
Listen to article
Loading audio...
Mumps is a contagious viral disease mainly affecting the salivary glands, causing swelling and discomfort. While it was once a common childhood illness, the introduction of vaccines has significantly reduced its occurrence. However, mumps still exists, particularly in people who have not received mumps immunisation.
Let's understand mumps, its causes, symptoms, complications, treatment, and prevention methods. Whether you are looking for information about mumps viral disease, its treatment, mumps disease symptoms, or how mumps immunisation can help, this guide will provide everything you need to know.
Synopsis
What is Mumps?
Mumps is a viral infection caused by the mumps virus. It is transmitted through respiratory droplets when an infected person coughs or sneezes. The virus mainly affects the parotid glands, which are located near the jaw and produce saliva. When infected, these glands swell, causing a puffy cheek appearance that is a classic sign of mumps.
Although mumps is generally mild, it can sometimes lead to complications, especially in adults. Getting the mumps immunisation is the best way to prevent this illness.
Causes of Mumps
Mumps is caused by the mumps virus, which belongs to the paramyxovirus family. The virus can spread in the following ways:
-
Airborne droplets: When an infected person coughs, sneezes, or talks, tiny virus-containing droplets enter the air and can be inhaled by others.
-
Direct contact: Sharing utensils, drinking glasses, or kissing an infected person can transmit the virus.
-
Contaminated surfaces: The virus can survive on surfaces. If a person touches an infected surface and then touches their nose, mouth, or eyes, they can also be infected by this virus.
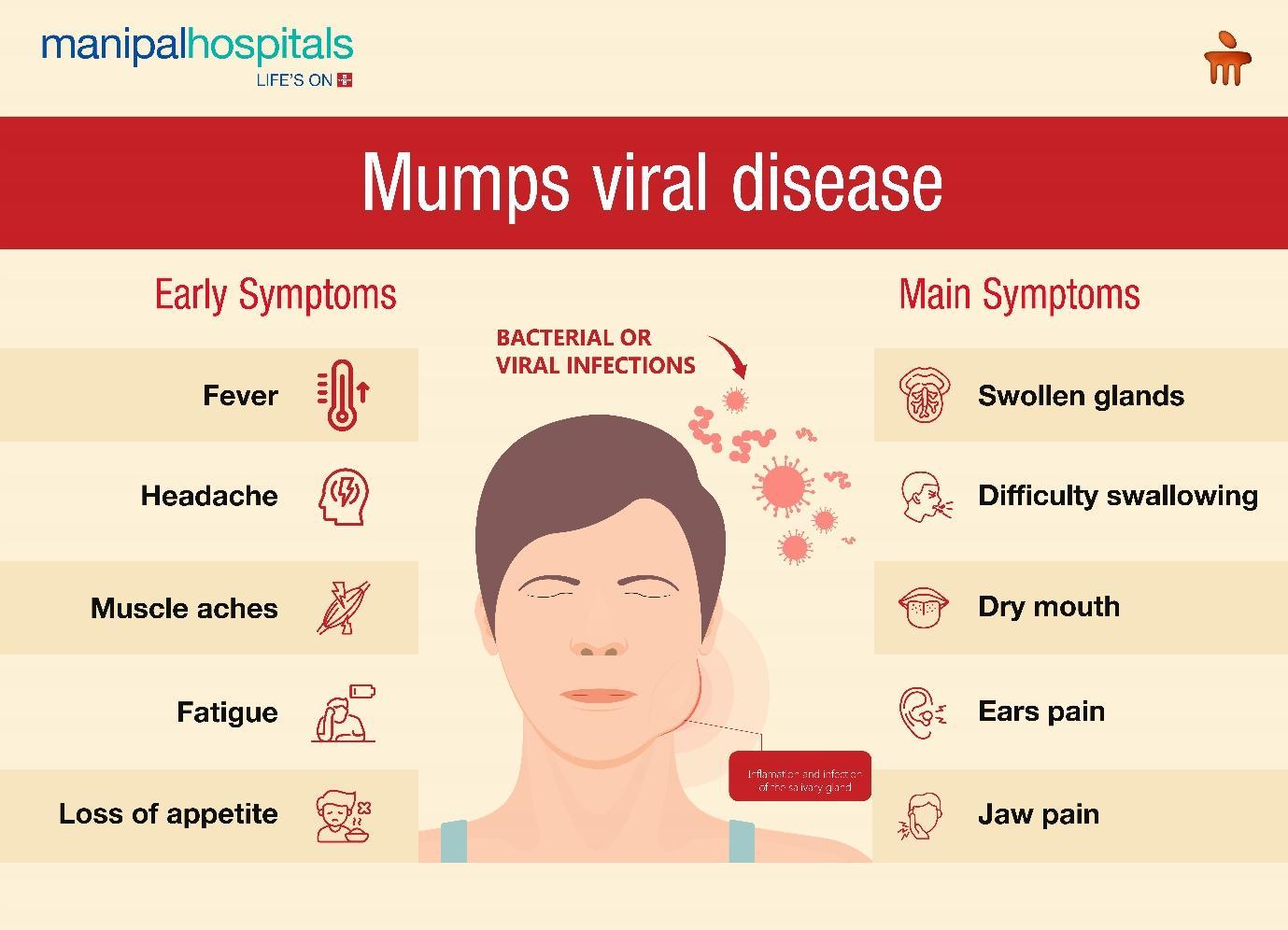
Mumps Disease Symptoms
Symptoms of mumps usually appear 2 to 3 weeks after exposure to the virus. Some individuals may have mild symptoms or no symptoms at all. However, common mumps viral disease symptoms include:
Early Symptoms:
-
Fever
-
Headache
-
Muscle aches
-
Fatigue
-
Loss of appetite
Main Symptoms:
-
Swollen, painful salivary glands (usually on one or both sides of the face)
-
Difficulty swallowing or chewing – Opening the mouth
-
Dry mouth
-
Pain in the ears or jaw
These symptoms typically last 7 to 10 days, and most people recover within one to two weeks without complications.
