
A brain stroke is a serious medical condition that occurs when the blood supply to a part of the brain is disrupted or reduced, preventing brain tissue from getting the oxygen and nutrients it needs. Early detection and prompt treatment can help save lives and reduce the effects of brain damage. Understanding the symptoms, causes, and available treatments is crucial to managing this life-threatening condition.
Synopsis
What is a Brain Stroke?
The simplest brain stroke definition is the interruption of blood flow to the brain, leading to brain cell death. There are two main types of brain strokes:
-
Ischemic Stroke: Caused by a blockage in an artery supplying blood to the brain. This type accounts for the majority of strokes.
-
Hemorrhagic Stroke: Occurs when a blood vessel in the brain bursts, causing bleeding into or around the brain.
Another condition, known as a Transient Ischemic Attack (TIA) or mini-stroke, is a temporary period of symptoms similar to those of a stroke but does not cause permanent damage.
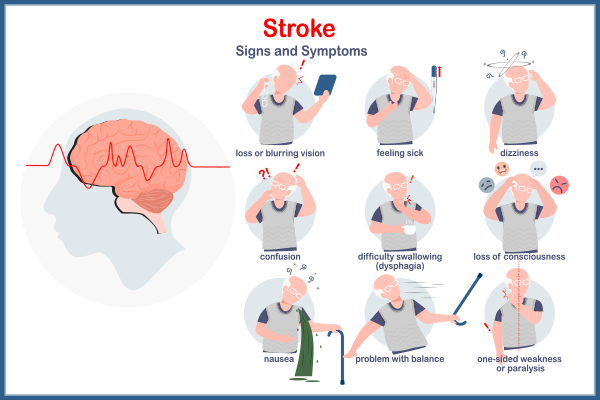
Symptoms of Brain Stroke
Recognizing the symptoms of a brain stroke early is critical for prompt medical attention. Use the acronym FAST as a quick reference:
-
Face: Does one side of the face droop?
-
Arms: Is one arm weak or numb?
-
Speech: Is speech slurred or difficult to understand?
-
Time: If any of these symptoms are present, call emergency services immediately.
Additional symptoms may include:
-
Sudden confusion or trouble understanding
-
Loss of coordination or balance
-
Sudden severe headache
-
Blurred or double vision
Reasons for Brain Stroke
Understanding the reasons for brain stroke is essential for prevention. The following factors may contribute:
-
High Blood Pressure: The leading risk factor for stroke, high blood pressure can damage arteries over time.
-
Smoking: Increases blood clot formation and narrows blood vessels.
-
Diabetes: High blood sugar can damage blood vessels, increasing stroke risk.
-
Heart Disease: Conditions like atrial fibrillation can cause blood clots to form, leading to a stroke.
-
Obesity: Excess weight is linked to several risk factors, including high cholesterol and hypertension.
-
Sedentary Lifestyle: Lack of exercise contributes to obesity, high blood pressure, and diabetes.
Also Read: World Stroke Day: All About Identifying a Stroke and the Right Treatment
Brain Stroke Causes Table
|
Type of Stroke |
Cause |
|
Ischemic Stroke |
Blood clot or narrowing of arteries |
|
Hemorrhagic Stroke |
Ruptured blood vessel or aneurysm |
|
Transient Ischemic Attack |
Temporary clot or blockage in blood flow |
Are Strokes Painful?
A common question is, “Are strokes painful?” This depends on the type and severity of the stroke.
Effects of a Brain Stroke
The brain stroke effects can vary widely depending on the severity and part of the brain affected:
-
Physical Effects: Weakness or paralysis on one side of the body, difficulty walking, and loss of coordination.
-
Cognitive Effects: Memory loss, difficulty concentrating, and problems with decision-making.
-
Emotional Effects: Depression, anxiety, and mood swings.
-
Speech and Language Issues: Difficulty speaking, understanding language, or reading and writing.
Treatment for Brain Stroke
Early brain stroke treatment is essential to minimize damage. Treatment options vary depending on the type of stroke.
1. Treatment for Ischemic Stroke
-
Thrombolytic Therapy (tPA): A clot-busting drug that dissolves the clot blocking the blood flow to the brain. It must be administered within 3-4.5 hours of symptom onset.
-
Mechanical Thrombectomy: A procedure to physically remove the clot using a catheter.
-
Antiplatelet and Anticoagulant Medications: These help prevent new clots from forming.
2. Treatment for Hemorrhagic Stroke
-
Blood Pressure Management: Medications to lower blood pressure and reduce the risk of further bleeding.
-
Surgical Procedures: In some cases, surgery is needed to repair the ruptured blood vessel or remove pooled blood.
-
Aneurysm Clipping or Coiling: These procedures help seal off a weakened blood vessel.
Lifestyle Changes to Prevent Brain Stroke
Prevention is key. Lifestyle changes can help reduce the risk:
-
Maintain a Healthy Diet: Focus on fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and low-fat dairy.
-
Exercise Regularly: Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate exercise per week.
-
Quit Smoking: Seek help if necessary to stop smoking.
-
Control Blood Pressure: Regular monitoring and medication can help keep blood pressure in check.
-
Manage Diabetes: Keep blood sugar levels under control with a proper diet and medication.
Brain Stroke Recovery Table
|
Recovery Area |
Support Options |
|
Physical Therapy |
Regain strength and mobility |
|
Speech Therapy |
Improve communication and language skills |
|
Occupational Therapy |
Relearn daily tasks and activities |
|
Emotional Support |
Counselling and stroke support groups |
Conclusion
Understanding the symptoms, causes, and treatments of a brain stroke is crucial for timely intervention and recovery. By making informed lifestyle choices and seeking prompt medical care, you can reduce the risk of strokes and improve overall brain health.
For advanced stroke care and comprehensive medical support, visit Manipal Hospital Kharadi. Their expert team is dedicated to providing top-notch Neurology treatment and rehabilitation services, ensuring the best outcomes for patients.
To learn more about comprehensive stroke care, visit our speciality page.
FAQ's
High blood pressure, smoking, and diabetes are leading causes of brain stroke.
Yes, adopting a healthy lifestyle with regular exercise, a balanced diet, and proper medical management can lower the risk.
Strokes can cause headaches or discomfort, especially hemorrhagic strokes, which are often accompanied by intense headaches.
Recovery varies widely, from weeks to months or even years, depending on the severity of the stroke and rehabilitation efforts.
Call emergency services immediately if you notice symptoms like facial drooping, arm weakness, or speech difficulties.



















 5 Min Read
5 Min Read


















