
The human heart is a remarkable organ that tirelessly pumps blood throughout the body. However, sometimes due to various conditions, it needs a helping hand. This is where cardiac surgery steps in, offering a range of procedures to address heart ailments. Among these, open heart and bypass surgery are two of the most commonly performed. While both sound similar, they have district purposes and approaches. Let’s delve into the world of open heart surgery vs. bypass surgery, clearing up the confusion and empowering with the conditions necessitating each and the associated risks.
Synopsis
- What is Open Heart Surgery and its Procedure?
- Conditions Requiring Open Heart Surgery
- Risks Associated with Open Heart Surgery
- What is Bypass Surgery and Its Procedures?
- Conditions Requiring Bypass Surgery
- Complications Associated with Bypass Surgery
- What is the Average Life Expectancy After Bypass Surgery?
- How Serious Is Bypass Surgery?
- Differences Between Bypass and Open Heart Surgery
- Bypass and Open-Heart Surgery Side Effects
- What Is the Survival Rate of Bypass vs. Open-Heart Surgery?
- How to Take Care of Patients After Both Surgeries?
- Post-Surgery Care
- Key Takeaway
What is Open Heart Surgery and its Procedure?
Open heart surgery refers to any surgical procedure where the chest is opened, and surgery is performed on the heart muscles, valves, arteries, or other heart structures. The most common type of open heart surgery is coronary artery bypass grafting (CABG), but the term can also encompass procedures such as valve replacement, heart transplant, or repair of congenital heart defects.
The procedure of open heart surgery:
Open Heart surgery is a complex procedure that takes four to five hours based on the complications and requirements. The procedure usually includes the following steps:
-
Anaesthesia: General anaesthesia is administered to ensure the patient is unconscious and pain-free.
-
Incision: A small incision is made in the chest, and the breastbone is carefully divided to access the heart.
-
Cardiopulmonary Bypass: During surgery, the heart may be stopped and a heart-lung machine will circulate blood and oxygen.
-
Surgical Repair: The specific heart problem is addressed, whether it’s grafting arteries in CABG, replacing a valve, or correcting a defect.
-
Closing the Incision: The chest incision is closed with sutures or staples after the heart is restarted and the heart-lung machine is disconnected
Conditions Requiring Open Heart Surgery
Open heart surgery is performed to treat several critical conditions, such as:
-
Coronary artery disease: Blockages in the coronary arteries that can lead to heart attacks.
-
Heart valve disease: Malfunctioning heart valves that need repair or replacement.
-
Congenital heart defects: A birth defect that causes structural problems with the heart.
-
Heart failure: A condition when the heart doesn’t pump sufficient blood.
-
Aneurysms: Bulging sections of the heart or aorta that need repair.
Risks Associated with Open Heart Surgery
Like any major surgery, open heart surgery carries some significant risks. The chances of having these complications are greater if one has obesity, diabetes COPD. Some of them are listed below:
-
Infection: Particularly at the incision site.
-
Bleeding: During or after the surgery.
-
Stroke: Caused by blood clots.
-
Heart attack: Especially if the surgery involves the coronary arteries.
-
Lung or kidney failure: Due to the stress of the surgery.
-
Arrhythmias: Irregular heartbeats.
What is Bypass Surgery and Its Procedures?
Heart bypass surgery, also known as coronary artery bypass grafting (CABG), is a type of open heart surgery aimed at improving blood flow to the heart. It involves grafting a healthy artery or vein from another part of the body to bypass blocked or narrowed coronary arteries.
The procedure includes
-
Anaesthesia: General anaesthesia will be administered to make the procedure pain-free. A breathing tube will also be placed into the windpipe.
-
Incision: A small incision will be made to open the chest, similar to other open heart surgeries.
-
Cardiopulmonary Bypass: Often used, but off-pump or “beating heart” surgery is also possible.
-
Grafting: A healthy artery or vein is harvested (commonly from the leg or chest) and attached to the coronary artery above and below the blocked area.
-
Closing the Incision: The heart is restarted if it is stopped, and the chest is closed.
Conditions Requiring Bypass Surgery
Bypass surgery may be considered for individuals who suffer from the following conditions:
-
Severe coronary artery blockage: When significant blockages limit blood flow to the heart, causing symptoms like chest pain (angina) or heart attacks, bypass surgery can improve blood supply and reduce the risk of future events.
-
Failed Angioplasty: If minimally invasive procedures like angioplasty (balloon opening of blocked arteries) fail to adequately improve blood flow, bypass surgery might be the next step.
Complications Associated with Bypass Surgery
Bypass surgery can result in various complications. Here are a few risks of bypass surgery-
-
Infection: At the incision site or graft site.
-
Bleeding: During or after the procedure.
-
Kidney problems: Due to the stress of the surgery.
-
Memory loss or cognitive decline: Especially in older patients.
-
Arrhythmias: Postoperative irregular heart rhythms.
Consult our cardiothoracic surgery hospital in Pune if you need to know more about the complications of coronary artery bypass surgery.
