Epilepsy is often covered in misconception but still affects millions worldwide. It's not a single condition but a spectrum of neurological disorders characterised by recurrent seizures. But beyond the stigma and unknowns lies hope. This article unveils the secrets of epilepsy - its signs, navigate its complexities, and discover effective management methods.
Synopsis
What is Epilepsy?
Epilepsy is a commonly occurring medical condition related to the brain cells and neurons. This condition leads to some unexpectedly abnormal discharges, which are not planned. The rippling electrical surges through the brain disrupt its delicate symphony. This situation triggers sudden episodes of altered awareness, behaviour, or sensations. These are called seizures.
While the seizures themselves can be unsettling, epilepsy is far more than just these moments. It's a spectrum of epileptic disorder encompassing diverse triggers, symptoms, and experiences.
The Medical Difference between Seizures and Epilepsy
A seizure is usually a single attack. If an individual gets a seizure, it does not necessarily mean that they have epilepsy. Epilepsy is when the same symptoms get repeated. It means somebody will have recurrent episodes of abnormal neuron discharges. So, generally, the symptoms stay the same for an epileptic patient. Simply speaking, multiple seizures imply epilepsy.
The Trigger Points of Epilepsy Seizures
While epilepsy resides within the brain, its triggers can weave through the tapestry of daily life. Uncovering these hidden instigators is crucial so a professional neurological consultant can assist you with proper diagnosis and treatment.
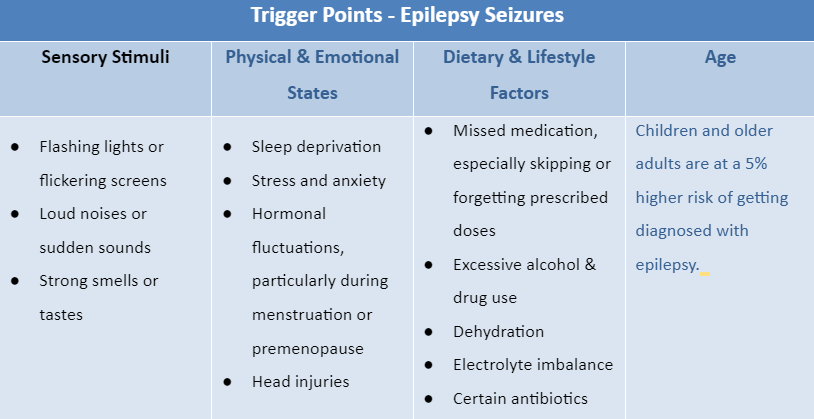
Be aware of your individualistic triggers to manage the issue better. Keeping a seizure diary to record the events surrounding each episode can help you and your doctor identify your unique vulnerabilities.
Symptoms of Epilepsy
The function of our brain is like a computer. It has a front load, motor strips, sensory areas, visual areas, and memory areas. Suppose some abnormal neuron discharges start from one’s memory area. One may remember some old memory; they may feel an incident has happened before; they may get some abnormal sensations. It may go on for 5-10 seconds.
When these electrical discharges spread onto the other parts of the brain, one may lose connection with the environment and remain still. There may be some oral movements, automatism, smacking a thing, and hand movements. One may just get up, walk around, and come back.
On the other hand, some attacks only occur during sleep. It is especially common in childhood epilepsy.
Some generic symptoms of epilepsy include:
- Sudden unconsciousness or unawareness
- Uncontrolled limb jerking movements or muscle stiffness
- Episodes of confusion or memory lapses
- Repetitive movements - lip-smacking or fidgeting
- Tongue biting, bleeding, or froth (foam on the mouth)
- Staring into space without knowledge
- Unexplained feelings of fear or anxiety
- Severe tiredness or exhaustion
There are certain pre-seizure warning signs, too. It includes tingling sensations, unusual smells, or sudden mood changes. Post-seizure, one may experience temporary confusion, drowsiness, headache, or muscle soreness.
In a nutshell, when you find anything happening again and again in the same pattern, it may be a red flag, stating that you may have epilepsy. So, it is important to consult a neurologist or epileptologist as soon as you suspect abnormalities or any sign of epilepsy and seizures.
Epilepsy: Diagnosis
There is a common misconception that epilepsy is diagnosed with tests. However, the truth is this condition is purely dependent on clinical diagnosis. This means that professionals study your symptoms and analyse your medical history. There is no investigational tool as such that can confirm one’s epileptic condition.
In case the doctor suspects epilepsy, they take the help of an EEG (electroencephalogram) which shows continuous abnormal electrical activity in the brain. Sometimes, specialised video-EEG monitoring is used to pinpoint the seizure source during an episode. Neurologists may also suggest further tests, like an MRI, to evaluate the structure of one’s brain.
