
When does unintentional weight loss become a concern?
Weight loss of up to 5% of your body weight in a year is typical. Beyond that, losing more than 5% of body weight within 6 to 12 months can be a matter of concern. This type of weight loss may suggest that a person could be suffering from a serious health condition. Medical research shows people who suffer unintentional body weight loss exceeding 10% face double the risk of developing cancer in one year. This blog will help you understand the causes of unintentional weight loss, how it can be diagnosed, and treatment measures.
Synopsis
What is Unintentional Weight Loss?
Weight loss occurring naturally with minimal influence from diet plans or exercise changes defines unintentional weight loss. When there’s weight loss without trying, it may signal the existence of hidden health concerns, which include infections, digestive disorders, and severe chronic diseases. Stress, improper nutrition, and unbalanced hormone levels contribute to unexpected weight loss. Early discovery of the reason behind weight changes leads to successful medical diagnosis and appropriate treatment procedures.

Common Causes of Weight Loss
The human body loses weight unintentionally due to various medical conditions and lifestyle choices. For proper treatment, it is important to identify the underlying cause of unintentional weight loss.
Below are the common causes of weight loss:
-
Malignancy (Cancer-related weight loss): Cancer increases metabolism, leading to rapid weight loss. Gastrointestinal, lung, and blood cancers are common culprits.
-
Gastrointestinal Diseases: Conditions like peptic ulcers, celiac disease, and inflammatory bowel diseases (e.g., Crohn’s disease, ulcerative colitis) affect digestion and nutrient absorption, causing weight loss. Therefore, consulting with an experienced gastroenterologist in Bangalore is highly recommended.
-
Mental Health Challenges: Stress, anxiety, depression, and eating disorders are common contributors to unintentional weight loss. They can reduce appetite and alter metabolism.
-
Endocrine Disorders: Hyperthyroidism and diabetes speed up metabolism, resulting in unintentional weight loss despite everyday eating habits.
-
Chronic Infections: Diseases like HIV and hepatitis weaken the immune system, increasing energy demands and causing weight loss.
-
Neurological Disorders: Stroke, dementia, and Parkinson’s disease can affect swallowing and appetite, leading to malnutrition and weight loss.
-
Medications and Substance Use: Certain drugs, alcohol, and stimulants like cocaine suppress appetite and contribute to weight loss.
Evaluating Unintentional Weight Loss
Unintentional weight loss requires a thorough medical evaluation to identify the underlying cause. Early diagnosis helps prevent complications and ensures proper treatment. A step-by-step approach helps in accurate assessment.
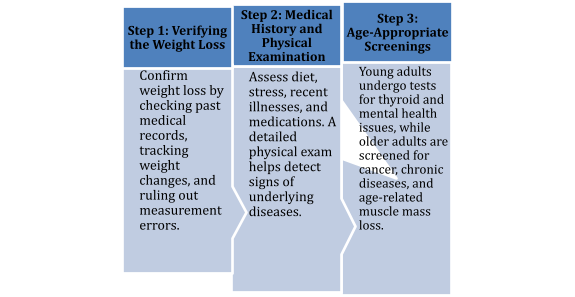
Key Tests and Diagnostic Workup
Identifying the cause of unintentional weight loss requires specific tests. These help detect infections, hormonal imbalances, digestive disorders, or cancers. Early diagnosis improves treatment outcomes and prevents complications.
Below are the key tests for diagnosing unintentional weight loss:
-
Blood Tests (CBC, Glucose, Liver Function, TSH): These detect anaemia, infections, diabetes, thyroid issues, and liver disorders affecting weight.
-
Imaging Tests (Chest X-ray, Abdominal Ultrasound, CT Scan) can identify tumours, lung infections, or digestive system abnormalities contributing to weight loss.
-
Endoscopic Procedures (Upper GI Endoscopy, Colonoscopy) help diagnose ulcers, gastritis, celiac disease, or cancer.
-
Age-Specific Screenings: Cancer screenings are recommended for unintentional weight loss in the elderly, while metabolic tests help younger individuals with unexplained weight loss.
When Should You Be Worried About Rapid Weight Loss?
Monitoring unintentional weight loss is crucial, mainly when no immediate cause is found. Ignoring it can delay diagnosis and worsen underlying health conditions. Regular follow-ups help track progress and identify concerns.
Below are the key situations when follow-up is necessary:
-
Persistent Weight Loss: Further tests are needed to rule out severe conditions if weight loss continues despite initial evaluation.
-
New or Worsening Symptoms: Symptoms like fatigue, pain, fever, or appetite loss indicate an underlying issue requiring medical attention.
-
No Clear Diagnosis: If initial tests are inconclusive, additional screenings for infections, autoimmune diseases, or cancers may be necessary.
-
High-Risk Groups: Older adults, cancer patients, and those with chronic diseases need closer monitoring for early intervention.
Treatment for Unintentional Weight Loss
Treating unintentional weight loss requires addressing its root cause. Simply gaining weight is not enough if an underlying condition remains untreated. A personalized treatment plan ensures better recovery and long-term health.
-
Treating Underlying Conditions: Managing diseases like cancer, thyroid disorders, or depression helps restore normal weight.
-
Nutritional Support: A high-calorie, nutrient-rich diet with supplements helps improve energy levels and muscle strength.
-
Medication Adjustments: Changing or stopping medications that cause weight loss can prevent further decline.
-
Physical Therapy and Exercise: Strength training and physiotherapy help maintain muscle mass and overall health.
-
Mental Health Support: Counseling and therapy help manage stress, depression, or eating disorders affecting appetite.
A well-planned treatment approach ensures effective weight management and overall well-being.
Conclusion
See a doctor if you experience fatigue, appetite loss, pain, or digestive issues. Early diagnosis prevents complications from conditions like cancer, diabetes, or infections. Delaying evaluation can worsen health outcomes. Seeking timely medical advice from the experts ensures proper diagnosis, treatment, and recovery, improving overall well-being.
FAQ's
Chronic stress increases metabolism and suppresses appetite, leading to weight loss. Stress-related hormonal changes can also affect digestion and nutrient absorption.
No, not always. Persistent weight loss can result from lifestyle changes, stress, or minor infections. However, to rule out severe conditions, it requires medical evaluation.
Lack of sleep disrupts hormones controlling hunger and metabolism. Poor sleep reduces appetite, increases energy expenditure, and may cause unintentional weight loss.
Conditions like lactose intolerance or gluten sensitivity can cause digestive issues, poor nutrient absorption, and unintentional weight loss.



















 6 Min Read
6 Min Read


-causes-symptoms-and-treatment.png)