What is the Average Life Expectancy After Bypass Surgery?
The average life expectancy after bypass surgery largely depends on factors like overall health, age, lifestyle choices, and how well the patient follows post-surgery care. Studies suggest that patients who undergo successful coronary artery bypass grafting (CABG) can live for 10-15 years or even longer if they manage risk factors like smoking, high blood pressure, and diabetes. Regular check-ups and a heart-healthy lifestyle can significantly improve life expectancy.
How Serious Is Bypass Surgery?
Bypass surgery is considered a serious procedure, yet it is also a common one. The seriousness depends on the patient's condition and whether they have other health issues. However, the success rate for bypass surgery is high. It also can greatly improve the quality of life.
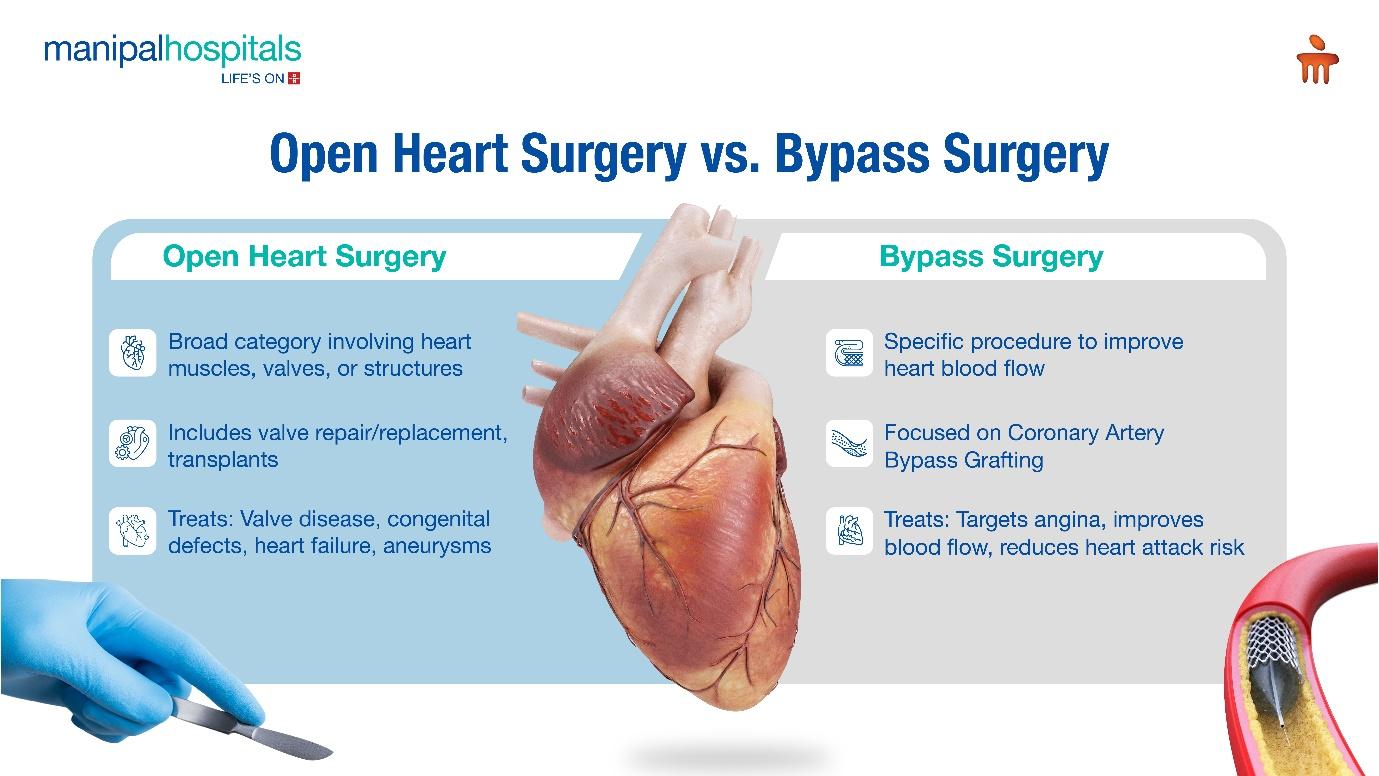
Differences Between Bypass and Open Heart Surgery
Both, open heart surgery and bypass surgery are performed to relieve heart conditions:
-
Open heart surgery is a broad category of surgery where the chest is opened to operate on the heart muscles, valves, arteries, or other heart structures. It includes procedures such as valve repair or replacement, heart transplants, congenital defect repairs and more. Bypass surgery focuses on improving blood flow to the heart. It primarily involves coronary artery bypass grafting (CABG), where blocked coronary arteries are bypassed using a graft from another part of the body.
-
Open heart surgery treats a variety of heart conditions, including valve disease, congenital defects, heart failure, and aneurysms. It addresses structural issues of the heart and improves overall heart function. Bypass surgery specifically targets coronary artery diseases, aiming to relieve angina, improve blood flow, and reduce the risk of heart attacks.
