An ectopic pregnancy is a serious medical condition that requires immediate attention. It occurs when a fertilised egg implants itself outside the uterus, most commonly in the fallopian tube. The fallopian tube can’t hold a growing embryo, leading to bleeding. An ectopic pregnancy can have significant risks to the mother if left untreated. In this blog, we’ll explore the causes, symptoms, and treatments of ectopic pregnancy to help you understand this condition better.
Synopsis
- What is an Ectopic Pregnancy?
- How Common are Ectopic Pregnancies in India?
- Causes of Ectopic Pregnancy: Why Does it Happen?
- What are the Symptoms of Ectopic Pregnancy?
- How to Diagnose Ectopic Pregnancy?
- Treatment Options for Ectopic Pregnancy
- Recovery and Future Pregnancies
- How to Prevent Ectopic Pregnancy
- Conclusion
What is an Ectopic Pregnancy?
In a normal pregnancy, the fertilised egg travels through the fallopian tube and implants in the uterus, where it grows into a baby. However, in an ectopic pregnancy, the egg implants somewhere else, usually in the fallopian tube (tubal pregnancy). Rarely, it can also implant in the ovary, abdominal cavity, or cervix.
The pregnancy cannot progress normally since these areas are not designed to support a growing embryo. If not treated promptly, it can lead to life-threatening complications, such as internal bleeding. This is a medical emergency and requires medical/ surgical intervention quickly to treat the condition.
How Common are Ectopic Pregnancies in India?
Ectopic pregnancies account for about 1% of all pregnancies in India. In India, ectopic pregnancies are a significant cause of maternal morbidity and mortality, especially when diagnosis and treatment are delayed. Factors like pelvic inflammatory disease (PID), untreated sexually transmitted infections (STIs), and lack of awareness contribute to the risk.
Early detection and timely medical intervention are crucial to reducing complications and improving outcomes.
Causes of Ectopic Pregnancy: Why Does it Happen?
Understanding the reasons for ectopic pregnancy can help you identify potential risk factors. While the exact cause isn’t always clear, several factors can increase the likelihood of this condition:
-
Damaged Fallopian Tubes: Scarring or damage to the fallopian tubes, often caused by pelvic inflammatory disease (PID) or previous surgeries, can prevent the egg from reaching the uterus.
-
Hormonal Imbalances: Abnormal hormone levels can affect the movement of the fertilised egg through the fallopian tubes.
-
Previous Ectopic Pregnancy: If you’ve had an ectopic pregnancy before, you’re at a higher risk of experiencing it again.
-
Smoking: Smoking can damage the fallopian tubes and increase the risk of ectopic pregnancy.
-
Fertility Treatments: Procedures like IVF can sometimes lead to ectopic pregnancies.
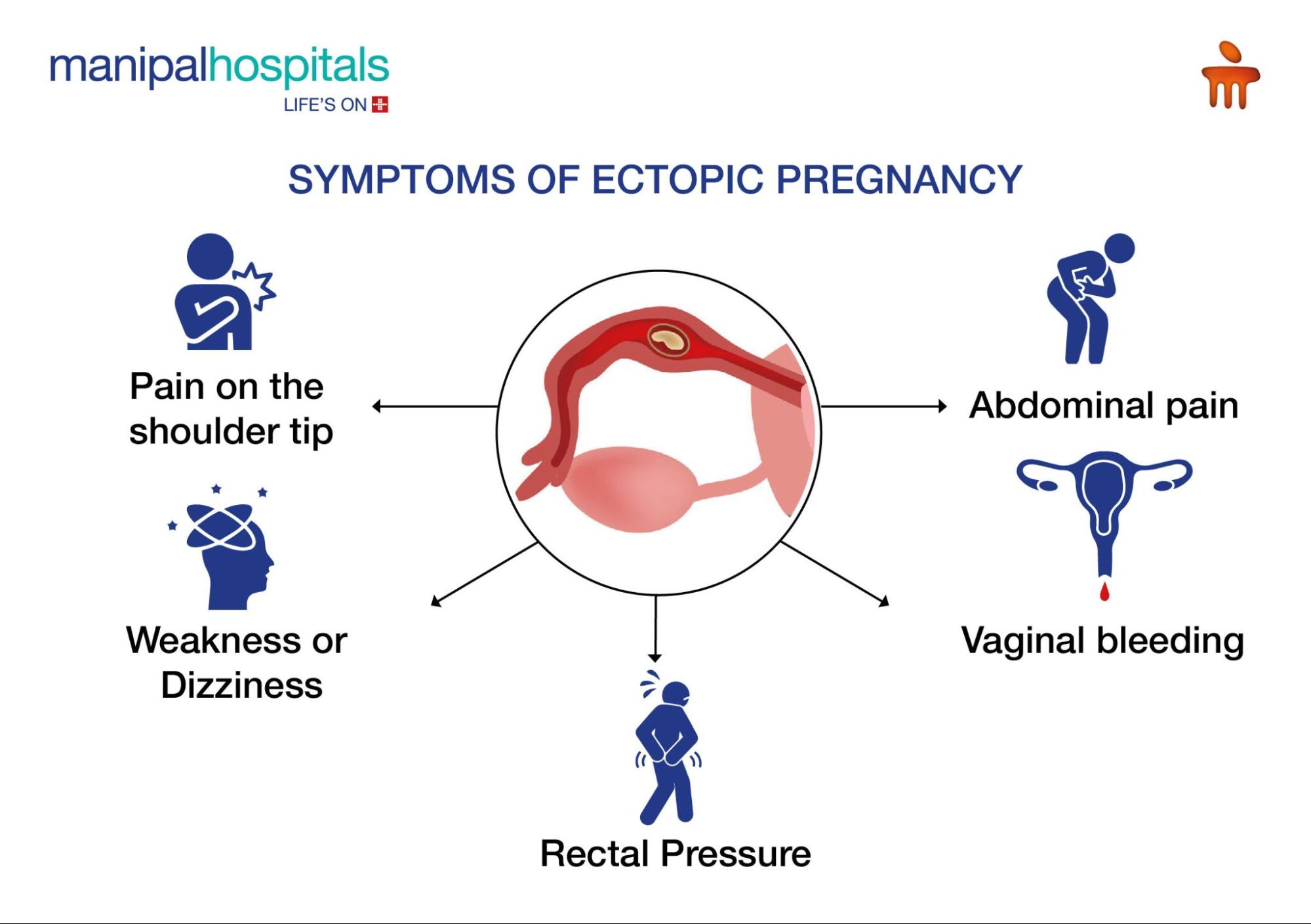
What are the Symptoms of Ectopic Pregnancy?