There are some other diagnostic tests, too, that can help doctors better understand one’s specific situation, such as PET Scans and Functional MRIs. These advanced methods are used in specific medical centres for more precise diagnosis. To avail the most precise diagnosis and treatment for epilepsy, consult the best neurology specialist at Manipal Hospital Millers Road, Bangalore.
How Is Epilepsy Managed?
1. Medications
There are multiple medications available with a history of effective management and epilepsy treatment. The choice of medication will entirely depend on the individual profile of the patient, including their weight, age, other health concerns, etc. For example, if someone is planning to conceive a child, they are prescribed medications that are safe to consume during pregnancy. Special care is taken for older adults and children as well.
2. Surgical Intervention
Although rare, it may be necessary for some individuals. When anti-epilepsy medicines no longer can control seizures, it is called refractory epilepsy. These patients require epilepsy surgery to relieve their symptoms and get back to normal life. A few surgical options for epilepsy include resective surgery, Laser interstitial thermal therapy (LITT), Deep brain stimulation, etc.
It is important to note that most patients do well with medications if they follow the prescribed dosages properly. There are some lifestyle changes, too, that help in managing epileptic conditions.
3. Lifestyle Modifications
Adequate sleep, regular exercise, stress management techniques, and avoiding triggering factors like alcohol and drugs are found to be effective in some patients with epilepsy. Certain dietary modifications, like the ketogenic diet, can also be helpful. Building a healthy routine empowers you to take proactive steps towards a balanced and seizure-free future.
4. Caution Related to Pregnancy
While both men and women should be cautious if they have epilepsy, there are certain factors to consider for pregnant women. Regular medical consultation carries the utmost importance. Around 2% of medications may have minor effects on pregnancy. So, choosing the right medication can keep the risks at bay. Medicines like folic acid can prevent the known side effects on the baby. Thus, if you are planning to conceive, discuss the condition with your doctor to make the right choices.
During pregnancy, your doctor may recommend regular drug monitoring. In this phase, there is a slight risk of seizures and for the baby to get hit by the medicines. So, medical specialists usually ensure that you are well-controlled for around a year before pregnancy. They will test your blood and check if the drug levels are maintained. The medicine levels usually keep dropping down, especially during the second and third trimesters of pregnancy. So, managing these levels is key to assuring a healthy therapeutic range for the woman.
Living with epilepsy can come with emotional challenges. Seeking professional help for depression, anxiety, etc., can significantly improve your overall well-being and strengthen your resilience in navigating the journey. Visit Manipal Hospital Millers Road and receive a comprehensive care plan from our top Neurologists and Epileptologists in Millers Road, Bangalore.
FAQ's
Absolutely! With proper diagnosis, effective epilepsy treatment, and lifestyle adjustments, seizures can be controlled, and you can live a normal, healthy life.
There is no definitive cure for epileptic disorder yet. However, medication, surgery, and lifestyle changes can significantly control seizures and allow individuals to live fulfilling lives.
Stay calm. Remove any harmful objects from around the person to avoid injury. Do not restrain them, and allow the seizure to run its course. If the seizure lasts more than 5 minutes, call emergency services for immediate medical attention.





















 5 Min Read
5 Min Read








10.png)



8.png)