-
Open heart surgery involves an incision in the chest, stopping the heart, and using a heart-lung machine to maintain circulation. It can include multiple types of repairs or replacements depending on the specific heart condition being treated. Bypass surgery also involves a chest incision and may use a heart-lung machine, but it can also be done on a beating heart.
Here is a comparison of the key differences between open heart surgery and bypass surgery:
|
Open Heart Surgery |
Bypass Surgery |
|---|---|
|
Broad category of surgery where the chest is opened to operate on heart muscles, valves, arteries, or structures. |
Specific type of open heart surgery focused on improving blood flow to the heart. |
|
Valve repair/replacement, heart transplants, congenital defect repairs, and more. |
Primarily coronary artery bypass grafting (CABG). |
|
Valve disease, congenital defects, heart failure, aneurysms. |
Aims to relieve angina, improve blood flow, and reduce the risk of heart attacks. |
|
Uses a heart-lung machine to maintain circulation by stopping the heart. |
May use the heart-lung machine but can also be done on a beating heart. |
|
Multiple types of repairs or replacements depending on the specific heart condition. |
Grafting a healthy artery or vein to bypass blocked coronary arteries. |
|
Treats a variety of heart conditions. |
Focuses on bypassing blocked coronary arteries to improve blood flow. |
|
Requires a comprehensive recovery and cardiac rehabilitation program. |
Similar recovery and rehabilitation program, focusing on maintaining graft patency and managing CAD. |
Consult our cardiothoracic surgeon in Pune if you need a bypass procedure or open heart surgery.
Bypass and Open-Heart Surgery Side Effects
Both bypass surgery and open-heart surgery come with potential side effects. These may include:
-
Pain and Discomfort: Some people experience pain at the site of incisions and in the chest after surgery.
-
Fatigue: After surgery, patients may feel tired and weak for several weeks.
-
Swelling: Leg or chest swelling may occur if veins were used for grafting.
-
Arrhythmias: Irregular heartbeats are a common short-term side effect after heart surgeries.
-
Infection: Incisions are prone to infection.
-
Cognitive Issues: Some patients report memory problems or confusion, often referred to as "postperfusion syndrome" or "pumphead," especially after open-heart surgery.
What Is the Survival Rate of Bypass vs. Open-Heart Surgery?
The survival rate for both bypass and open-heart surgery is generally high, especially when performed in high-quality medical centres. For bypass surgery, the ten-year survival rate is around 77-90%, depending on the patient's overall health. Open-heart surgery, which includes procedures like valve replacements, also boasts a strong survival rate, usually over 82-94%. However, it depends entirely on the patient's age and health condition. In both cases, outcomes improve when patients adhere to post-surgery care instructions.
How to Take Care of Patients After Both Surgeries?
Post-surgery care is essential for both bypass and open-heart surgery patients. Here are some important steps:
-
Medication: Patients must follow their prescribed medication schedule to manage pain, prevent blood clots, and regulate heart function.
-
Diet: A heart-healthy diet low in salt, cholesterol, and saturated fats is critical. Nutrient-rich foods help with recovery.
-
Physical Activity: Light exercise, such as walking, is recommended, but patients must avoid strenuous activity until cleared by the doctor.
-
Emotional Support: It’s common for patients to feel anxious or depressed post-surgery, so emotional and psychological support is vital.
Post-Surgery Care
Recovery Process
It usually takes 6-12 weeks for bypass surgery patients to recover, while open-heart patients may need around 12 weeks to recover. During this period, patients should gradually increase their physical activity under medical supervision. Driving, heavy lifting, and strenuous activities should be avoided until the surgeon approves. For both surgeries, it’s important to follow up with your doctor regularly to monitor heart health, blood pressure, and the effectiveness of medications.
Patient Care Tips
-
Monitor symptoms such as chest pain, shortness of breath, or swelling in the leg.
-
Offer emotional support to help the patient stay positive.
-
Ensure a balanced heart-healthy diet.
-
Enrol the patient in a cardiac rehabilitation program to improve cardiovascular health.
Key Takeaway
Understanding the difference between bypass procedures and open heart surgery is crucial for patients facing these procedures. Open heart surgery encompasses a wide range of heart surgeries, while bypass surgery specifically targets coronary artery blockages. Both procedures carry significant risks and are vital for treating severe heart conditions. By distinguishing between the two, patients can better understand their treatment options and engage in informed discussions with their healthcare providers.
FAQ's
No, bypass surgery is a specific type of open heart surgery. While all bypass surgeries are open heart surgeries, not all open heart surgeries are bypass surgeries.
Yes, you will have a scar from the incision made in your chest during the surgery.
No, bypass surgery is a major operation that requires hospitalization for several days, followed by a period of recovery at home.
Yes, with your doctor's approval, you can gradually resume physical activity after bypass surgery. Regular exercise is important for heart health
Yes, you will likely need to take medications to manage blood pressure, cholesterol, and blood thinners to prevent blood clots.



















 8 Min Read
8 Min Read












