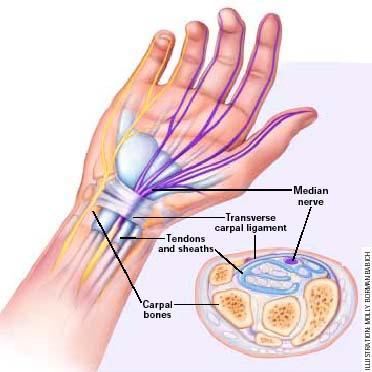
Carpal Tunnel Syndrome is a condition where one of the major nerves controlling the functioning of the hand and fingers called the median nerve becomes compressed inside a “tunnel” in the wrist.
The carpal tunnel is a small passage inside the wrist which is made up of several fine bones of the wrist forming the floor and the sides of the tunnel. This tunnel has several tendons and a median nerve as its content. The median nerve carries most of the sensations of the hand, particularly to the thumb, index and middle fingers, the thumb half of the palm, and the outer side of the hand. Carpal tunnel syndrome most often occurs after the age of 30 years, with women affected more than men by a factor of 3.
It is also one of the most-common job-related conditions. Median nerve entrapment can result in sensory and motor impairment, as well as pain in the hand or arm. There is no single reference standard for diagnosis of the syndrome, and a combination of symptoms, signs, and tests are used to characterize the disorder. Visit a top hospital for carpal tunnel syndrome treatment in Mangalore.
Causes of Carpal Tunnel Syndrome
We do not always know what causes carpal tunnel syndrome. In fact, in most cases, the exact reason can’t be found. Any condition that reduces the amount of space in the carpal tunnel and any condition that causes pressure on the median nerve at the wrist can lead to carpal tunnel syndrome. The causes can be broadly divided into work or occupation-related causes or secondary to any underlying conditions.
-
Occupational risk factors
Repetitive tasks such as force, posture, and vibration have been one of the most common causes of carpal tunnel syndrome.
-
Secondary causes
-
Obesity
-
Rheumatoid arthritis
-
Hypothyroidism
-
Diabetes Mellitus
-
Pregnancy due to hormonal changes
-
Fractures
Symptoms of Carpal Tunnel Syndrome
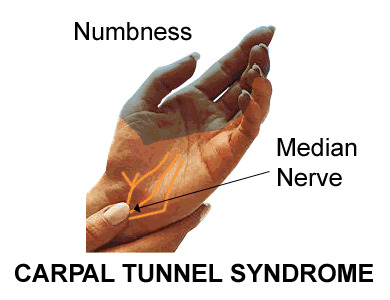
Carpal tunnel syndrome symptoms typically include pain,tingling, numbness, or a combination of the three. The numbness or tingling most often occurs in the thumb, index, middle and ring fingers. The symptoms usually are felt more during the night. Symptoms can awaken patients from sleep and cause sleep deprivation.
-
Patients often flick their wrists as if shaking down a thermometer to get relief from the symptoms.
-
These symptoms may be noticed during daily activities such as driving, writing, cooking, typing, etc.
-
Patients may sometimes feel a weaker grip, occasional clumsiness and a tendency to drop things.
-
In severe cases, the sensation is lost permanently and the muscles of the thumb and hand slowly shrink (thenar atrophy)
Diagnosis of Carpal Tunnel Syndrome
There is no single gold standard diagnostic modality for the diagnosis of carpal tunnel syndrome. A combination of described symptoms, clinical findings, electrophysiological testing, sonography and sensation, and higher investigation modalities like MRI, etc., are used by many doctors. For diagnosis and treatment consult a top ortho doctor in Mangalore.
Treatment of Carpal Tunnel Syndrome
Conservative treatment
-
Wrist splints
Probably this treatment is most effective when applied within three months of the onset of symptoms. For the best results, one should wear braces at night and, if possible, during activity that primarily causes stress on the wrists.

-
Oral medications
Analgesics and anti-inflammatory drugs given are only for symptomatic relief and not a permanent cure.
-
Local injection
Corticosteroid injections may be effective for temporary relief from symptoms.
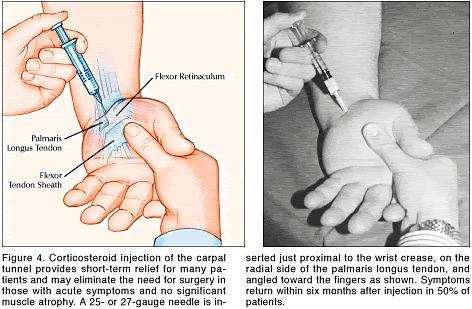
Surgical Treatment
Surgical management deals with relieving the symptoms by reducing the pressure over the median nerve. Surgical management can either be in the form of conventional open carpal tunnel or endoscopic carpal tunnel release. Endoscopic carpal tunnel release is a minimally invasive procedure that has faster post-operative recovery than open release.
