness worldwide.
-
Starts with night blindness and progresses to corneal ulceration if untreated.
2. Increased Risk of Infections
-
Vitamin A deficiency weakens the immune system, making individuals prone to respiratory infections, measles, and diarrhea.
3. Keratinization of Skin
-
Skin cells harden, leading to rough and scaly patches.
4. Growth Retardation in Children
-
Lack of Vitamin A affects bone development and overall growth in children.
5. Pregnancy Complications
-
Deficiency increases the risk of maternal mortality and birth defects in newborns.
How Much Vitamin A Do You Need? (Daily Recommended Intake)
The recommended daily intake of Vitamin A varies by age and gender:
-
Infants (0-12 months): 400-500 mcg
-
Children (1-8 years): 300-400 mcg
-
Men (14+ years): 900 mcg
-
Women (14+ years): 700 mcg
-
Pregnant Women: 770 mcg
-
Lactating Mothers: 1,200 mcg
Ensuring sufficient intake through diet or supplements can help avoid vitamin A deficiency disease symptoms.
Best Food Sources of Vitamin A
To prevent deficiency, include these Vitamin A-rich foods in your diet:
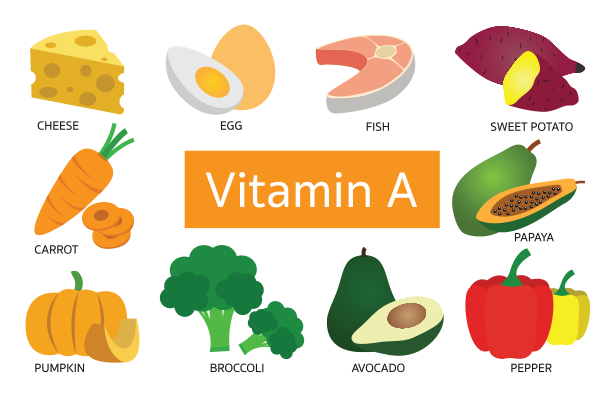
-
Animal Sources: Beef liver, fish, dairy products, eggs.
-
Plant Sources: Carrots, sweet potatoes, spinach, kale, mangoes, and bell peppers.
A balanced diet with a variety of these foods ensures you get the required Vitamin A naturally.
Can You Get Too Much Vitamin A? (Toxicity Risks)
While Vitamin A deficiency is dangerous, excess Vitamin A can also cause toxicity. Symptoms include:
Avoid excessive supplementation unless prescribed by a doctor.
Who Is Most at Risk for Vitamin A Deficiency?
Certain groups are more prone to vitamin A deficiency diseases:
-
Infants and Young Children
-
People with Digestive Disorders (Crohn’s, Celiac Disease, Liver Disease)
-
Vegans and Those with Poor Diets
Vitamin A Deficiency Treatment
The vitamin A deficiency diseases treatment options include:
|
Treatment |
Description |
|
Dietary Changes |
Increase intake of Vitamin A-rich foods. |
|
Vitamin A Supplements |
Prescribed for severe deficiencies. |
|
Fortified Foods |
Consuming foods fortified with Vitamin A, such as milk and cereals. |
|
Medical Intervention |
In cases of severe deficiency, doctors may administer high-dose Vitamin A therapy. |
Conclusion
If you suspect vitamin A deficiency disease symptoms, consult experts at Manipal Hospital. Our specialists provide comprehensive diagnosis and treatment plans to help you achieve optimal health. Schedule a consultation today to ensure you are getting the right nutrients for a healthy life.
Stay informed, eat well, and take care of your health!
FAQ's
A blood test measuring retinol levels can confirm deficiency. Consult a doctor for an accurate diagnosis.
Yes, it helps maintain good eyesight and prevents night blindness, but it does not cure existing vision problems like nearsightedness.
Yes, with proper diet and supplementation, symptoms can improve significantly.
Only if prescribed by a doctor. Excess Vitamin A can be harmful.
Increase consumption of Vitamin A-rich foods and take supplements if necessary.



















 5 Min Read
5 Min Read