Recognising the signs and symptoms of ectopic pregnancy early is crucial for timely treatment. Early signs can mimic those of a normal pregnancy, such as a missed period, nausea, or breast tenderness. However, as the pregnancy progresses, specific symptoms may appear:
-
Abdominal Pain: Sharp or stabbing pain in the lower abdomen, often on one side.
-
Vaginal Bleeding: Light to heavy bleeding, which may be different from a normal period.
-
Shoulder Tip Pain: Pain where the shoulder ends and the arm begins, caused by internal bleeding irritating the diaphragm.
-
Weakness or Dizziness: Feeling faint or lightheaded due to blood loss.
-
Rectal Pressure: A feeling of pressure in the rectum, often due to internal bleeding.
If you experience any of these ectopic symptoms, especially severe pain or heavy bleeding, seek medical help immediately.
How to Diagnose Ectopic Pregnancy?
Doctors use several methods to diagnose an ectopic pregnancy, especially if one shows the signs of ectopic pregnancy:
-
Pelvic Exam: To check for tenderness or masses in the pelvic area.
-
Blood Tests: To measure pregnancy hormone (hCG) levels. In an ectopic pregnancy, hCG levels may rise more slowly than in a normal pregnancy.
-
Ultrasound: To locate the pregnancy. A transvaginal ultrasound is often used to get a clearer image.
Treatment Options for Ectopic Pregnancy
An ectopic pregnancy is a complicated condition, and most of the time it cannot be saved as the developing embryo cannot survive outside of the womb. The goal of treatment is to remove the pregnancy and protect the mother’s health. Treatment options depend on the size and location of the pregnancy, as well as the patient’s overall health.
1. Medication (Methotrexate): If the pregnancy is detected early and the fallopian tube hasn’t ruptured, methotrexate may be used. This stops the growth of the pregnancy, allowing the body to absorb it over time.
2. Surgery: If the pregnancy is more advanced or the fallopian tube has ruptured, surgery is necessary. There are two types:
-
Laparoscopy: A minimally invasive procedure where the ectopic pregnancy is removed through small incisions.
-
Laparotomy: A more extensive surgery used in emergencies, such as severe internal bleeding.
3. Monitoring: After treatment, blood tests are done to ensure hCG levels return to zero, confirming the pregnancy has ended.
If you are looking for the world class treatment from the best Obstetrician in Manglore, you should visit Manipal Hospitals.
Recovery and Future Pregnancies
Recovery from an ectopic pregnancy depends on the treatment method. With medication, recovery is usually quick, while surgery may require a longer healing period. Emotionally, it can be challenging, and counselling or support groups may help.
Many women go on to have healthy pregnancies after an ectopic pregnancy. However, the risk of another ectopic pregnancy is slightly higher, so early monitoring in future pregnancies is essential.
How to Prevent Ectopic Pregnancy
While not all ectopic pregnancies can be prevented, you can reduce your risk by:
-
One should quit smoking before trying for conception.
-
Practising safe sex to avoid sexually transmitted infections (STIs) that can damage the fallopian tubes.
-
Seeking prompt treatment for pelvic infections.
Conclusion
An ectopic pregnancy is a very complicated, unexpected and scary condition. It not only puts one into the pool of emotions but also brings a lot of health trauma. This condition requires immediate medical attention and emotional support. Knowing its causes, symptoms, and treatments can help you recognise the signs early and seek timely care. If you suspect an ectopic pregnancy, don’t delay, contact your healthcare provider right away. At KMC Hospital, we’re committed to providing accurate medical information and compassionate care. If you have any concerns about ectopic pregnancy or need support, our team of experts is here to help.
FAQ's
No, we can’t move an ectopic pregnancy to the uterus. The fertilised egg cannot be relocated once it implants outside the uterus. The pregnancy must be managed appropriately to prevent complications.
An ectopic pregnancy can often be detected as early as 4 to 6 weeks after the last menstrual period through blood tests and transvaginal ultrasound.
Not always. Some women may have mild or no symptoms in the early stages. However, as it progresses, symptoms like severe pain, bleeding, and dizziness can develop.
An ectopic pregnancy can rupture if left untreated. This will lead to internal bleeding and life-threatening complications. Immediate medical attention is necessary.
Yes, many women can have a successful pregnancy after an ectopic pregnancy, but the risk of recurrence may be higher. It is advisable to have a consultation with a doctor before attempting to conceive.





















 5 Min Read
5 Min Read