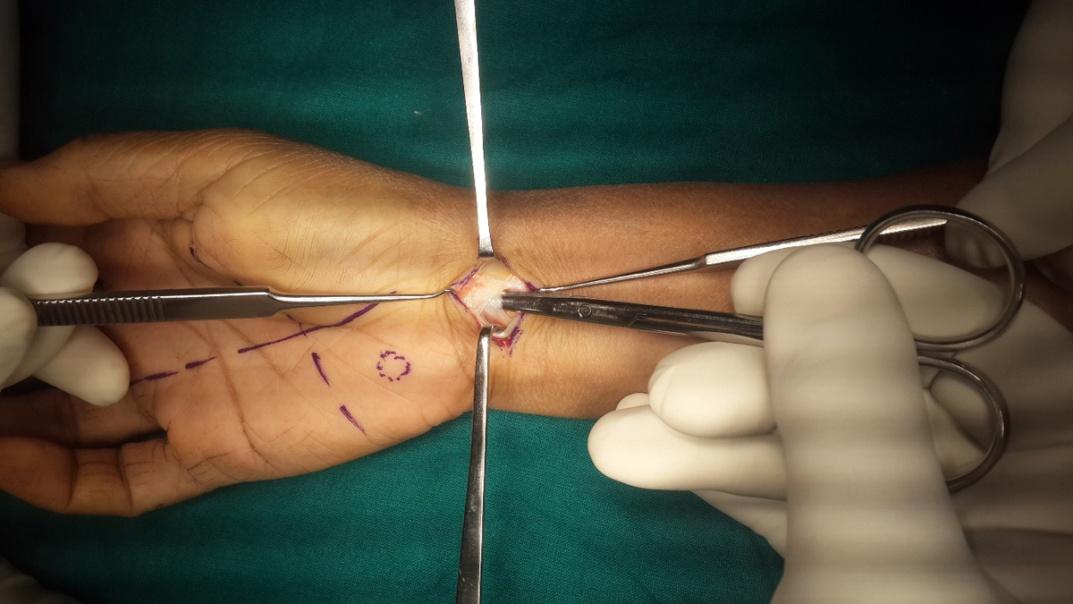
Surgical release
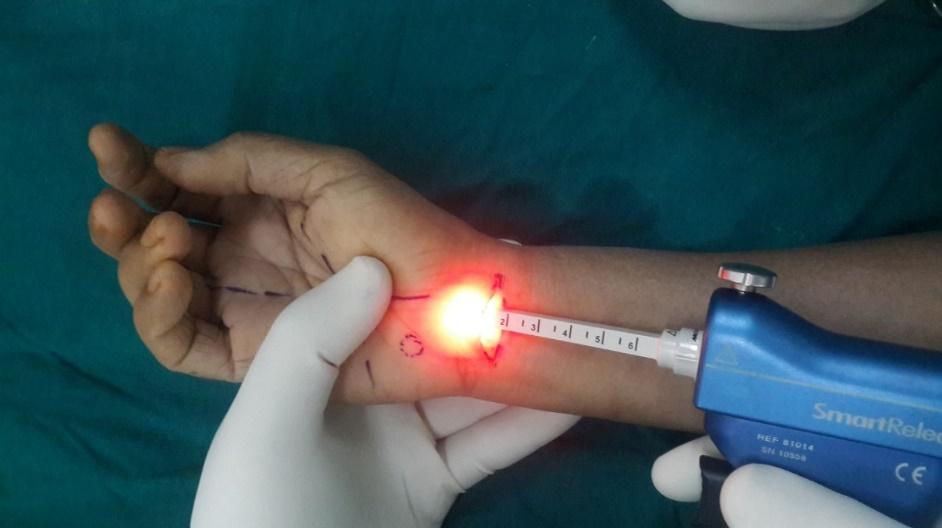
Minimal Invasive Endoscopic Carpal Tunnel Release
Prevention of Carpal Tunnel Syndrome
Healthy habits such as avoiding repetitive stress, work modification through the use of ergonomic equipment (wrist rest, mouse pad), taking proper breaks, and using keyboard alternatives (digital pen, voice recognition, and dictation) have been proposed as methods to help prevent carpal tunnel syndrome.
Department of Orthopaedics
KMC Hospital, Mangalore





















 4 Min Read
4 Min Read