How is Mumps Diagnosed?
Doctors diagnose mumps viral disease based on:
-
Physical examination: Checking or examining the swollen salivary glands.
-
Medical history: Reviewing symptoms and recent exposure to infected individuals.
-
Lab tests: A Blood test can confirm the presence of the mumps virus.
In some cases, imaging tests like an ultrasound of the neck region are needed. Visit Manipal Hospitals for diagnosis from the best paediatrician in Mangalore.
Mumps Virus Treatment
There is no specific antiviral treatment for mumps. Since it is a viral infection, antibiotics do not work. Treatment focuses on relieving symptoms until the body fights off the virus.
Home Care for Mumps Virus Treatment:
-
Rest: Get plenty of rest to help the body fight the virus. Also, to allow your body to recover, you should sleep as much as possible.
-
Fluids: Drink lots of water to stay hydrated. You can also drink herbal tea and clear soups to maintain the water intake in your body.
-
Pain relief: Over-the-counter painkillers can help reduce fever, pain and discomfort.
-
Soft foods: Eating soups, mashed potatoes, and yoghurts can reduce discomfort while chewing.
-
Warm or cold compress: Applying a compress to swollen glands can ease pain.
Most cases of mumps improve within 7 to 10 days without medical intervention.
Mumps Immunisation: The Best Prevention
The MMR vaccine, which is also called Measles, Mumps, and Rubell, is the best way to protect oneself from the virus. It helps to provide effective protection against mumps. It is usually given in two doses:
-
First dose: At of age 9 months
-
Second dose: At the age of 15 months
For adults who have not been vaccinated, it is recommended to get at least one dose of the MMR vaccine. Mumps immunisation not only protects individuals but also helps prevent outbreaks.
What Happens if Mumps is Left Untreated?
If mumps are left untreated, symptoms may worsen, leading to severe complications. The virus can spread to others, increasing the risk of outbreaks.
Without proper care, mumps can result in:
-
Severe gland swelling, leading to difficulty breathing or swallowing
-
Chronic pain in the jaw and ears
-
Increased risk of infertility in males
-
Permanent hearing loss
This is why early diagnosis and symptom management are crucial.
When to See a Doctor?
Seek medical help if:
-
The swelling becomes severe or affects breathing.
-
There is persistent high fever, above 102.2 °F.
-
Severe headache or neck stiffness occurs.
-
You experience testicular pain (in males).
-
You have difficulty eating or drinking due to severe swelling.
Conclusion
Mumps is a highly contagious viral disease that can cause painful swelling of the salivary glands. While most cases are mild and resolve on their own, complications can occur, even in children, but it is rare, particularly in adults. The best way to prevent mumps viral disease is through mumps immunisation with the MMR vaccine. If you or your child has mumps disease symptoms, rest, stay hydrated, and manage discomfort with home remedies. For severe mumps disease symptoms, consult a doctor to rule out complications. Staying vaccinated and practising good hygiene can help prevent the spread of mumps. You can also connect to KMC Hospital, Mangalore, for any further assistance.
FAQ's
Yes, some people with mumps may not show any visible symptoms but can still spread the virus to others. This makes mumps immunisation even more important for protection.
A person with mumps is contagious for about 2 days before symptoms appear and up to 5 days after gland swelling begins. During this time, it is best to stay isolated to prevent the spread of the virus.
Pregnant women with mumps may have a higher risk of miscarriage, especially in the first trimester. This is why immunisation for mumps is crucial before pregnancy.
Most people develop lifelong immunity after recovering from mumps. However, in very rare cases, someone with a weakened immune system may get infected again.



















 6 Min Read
6 Min Read

















