
Have you ever experienced the agonizing discomfort of an earache during a common cold? It's as if a tiny jackhammer is relentlessly pounding inside your ear, leaving you feeling helpless and irritable. While colds themselves are no stranger to most of us, what can make this experience truly unbearable is when it brings along a companion - ear pain. Ear pain during a cold can indeed be a miserable experience, impacting your overall health and mood. In this case, you may wonder why it happens and how you can prevent ear pain during cold. In this blog, figure out why ear pain is induced by a common cold, exploring its causes, symptoms, medical treatments, precautions, and when it's time to consult a medical professional.
Synopsis
Why Does a Cold Cause Ear Pain?
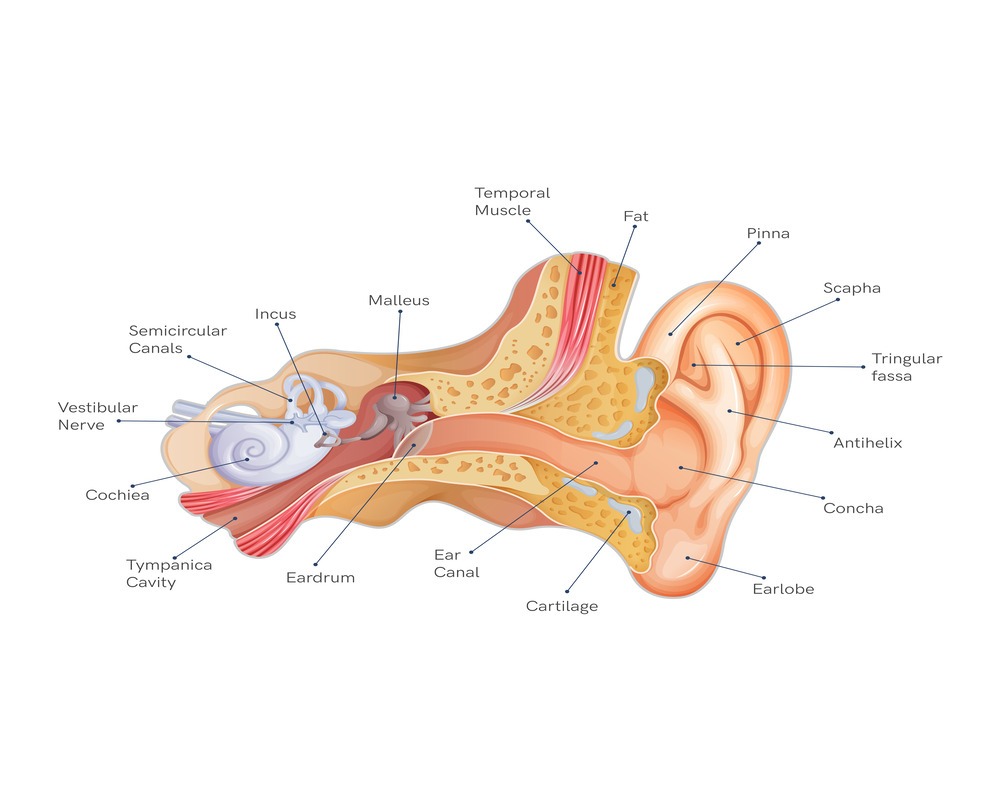
First things first, why does a seemingly innocent common cold have the audacity to cause ear pain? To understand this, we need to venture into the intricate anatomy of our ears.
An ear consists of three parts: an outer ear, a middle, and an inner ear. The middle ear is connected to the back of your nose by a small tube called the Eustachian tube. When you have a cold, the viral infection can lead to inflammation and congestion in your throat, nose, and sinuses. This infection can in turn reach the ear through this tube or the tube in itself can get inflamed and blocked. This block will cause hindrance to the normal function of the eustachian tube and result in secretion and pus getting collected within the small confined space of the middle ear. This inflammation and pressure in the middle ear is what causes ear pain.
