
Listen to article
Loading audio...
Fractures, or broken bones, are common injuries that can occur due to various reasons such as trauma, sports injuries, or medical conditions like osteoporosis. They can be classified into different types, including simple, compound, greenstick, comminuted, and stress fractures. Symptoms typically include pain, swelling, bruising, and difficulty moving the affected area. Diagnosis often involves physical examinations and imaging techniques like X-rays. Treatment options range from immobilization with casts to surgical interventions, followed by physical therapy for rehabilitation. Preventive measures include safety practices, proper nutrition, and regular exercise.
Synopsis
Common Types of Fractures
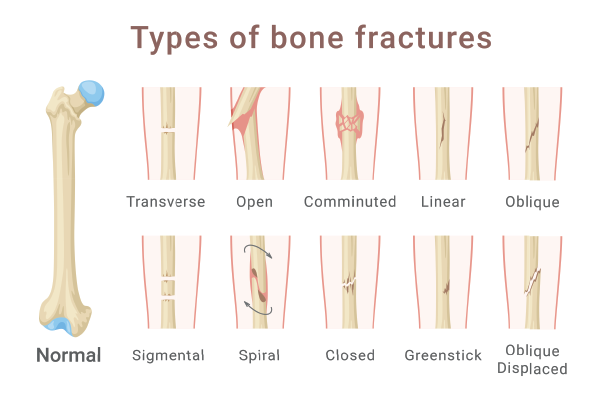
Fractures can be classified into several types based on their characteristics:
-
Simple vs. Compound Fractures: Simple fractures involve a clean break without piercing the skin, while compound fractures involve the bone breaking through the skin, increasing the risk of infection.
-
Greenstick Fractures: Common in children, these fractures occur when the bone bends and cracks, rather than breaking completely.
-
Comminuted Fractures: These involve bone-shattering into multiple pieces, often requiring surgical intervention.
-
Stress Fractures: Small cracks in the bone caused by repetitive force or overuse, frequently seen in athletes.
Causes of Fractures
Fractures can result from various reasons. Here are the major fracture causes:
-
Traumatic Injuries: Falls, car accidents, and direct blows can cause bones to break.
-
Sports Injuries: High-impact sports like football, basketball, and skiing often lead to fractures.
-
Osteoporosis and Other Medical Conditions: Conditions that weaken bones, such as osteoporosis, increase the risk of fractures.
-
Overuse and Repetitive Motion: Activities that put continuous stress on bones, like running or jumping, can lead to stress fractures.
Symptoms of Fractures
Recognizing the fracture symptoms is crucial for timely treatment:
-
Pain and Swelling: Immediate and severe pain at the injury site, accompanied by swelling.
-
Bruising and Discoloration: The area around the fracture may become bruised and discoloured.
-
Deformity or Misalignment: Visible deformity or abnormal positioning of the limb.
-
Difficulty Moving the Affected Area: Limited mobility and inability to bear weight on the affected limb.
Diagnosis of Fractures
Accurate diagnosis is essential for effective treatment:
-
Physical Examination: Initial assessment by a healthcare provider to check for signs of fracture.
-
Imaging Techniques: X-rays are the most common method to visualize fractures. MRI and CT scans may be used for more complex cases.
-
Bone Density Tests: Used to diagnose underlying conditions like osteoporosis that may contribute to fractures.
Treatment Options
Treatment varies based on the fracture types and severity of the fracture:
-
Immobilization: Casts and splints are used to keep the bone in place during healing.
-
Surgical Interventions: Pins, plates, and screws may be required to stabilize severe fractures.
-
Physical Therapy and Rehabilitation: Essential for restoring strength and mobility post-treatment.
-
Pain Management Strategies: Medications and other techniques to manage pain during recovery.
Consult our orthopaedic hospital in Pune if you need fracture treatment.
Complications and Risks
Fractures can lead to several complications:
-
Infection: Particularly in compound fractures where the bone pierces the skin.
-
Delayed Healing or Nonunion: Sometimes bones take longer to heal or fail to heal properly.
-
Nerve or Blood Vessel Damage: Fractures can damage surrounding nerves and blood vessels.
-
Long-term Mobility Issues: Some fractures may result in permanent mobility limitations.
|
Prevention Strategy |
Description |
|
Safety Measures in Daily Activities |
Using handrails, wearing seatbelts, and avoiding slippery surfaces. |
|
Protective Gear for Sports |
Helmets, pads, and proper footwear can reduce the risk of sports injuries. |
|
A diet rich in calcium and vitamin D supports bone strength. |
|
|
Regular Exercise and Strength Training |
Weight-bearing exercises help maintain bone density. |
Recovery and Rehabilitation
Recovery from a fracture involves several stages:
-
Stages of Healing: Inflammation, bone production, and bone remodelling are the key stages.
-
Importance of Follow-up Care: Regular check-ups to monitor healing progress.
-
Exercises to Regain Strength and Mobility: Physical therapy exercises tailored to the specific fracture.
-
Psychological Impact and Coping Strategies: Addressing the mental health aspects of recovery.
|
Advancement |
Description |
|
Latest Surgical Techniques |
Minimally invasive procedures and advanced fixation methods. |
|
Innovations in Medical Devices |
Development of smart casts and other supportive devices. |
|
Research on Bone Regeneration |
Studies on enhancing bone healing through biological and technological means. |
Pediatric Fractures
Children's fractures require special attention:
-
Unique Considerations in Children: Growth plates and developing bones need careful management.
-
Growth Plate Injuries: Specific fractures that affect the growth areas of bones.
-
Treatment Approaches for Young Patients: Tailored treatments to ensure proper healing and growth.
Geriatric Fractures
Elderly individuals face unique challenges with fractures:
-
Common Fractures in the Elderly: Hip, wrist, and spine fractures are prevalent.
-
Impact of Osteoporosis: Increased fracture risk due to weakened bones.
-
Special Care and Treatment Needs: Comprehensive care plans to address the needs of older adults.
Fractures in Athletes
Athletes are at high risk for fractures:
-
High-Risk Sports: Identifying sports with higher fracture risks.
-
Prevention Strategies for Athletes: Training and equipment to minimize injury risk.
-
Rehabilitation for Sports-Related Fractures: Specialized rehab programs to return athletes to peak performance.
|
Technology |
Description | Benefits |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Conclusion
By exploring these subtopics, readers can gain a thorough understanding of fractures, from their causes and symptoms to the latest advancements in treatment and recovery. Whether you're a patient, caregiver, or simply interested in learning more, this comprehensive guide offers valuable insights into the world of fractures.
For expert care and advanced treatment options, consider visiting Manipal Hospitals. With a team of experienced orthopaedic specialists and state-of-the-art facilities, Manipal Hospitals is dedicated to providing the highest quality care for all types of fractures.
FAQ's
Some fractures, particularly incomplete or non-displaced fractures, may heal on their own with proper immobilization. However, medical evaluation is essential to ensure proper alignment and healing.
Complications can include infection (especially in compound fractures), delayed healing or nonunion, nerve or blood vessel damage, and long-term mobility issues.
Preventive measures include using safety measures in daily activities (handrails, seatbelts), wearing protective gear for sports, maintaining bone health through proper nutrition (calcium and vitamin D), and engaging in regular exercise and strength training.
Recovery involves several stages, including inflammation, bone production, and bone remodelling. Follow-up care, physical therapy exercises, and addressing the psychological impact are crucial for complete recovery.
Diagnosis often involves a physical examination and imaging techniques such as X-rays, MRI, or CT scans. Bone density tests may also be used to diagnose underlying conditions like osteoporosis.



















 6 Min Read
6 Min Read
