Consult our ENT hospital in Mangalore if you need to know more cause of earache.
Ear infection and its symptoms
Ear infection may start with a sense of reduced hearing or irritation in the ear, especially while swallowing during an attack of the common cold. Later you may develop ear pain, fever and when complicated can result in ear discharge, facial asymmetry, pain around the ear, headache etc. For newborns and children who can’t convey the pain often have excessive crying and may be associated with episodes of fever.
Precautions for Not developing ear infections
-
Early and prompt treatment of upper respiratory tract infection.
-
Avoid forceful blowing of the nose during the attacks of the common cold
-
Maintain adequate hydration during the attack of the common cold.
-
Many vaccinations against the common cold can prevent the frequent attacks of ear infection
-
Stop smoking (Smoking has been shown to increase the risk of developing ear infections)
-
The use of Chewing gum has been shown to be protective
-
For children- Breastfeeding and avoidance of supine feeding are shown to be protective.
Medical Treatments
Mild ear pain due to cold might resolve with simple over-the-counter analgesics. Whereas severe or persistent ear pain may require medical intervention. After a thorough medical examination, you will be started on medication which may include antibiotics, antiviral, oral/nasal decongestants, analgesics, ear drops etc. Early medical treatment is mandatory in cases of ear infection to avoid unwanted complications although rare. Myringotomy: In severe cases, a doctor may need to make a small incision in the eardrum to drain fluid from the middle ear, a procedure known as myringotomy.
Precautions When Treating a Cold-Induced Ear Pain
While treating ear pain during a cold, it's essential to take some precautions to avoid worsening the condition or causing further complications:
-
Avoid inserting objects into your ears, as this can damage the delicate ear canal or eardrum.
-
Do not use earwax removal kits unless directed by a healthcare professional.
-
If ear pain due to cold persists or worsens despite home remedies, seek medical attention promptly.
-
Follow your doctor's instructions and complete the full course of any prescribed medications, such as antibiotics.
When to Consult a Medical Professional
While home remedies can often provide relief, there are times when you should seek medical attention for ear pain during a cold:
-
Persistent or worsening pain.
-
Fever accompanying ear pain.
-
Drainage of pus from the ear.
-
Severe ear pain in children.
-
Hearing loss or dizziness.
-
Asymmetry of face or inability to close eyes associated with ear pain.
Ear Specialists in Mangalore
If you require specialized care in Mangalore for ear pain during a cold, you can consult Ear Specialists at KMC Hospital, Mangalore, who are experienced in diagnosing and treating ear-related issues. They can provide personalized treatment options and ensure your ear's health is in good hands.
Conclusion
Ear pain brought on by a common cold can be a tough time to deal with, but armed with knowledge and the right remedies, we can find relief and make the journey through the cold a bit more bearable. Children are particularly susceptible to earaches during colds due to their anatomy, so extra care and attention are necessary. Don't hesitate to seek medical advice if the pain persists or worsens. The key to a quick recovery is to address both the cold symptoms and the associated earache. So, the next time a cold try to bring you down, you'll be well-prepared to combat the discomfort and bounce back to good health.
FAQ's
Usually the ear pain from a cold is not serious. Most ear pain from colds improves as the cold resolves. However, it can sometimes lead to an ear infection. A doctor should be consulted if the pain becomes severe or doesn't improve with time.
Ear infections, swimmer's ear, earwax build-up, and injury are common causes. See a doctor if the pain persists or worsens.
Apply a warm compress, use pain relievers (consult a doctor for dosage), and elevate your head while sleeping.
Eardrops can address ear pain caused by infection (antibiotic/antifungal) or swimmer's ear (acetic acid). Consult a doctor for diagnosis and appropriate eardrops.
Yes, for mild pain, try a warm compress or over-the-counter pain relievers like acetaminophen or ibuprofen. Home remedies may not address the underlying cause.



















 5 Min Read
5 Min Read










